Dual-Device Backup Principles
Related Concepts
VRRP
VRRP is a fault-tolerant protocol that groups several routers into a virtual router. If the next hop of a host is faulty, VRRP switches traffic to another router, which ensures communication continuity and reliability.
For details about VRRP, see the chapter "VRRP" in NetEngine 8000 F Feature Description - Network Reliability.
RUI
RUI is a Huawei-specific redundancy protocol that is used to back up user information between devices. RUI, which is carried over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), specifies which user information can be transmitted between devices and the format and amount of user information to be transmitted.
RBS
The remote backup service (RBS) is an RUI module used for inter-device backup. A service module uses the RBS to synchronize service control data from the master device to the backup device. When a master/backup VRRP switchover occurs, service traffic quickly switches to a new master device.
RBP
The remote backup profile (RBP) is a configuration template that provides a unified user interface for dual-device backup configurations.
E-Trunk
E-Trunk implements inter-device link aggregation, providing device-level reliability. E-Trunk aggregates data links of multiple devices to form a link aggregation group (LAG). If a link or device fails, services are automatically switched to the other available links or devices in the E-Trunk, improving link and device-level reliability.
For details about E-Trunk, see "E-Trunk" in NetEngine 8000 F Feature Description - LAN Access and MAN Access.
Implementation
There are two primary backup protocols, VRRP and E-Trunk. The following takes ARP dual-system backup and IGMP Snooping backup as an example.
- Dual-device ARP hot backup enables the master device to back up the ARP entries at the control and forwarding layers to the backup device in real time. When the backup device switches to a master device, it uses the backup ARP entries to generate host routing information without needing to relearn ARP entries, ensuring downlink traffic continuity.
- Manually triggered dual-device ARP hot backup: You must manually establish a backup platform and backup channel for the master and backup devices. In addition, you must manually trigger ARP entry backup from the master device to the backup device. This backup mode has complex configurations.
- Automatically enabled dual-device ARP hot backup: You need to establish only a backup channel between the master and backup devices, and the system automatically implements ARP entry backup. This backup mode has simple configurations.
Figure 1 VRRP networking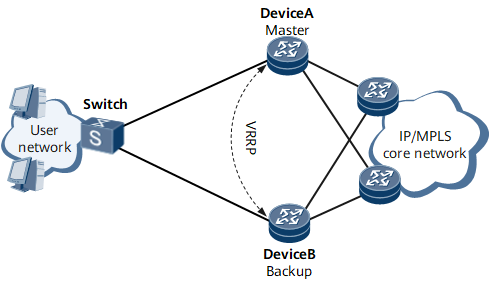
Dual-device IGMP snooping hot backup enables the master device to back up IGMP snooping entries to the backup device in a master/backup E-Trunk scenario. If the master device or the link between the master device and user fails, the backup device switches to a master device and takes over, ensuring multicast service continuity.
Figure 2 E-Trunk Networking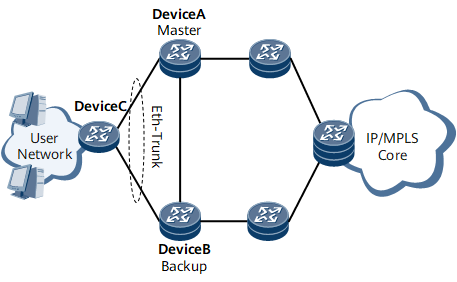
Benefits
Dual-device backup provides a unified platform for backing up service control data from the master device to the backup device.
- IPv4 Multicast Forwarding Control
- This section describes how to control IPv4 multicast service forwarded to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) set top box (STB) along the SmartLink or enhanced trunk (E-Trunk) active and standby links.