OSPFv3 LSA Format
Each router in an autonomous system (AS) generates one or more types of link state advertisements (LSAs), depending on the router's type. Multiple LSAs form a link state database (LSDB). OSPFv3 encapsulates routing information into LSAs for transmission. Commonly used LSAs include:
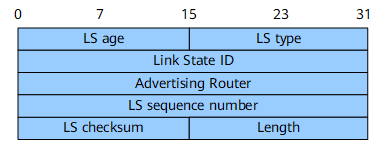
LSA Header Format
All LSAs have the same header. Figure 1 shows an LSA header.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
LS age |
16 bits |
Time that elapses after the LSA is generated, in seconds. The value of this field continually increases regardless of whether the LSA is transmitted over a link or saved in an LSDB. |
LS type |
16 bits |
Type of the LSA. The values are as follows:
|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
This field together with the LS type field describes an LSA in an area. |
Advertising Router |
32 bits |
Router ID of the router that generates the LSA. |
LS sequence number |
32 bits |
Sequence number of the LSA. routers can use this field to identify the latest LSA. |
LS checksum |
16 bits |
Checksum of all fields except the LS age field. |
Length |
16 bits |
Length of the LSA including the LSA header, in bytes. |
Router-LSA
A router-LSA (Type 1) describes the link status and cost of a router. Router-LSAs are generated by a router and advertised within the area to which the router belongs. Figure 2 shows the format of a router-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Nt (NSSA translation) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is an NSSA border router, this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. When this field is set to 1, the router unconditionally translates NSSA-LSAs into AS-external-LSAs. |
x |
1 bit |
This field is deprecated. |
V (Virtual Link) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is located at one end of a virtual link, this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
E (External) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is an autonomous system boundary router (ASBR), this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
B (Border) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is an area border router (ABR), this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
Options |
24 bits |
The optional capabilities supported by the router. |
Type |
8 bits |
Type of the router link. The values are as follows:
|
metric |
16 bits |
Cost of the link. |
Interface ID |
32 bits |
The Interface ID assigned to the interface. |
Neighbor Interface ID |
32 bits |
Neighbor's interface ID.
|
Neighbor Router ID |
32 bits |
Router ID of the neighbor.
|
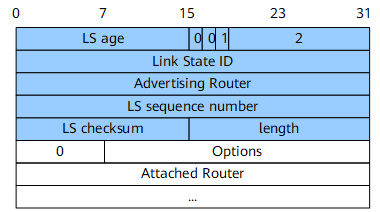
Network-LSA
A network-LSA (Type 2) records the router IDs of all routers on the local network segment. Network-LSAs are generated by a DR on a broadcast or non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) network and advertised within the area to which the DR belongs. Figure 3 shows the format of a network-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Options |
24 bits |
The optional capabilities supported by the router. |
Attached Router |
32 bits |
Router IDs of all routers on the same network, including the router ID of the DR |
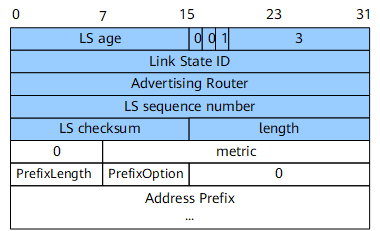
Inter-Area-Prefix-LSA
An inter-area-prefix-LSA (Type 3) describes routes on a network segment in an area. It is generated by the ABR. The routes are advertised to other areas.
Figure 4 shows the format of an inter-area-prefix-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
PrefixLength |
8 bits |
Length of the prefix. |
PrefixOption |
8 bits |
Prefix-related capability option, indicating the length in the packet. |
Address Prefix |
32 bits |
Address prefix. |
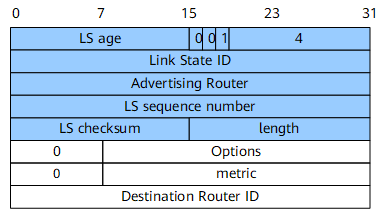
Inter-Area-Router-LSA
An inter-area-router-LSA (Type 4) describes routes to the ASBR in other areas. It is generated by the ABR. The routes are advertised to all related areas except the area that the ASBR belongs to.
