Layer 2 Multicast Instance
Background
In conventional multicast on-demand mode, if users of a Layer 2 multicast device in different VLANs or VSIs request for the same multicast group's data from the same source, the connected upstream Layer 3 device has to send a copy of each multicast flow of this group for each VLAN or VSI. Such implementation wastes bandwidth resources and burdens the upstream device.
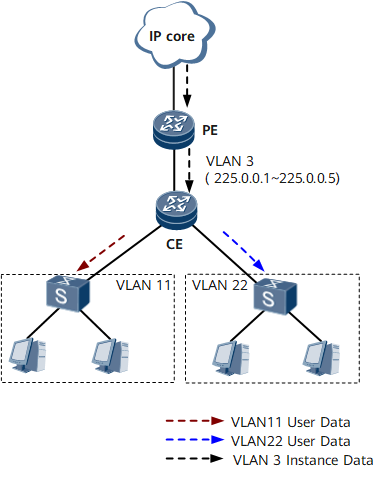
The Layer 2 multicast instance feature, which is an enhancement of multicast VLAN, resolves these issues by allowing multicast data replication across VLANs and VSIs and supporting multicast data transmission of the same multicast group across instances. These functions help save bandwidth resources and simplify multicast group management. A Layer 2 network supports multiple Layer 2 multicast instances. For example, on the network shown in Figure 1, if users in VLAN 11 and VLAN 22 request for multicast data from channels in the range of 225.0.0.1 to 225.0.0.5, Layer 2 multicast instances can be deployed on the CE. Then, the CE requests for only a single copy of each multicast data flow through VLAN 3 from the PE, replicates the multicast data flow, and sends a copy to each VLAN. This implementation greatly reduces bandwidth consumption.
Layer 2 multicast instances allow devices to replicate multicast data flows across different types of instances, such as flow replication from a VPLS to a VLAN or from a VLAN to a VPLS.
Related Concepts
Multicast instance
An instance to which the interface connected to a multicast source belongs. A multicast instance aggregates multicast flows.
User instance
An instance to which the interface connected to a multicast receiver belongs. A user instance receives multicast flows from a multicast instance.
A multicast instance can be associated with multiple user instances.
- Multicast channel
A multicast channel consists of one or more multicast groups. To facilitate service management, multicast content providers generally operate different types of channels in different Layer 2 multicast instances. Therefore, multicast channels need to be configured for Layer 2 multicast instances.
Implementation
After receiving a multicast data packet from an upstream device, a Layer 2 device searches for a matching entry in the multicast forwarding table based on the multicast instance ID and the destination address (multicast group address) contained in the packet. If a matching forwarding entry exists, the Layer 2 device obtains the downstream interfaces and the VLAN IDs or VSI names, replicates the multicast data packet on each downstream interface, and sends a copy of the packet to all involved user instances. If no matching forwarding exists, the Layer 2 device broadcasts the multicast data packet in the local multicast VLAN or VSI. This implementation is similar to multicast VLAN implementation.
Usage Scenario
Layer 2 multicast instances apply to VLAN and VPLS networks.
Benefits
- Reduced bandwidth consumption
- Improved network security
- Isolated unicast and multicast domains to prevent user traffic from affecting each other