MLD Snooping
Definition
Multicast Listener Discovery Snooping (MLD snooping) is an IPv6 Layer 2 multicast protocol. The MLD snooping protocol maintains information about the outbound interfaces of multicast packets by snooping multicast protocol packets exchanged between the Layer 3 multicast device and user hosts. MLD snooping manages and controls multicast packet forwarding at the data link layer.
Purpose
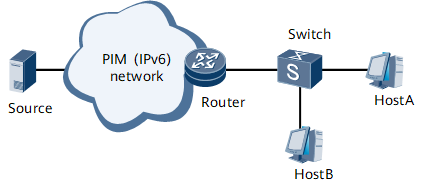
Similar to an IPv4 multicast network, multicast data on an IPv6 multicast network (especially on an LAN) have to pass through Layer 2 switching devices. As shown in Figure 1, a Layer 2 switch locates between multicast users and the Layer 3 multicast device, Router.
After receiving multicast packets from Router, Switch forwards the multicast packets to the multicast receivers. The destination address of the multicast packets is a multicast group address. Switch cannot learn multicast MAC address entries, so it broadcasts the multicast packets in the broadcast domain. All hosts in the broadcast domain will receive the multicast packets, regardless of whether they are members of the multicast group. This wastes network bandwidth and threatens network security.
MLD snooping solves this problem. MLD snooping is a Layer 2 multicast protocol on the IPv6 network. After MLD snooping is configured, Switch can snoop and analyze MLD messages between multicast users and Router. The Layer 2 multicast device sets up Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries to control forwarding of multicast data. In this way, multicast data is not broadcast on the Layer 2 network.
Principles
MLD snooping is a basic IPv6 Layer 2 multicast function that forwards and controls multicast traffic at Layer 2. MLD snooping runs on a Layer 2 device and analyzes MLD messages exchanged between a Layer 3 device and hosts to set up and maintain a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table. The Layer 2 device forwards multicast packets based on the Layer 2 multicast forwarding table.
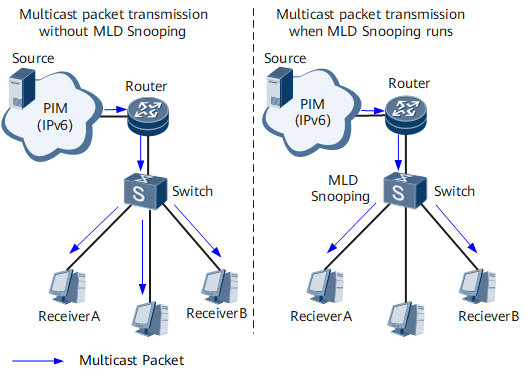
On an IPv6 multicast network shown in Figure 2, after receiving multicast packets from Router, Switch at the edge of the access layer forwards the multicast packets to receiver hosts. If Switch does not run MLD snooping, it broadcasts multicast packets at Layer 2. After MLD snooping is configured, Switch forwards multicast packets only to specified hosts.
With MLD snooping configured, Switch listens on MLD messages exchanged between Router and hosts. It analyzes packet information (such as packet type, group address, and receiving interface) to set up and maintain a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table, and forwards multicast packets based on the Layer 2 multicast forwarding table.
Concepts
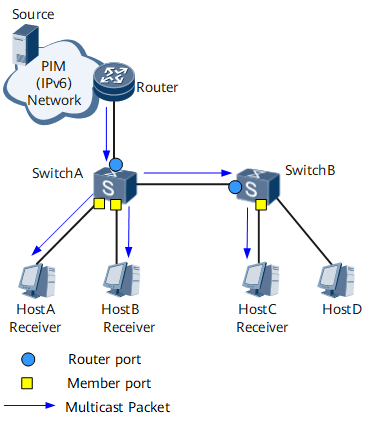
As shown in Figure 3, Router connects to the multicast source. MLD snooping is configured on SwitchA and SwitchB. HostA, HostB, and HostC are receiver hosts.
Figure 3 shows MLD snooping ports. The following table describes these ports.
Port Role |
Function |
Generation |
|---|---|---|
Router port Ports marked as blue points on SwitchA and SwitchB. NOTE:
A router port is a port on a Layer 2 multicast device and connects to an upstream multicast router. |
A router port receives multicast packets from a Layer 3 multicast device such as a designated router (DR) or MLD querier. |
|
Member port Ports marked as yellow points on SwitchA and SwitchB. |
A member port is a member of a multicast group. A Layer 2 multicast device sends multicast data to the receiver hosts through member ports. |
|
The router port and member port are outbound interfaces in Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries. A router port functions as an upstream interface, while a member port functions as a downstream interface. Port information learned through protocol packets is saved as dynamic entries, and port information manually configured is saved as static entries.
- Multicast group addresses can be multicast IP addresses or multicast MAC addresses mapped from multicast IP addresses. In MAC address-based forwarding mode, multicast data may be forwarded to hosts that do not require the data because multiple IP addresses are mapped to the same MAC address. The IP address-based forwarding mode can prevent this problem.
- The VLAN ID specifies a Layer 2 broadcast domain. After multicast VLAN is configured, the inbound VLAN ID is the multicast VLAN ID, and the outbound VLAN ID is a user VLAN ID. If multicast VLAN is not configured, both the inbound and outbound VLAN IDs are the ID of the VLAN to which a host belongs.
