IGMP Fundamentals
IGMP Messages
Figure 1 shows the IGMP message types.
IGMP Query message: This type of message is sent by a router to hosts to learn whether multicast receivers exist on a specific network segment. IGMP Query messages are sent only by queriers. IGMP Query messages are categorized into the following types:
General Query message: It does not contain specific source or group information.
Group-specific Query message: It contains specific multicast group information, but does not contain specific source information.
Group-and-Source-Specific Query message: It contains both specific multicast source and group information.
IGMP Report message: It is sent by a host to an upstream device when the host wants to join a multicast group.
IGMP Leave message: It is sent by a host to an upstream device when the host wants to leave a multicast group.

IGMPv2 and IGMPv3 support leave messages, but IGMPv1 does not.
IGMP Querier and Non-Querier
An IGMP multicast device can either be a querier or a non-querier:
Querier
A querier is responsible for sending IGMP Query messages to hosts and receiving IGMP Report messages and Leave messages from hosts. A querier can then learn which multicast group has receivers on a specified network segment.
Non-querier
A non-querier only receives IGMP Report messages from hosts to learn which multicast group has receivers. Then, based on the querier's action, the non-querier identifies which receivers leave multicast groups.
Generally, a network segment has only one querier. Multicast devices follow the same principle to select a querier. The process is as follows (using DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC as examples):
After IGMP is enabled on DeviceA, DeviceA considers itself a querier in the startup process by default and sends IGMP Query messages. If DeviceA receives IGMP Query messages from DeviceB that has a lower IP address, DeviceA changes from a querier to a non-querier. DeviceA starts the another-querier-existing timer and records DeviceB as the querier of the network segment.
If DeviceA is a non-querier and receives IGMP Query messages from the querier DeviceB, the another-querier-existing timer is updated; if DeviceA is a non-querier and receives IGMP Query messages from DeviceC that has a lower IP address than the querier DeviceB, the querier is changed to DeviceC, and the another-querier-existing timer is updated.
If DeviceA is a non-querier and the another-querier-existing timer expires, DeviceA changes to a querier.

IGMPv1 does not support querier election. An IGMPv1 querier is designated by the upper-layer protocol, such as PIM. In this version, querier election can be implemented only among multicast devices that run the same IGMP version on a network segment.
IGMP Implementation
IGMP enables a multicast router to identify receivers by sending IGMP Query messages to hosts and receiving IGMP Report messages and Leave messages from hosts. A multicast router forwards multicast data to a network segment only if the network segment has multicast group members. Hosts can decide whether to join or leave a multicast group.
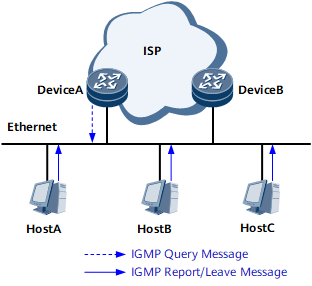
As shown in Figure 2, IGMP-enabled DeviceA functions as a querier to periodically send IGMP Query messages. All hosts (Host A, Host B, and Host C) on the same network segment of DeviceA can receive these IGMP Query messages.
When a host (for example, Host A) receives an IGMP Query message of a multicast group G, the processing flow is as follows:
If Host A is already a member of group G, Host A replies with an IGMP Report message of group G at a random time within the response period specified by DeviceA.
After receiving the IGMP Report message, DeviceA records information about group G and forwards the multicast data to the network segment of the host interface that is directly connected to DeviceA. Meanwhile, DeviceA starts a timer for group G or resets the timer if it has been started. If no members of group G respond to DeviceA within the interval specified by the timer, DeviceA stops forwarding the multicast data of group G.
If Host A is not a member of any multicast group, Host A does not respond to the IGMP Query message from DeviceA.
When a host (for example, Host A) joins a multicast group G, the processing flow is as follows:
Host A sends an IGMP Report message of group G to DeviceA, instructing DeviceA to update its multicast group information. Subsequent IGMP Report messages of group G are triggered by IGMP Query messages sent by DeviceA.
When a host (for example, Host A) leaves a multicast group G, the processing flow is as follows:
Host A sends an IGMP Leave message of group G to DeviceA. After receiving the IGMP Leave message, DeviceA triggers a query to check whether group G has other receivers. If DeviceA does not receive IGMP Report messages of group G within the period specified by the query message, DeviceA deletes the information about group G and stops forwarding multicast traffic of group G.
Message Processing Characteristics in Different IGMP Versions
IGMP Version |
Characteristic |
|---|---|
IGMPv1 |
|
IGMPv2 |
NOTE:
Both IGMP queriers and non-queriers can process IGMP Report message, while only queriers can forward IGMP Report messages. IGMP non-queriers cannot process IGMP Leave messages. |
IGMPv3 |
|
Advantages of IGMPv2 over IGMPv1 |
|
Advantages of IGMPv3 over IGMPv2 |
|
IGMP Group Compatibility
In IGMP group compatibility mode, a multicast device of a later IGMP version is compatible with the hosts of an earlier IGMP version. For example, an IGMPv2 multicast device can process join requests of IGMPv1 hosts; an IGMPv3 multicast device can process join requests of IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 hosts.
In IGMP group compatibility mode, if a multicast device receives IGMP Report messages from hosts running an earlier IGMP version, the multicast device automatically changes the version of the corresponding multicast group to be the same as that of the hosts and then operates in the earlier IGMP version. The process works as follows:
When an IGMPv2 multicast device receives an IGMPv1 Report message from a multicast group, the multicast device lowers the IGMP version of the multicast group to IGMPv1. Then, the multicast device ignores the IGMPv2 Leave messages of the multicast group.
When an IGMPv3 multicast device receives IGMPv2 Report messages from a multicast group, the multicast device lowers the IGMP version of the multicast group to IGMPv2. Then, the multicast device ignores the IGMPv3 BLOCK messages and the multicast source list in the IGMPv3 TO_EX messages. The multicast source-selecting function of IGMPv3 messages is then disabled.
When an IGMPv3 multicast device receives IGMPv1 Report messages from a multicast group, the multicast device lowers the IGMP version of the multicast group to IGMPv1. Then, the multicast device ignores the IGMPv2 Leave messages, IGMPv3 BLOCK messages, IGMPv3 TO_IN messages, and multicast source list in the IGMPv3 TO_EX messages.
If you manually change the IGMP version of a multicast device to a later version, the multicast device still operates in the original version if group members of the original version exist. The multicast device upgrades its IGMP version only after all group members of the original version leave.
Router-Alert Option for IGMP
Generally, a packet is sent to and processed by the routing protocol layer only if the packet's destination IP address is the IP address of a local interface. An IGMP packet's destination IP address is usually a multicast address, so that IGMP packets may not be sent to the routing protocol layer for processing.
To allow IGMP packets to be sent to the routing protocol layer, the Router-Alert option mechanism is used to mark protocol packets. If a packet contains the Router-Alert option, the packet must be sent to and processed by the routing protocol layer.
After a multicast device receives an IGMP packet:
If the multicast device does not check the Router-Alert option and sends the IGMP packet to the routing protocol layer, irrespective of whether the IGMP packet contains the Route-Alert option.
If the multicast device is configured to check the Router-Alert option, the multicast device sends the IGMP packet to the routing protocol layer only if the packet contains the Route-Alert option.