IP FPM Applications on Seamless MPLS
Networking Description
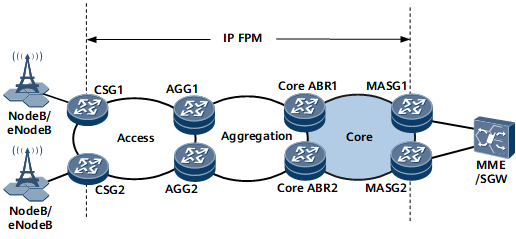
Seamless MPLS supports highly flexible deployment and high scalability. LSPs established among nodes allow for service rollouts or node addition between any two nodes. In a seamless MPLS scenario, IP FPM can be performed in either per-node proactive or on-demand mode to measure service performance. Therefore, IP FPM monitors per-hop packet loss and delay, which helps locate faults.
Seamless MPLS allows a BGP LSP to be established across the access, aggregation, and core layers, implementing E2E service transmission. An LSP is established between each pair of nodes on a network to transmit upstream and downstream traffic. Such a network architecture maximizes service scalability. Only signaling needs to be configured on a service access point for all services. The same transport-layer convergence technique is used to handle network-side faults, whereas the service layer does not need to discern the faults.
Feature Deployment
On the Seamless MPLS shown in Figure 1, various carriers may operate the transport network between CSG and MASG and the wireless networks between NodeBs/eNodeBs and CSG and between MASG and MME/SGW. The transport network quality, as indicated by the packet loss rate, delay, and jitter, also affect the wireless service quality. This requires that the transport network carrier use reliable performance measurement measures to monitor the transport network. When the wireless service quality deteriorates, the transport network carrier can promptly identify whether the fault has occurred on the transport network or wireless network using the transport network performance data.
The following example uses the application of IP FPM in the intra-Seamless MPLS scenario.
Seamless MPLS Solution |
IP FPM Deployment |
|---|---|
Intra-Seamless MPLS |
|