Implementation
After MLD snooping is configured, the Layer 2 multicast device processes the received MLD protocol packets in different ways and sets up Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries.
MLD Working Phase |
MLD Message Received on a Layer 2 Device |
Processing Method |
|---|---|---|
General query The MLD querier periodically sends General Query messages to all hosts and the router (FF02::1) on the local network segment, to check which multicast groups have members on the network segment. |
MLD General Query message |
A Layer 2 device forwards MLD General Query messages to
all ports excluding the port receiving the messages. The Layer 2 device
processes the receiving port as follows:
|
Membership report Membership Report messages are used
in two scenarios:
|
MLD Report message |
A Layer 2 device forwards an MLD Report message to all router
ports in a VLAN. The Layer 2 device obtains the multicast group address
from the Report message and performs the following operations on the
port receiving the message:
NOTE:
Aging time of a dynamic router port = Robustness variable × General query interval + Maximum response time for General Query messages |
Leave of multicast members There are two phases:
|
MLD Leave message |
The Layer 2 device determines whether the multicast group
matches a forwarding entry and whether the port that receives the
message is in the outbound interface list.
The following assumes that the port receiving an MLD Leave
message is a dynamic member port. Within the aging time of the member
port:
|
Multicast-Address-Specific Query/Multicast-Address-and-Source-Specific Query message |
A Multicast-Address-Specific Query/Multicast-Address-and-Source-Specific Query message is forwarded to the ports connected to members of specific groups. |
- If the port is included in the router port list, the device resets the aging timer of the router port.
- If the port is not in the router port list, the device adds it to the list and starts the aging timer.

When the Layer 2 device receives an IPv6 PIM Hello message, it sets the aging time of the router port to the Holdtime value in the Hello message.
If a static router port is configured, the Layer 2 device forwards received MLD Report and Done messages to the static router port. If a static member port is configured for a multicast group, the Layer 2 device adds the port to the outbound interface list for the multicast group.
After a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table is set up, the Layer 2 device searches the multicast forwarding table for outbound interfaces of multicast data packets according to the VLAN IDs and destination addresses (IPv6 group addresses) of the packets. If outbound interfaces are found for a packet, the Layer 2 device forwards the packet to all the member ports of the multicast group. If no outbound interface is found, the Layer 2 device drops the packet or broadcasts the packet in the VLAN.
MLD Snooping Proxy
Principles
MLD snooping proxy can be configured on a Layer 2 device. The Layer 2 device then functions as a host to send MLD Report messages to the upstream Layer 3 device. This function reduces the number of MLD Report and MLD Done messages sent to the upstream Layer 3 device. A device configured with MLD snooping proxy functions as a host for its upstream device and a querier for its downstream hosts.
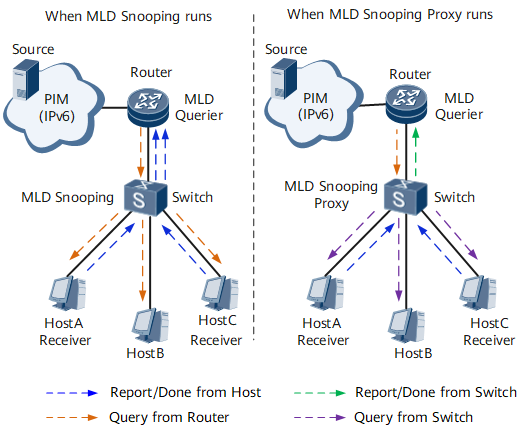
As shown in Figure 4, when Switch runs MLD snooping, it forwards MLD Query, Report, and Done messages transparently to the upstream Router. When numerous hosts exist on the network, redundant MLD messages increase the burden of Router.
With MLD snooping proxy configured, Switch can terminate MLD Query messages sent from Router and MLD Report/Done sent from downstream hosts. When receiving these messages, Switch constructs new messages to send them to Router.
After MLD snooping proxy is deployed on the Layer 2 device, the Layer 3 device considers that it interacts with only one user. The Layer 2 device interacts with the upstream device and downstream hosts. The MLD snooping proxy function conserves bandwidth by reducing MLD message exchanges. In addition, MLD snooping proxy functions as a querier to process protocol messages received from downstream hosts and maintain group memberships. This reduces the load of the upstream Layer 3 device.
Implementation
A device that runs MLD snooping proxy sets up and maintains a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table and sends multicast data to hosts based on the multicast forwarding table. Table 3 describes how the MLD snooping proxy device processes MLD messages.
MLD Message |
Processing Method |
|---|---|
MLD General Query message |
The Layer 2 device forwards the message to all ports excluding the port receiving the message. The device generates an MLD Report message based on the group memberships and sends the MLD Report message to all router ports. |
Multicast-Address-Specific Query/Multicast Address and Source Specific Query message |
If the group specified in the message has member ports in the multicast forwarding table, the Layer 2 device responds with an MLD Report message to all router ports. |
MLD Report message |
|
MLD Done message |
The Layer 2 device sends a Group-Specific Query message to the port that receives the MLD Done message. The Layer 2 device sends an MLD Done message to all router ports only when the last member port is deleted from the forwarding entry. |