L2TPv3 Basic Concepts
L2TPv3 over IPv4/IPv6
L2TPv3 over IPv4/IPv6 is used to establish L2TPv3 tunnels on an IPv4/IPv6 public network, so that Layer 2 user packets can be transparently transmitted across the IPv4/IPv6 public network. L2TPv3 over IPv4/IPv6 establishes tunnels based on static configurations and does not require dynamic negotiation for tunnel establishment or tear-down.
L2TPv3 uses unique source or destination IPv4/IPv6 addresses to identify tunnels, leveraging the key property that IPv6 offers, a vast number of unique IP addresses. User packets transmitted over an L2TPv3 tunnel are identified by unique source or destination IPv4/IPv6 addresses. L2TPv3 identifies Layer 2 access links by source or destination IP addresses of tunnels. In this case, processing of the L2TPv3 session ID may be bypassed upon receipt because each tunnel has only one associated session.
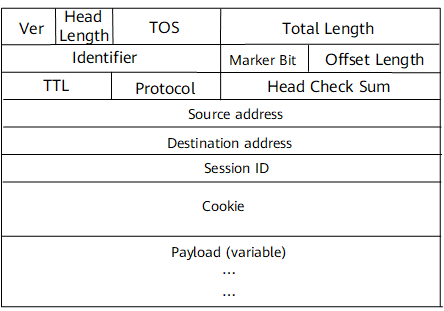
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Ver |
A 4-bit field used to indicate the version number. The value is set to 4 for IPv4. |
Head Length |
A 4-bit field used to indicate the packet header length. |
TOS |
An 8-bit field used to indicate the type of service. |
Total Length |
A 16-bit field used to indicate the total packet header length. |
Identifier |
A 16-bit field used to indicate the identifier. |
Mark Bit |
A 3-bit field used to indicate the flag. |
Offset Length |
A 13-bit field used to indicate the offset value. |
Head Check Sum |
A 16-bit field used to indicate the check sum of the packet header. |
TTL |
A 4-bit field used to indicate the time to live. |
Protocol |
A 4-bit field used to indicate the L2TPv3 protocol ID of 115. |
Source Address |
A 32-bit field used to indicate the IPv4 source address for the tunnel. The IPv4 source address is a loopback address of the local device. |
Destination Address |
A 32-bit field used to indicate the IPv4 destination address for the tunnel. The IPv4 destination address is a loopback address of the remote device. |
Session ID |
A 32-bit field used to indicate the session ID, which is unique globally. |
Cookie |
A 64-bit field. All packets must match the configured Cookie value or be discarded. This field is used in security checks performed at the endpoints of a tunnel to prevent network spoofing and attacks. The local Cookie value must match the remote one. The Cookie field can be dynamically configured. |
Payload |
Original Layer 2 user packet with the S-Tag or C-Tag removed. The FCS is stripped before encapsulation. A new FCS will be added at each hop when the IP packet is transmitted. |
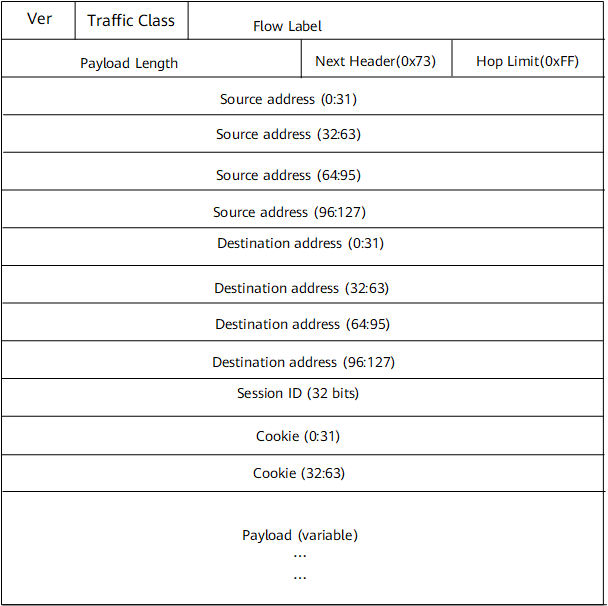
The following table describes the meaning of each field in the packet.
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Ver |
A 4-bit field used to indicate the version number. The value is set to 6 for IPv6. |
Traffic Class |
An 8-bit field used to indicate the traffic class. This field functions in a way similar to the ToS field in IPv4. |
Flow Label |
A 20-bit field used to indicate the flow label. Flow labels are used to differentiate packets at the network layer. |
Payload Length |
A 16-bit field used to indicate the length of the packet excluding the IPv6 header, that is, the length from the session ID to the end of the packet. |
Next Header |
An 8-bit field used to identify the type of header immediately following the current header (either basic or extension header). The value is set to 0x73 to indicate that the next header is an L2TPv3 header. |
Hop Limit |
An 8-bit field used to indicate the hop limit. This field functions in a way similar to the TTL field in IPv4. This field is decremented by one by each node in the path to the egress router. A packet is dropped after this field is decremented to 0. The initial value is 0xFF. |
Source Address |
A 128-bit field used to indicate the IPv6 source address for the tunnel. The IPv6 source address is a loopback address of the local device. |
Destination Address |
A 128-bit field used to indicate the IPv6 destination address for the tunnel. The IPv6 destination address is a loopback address of the remote device. |
Session ID |
A 32-bit field used to indicate the session ID. In a static 1:1 mapping case, the IPv6 address directly resolves to an L2TPv3 session and therefore the session ID can be ignored upon receipt. For compatibility with other tunnel termination platforms, the session ID must be configurable. The session ID of 0 is reserved for use by L2TP control messages. |
Cookie |
A 64-bit field. All packets must match the configured Cookie value or be discarded. This field is used in security checks performed at the endpoints of a tunnel to prevent network spoofing and attacks. The local Cookie value must match the remote one. The Cookie field can be dynamically configured. |
Payload |
Original Layer 2 user packet with the S-tag and C-tag removed. The FCS is stripped before encapsulation. A new FCS will be added at each hop when the IP packet is transmitted. |