Figure 5 shows the format of an inter-area-router-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Destination Router ID |
32 bits |
The router ID of the router described by the LSA. |
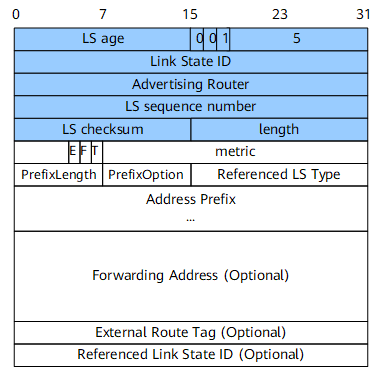
AS-External-LSA
An AS-external-LSA describes a route to a destination outside the AS and is generated by an ASBR.
Figure 6 shows the format of an AS-external-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
E |
1 bit |
Type of external metric.
|
F |
1 bit |
Whether a Forwarding Address has been included in the LSA.
|
T |
1 bit |
Whether an External Route Tag has been included in the LSA.
|
Referenced LS Type |
16 bits |
Referenced LS type. If this value is not 0, an LSA with this LS type is to be associated with this LSA (see Referenced Link State ID below). |
Forwarding Address |
128 bits |
A fully qualified global IPv6 address. |
External Route Tag |
32 bits |
External route tag, which can be used to communicate additional information between ASBRs. |
Referenced Link State ID |
32 bits |
Referenced link state ID. |
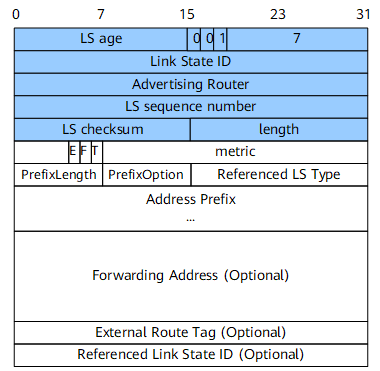
NSSA-LSA
NSSA-LSAs are originated by ASBRs within an NSSA and describe routes to destinations external to the AS.
Figure 7 shows the format of an NSSA-LSA.
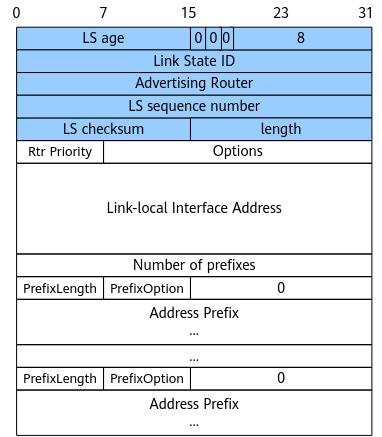
Link-LSA
Each router generates a link LSA for each link. A link LSA describes the link-local address and IPv6 address prefix associated with the link and the link option set in the network LSA. It is transmitted only on the link.
Figure 8 shows the format of a link-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Rtr Priority |
8 bits |
Router priority of the interface. |
Options |
24 bits |
Set of options that may be set in the network-LSA generated by the DR on broadcast or NBMA links. |
Link-local Interface Address |
128 bits |
The originating router's link-local interface address on the link. |
Number of prefixes |
32 bits |
Number of IPv6 address prefixes contained in the LSA. |
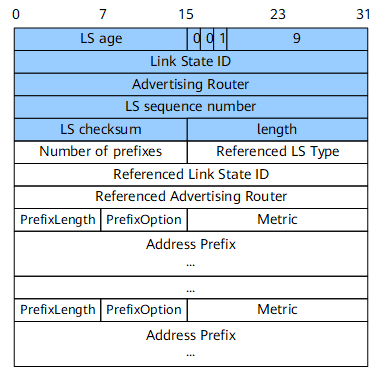
Intra-Area-Prefix-LSA
Each router and DR generates one or such LSAs and transmits them in the local area.
An LSA generated on a router describes the IPv6 address prefix associated with the router LSA.
Such LSAs generated by a DR describe the IPv6 address prefixes associated with network LSAs.
Figure 9 shows the format of an intra-area-prefix-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Referenced LS Type |
16 bits |
Router-LSA or network-LSA with which the IPv6 address prefixes should be associated.
|
Referenced Link State ID |
32 bits |
Referenced link state ID.
|
Referenced Advertising Router |
32 bits |
ID of the referenced advertising router.
|