Networking Description
Currently, IP radio access network (RAN) solutions have been developed to provide more access modes to maximize carriers' return on investment, reduce network construction costs, and smoothly evolve existing networks into Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks.
Figure 1 IP RAN solution networking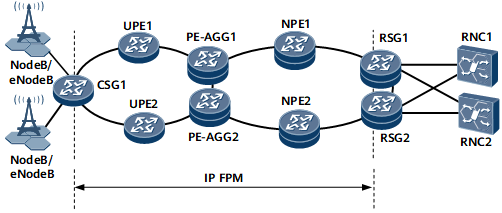
Various value-added services, such as IPTV, video conferencing, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) are widely used. As these services rely heavily on high speed and robust networks, link connectivity and network performance are essential to service transmission.
- When voice services are deployed, users will not detect any change in the voice quality if the packet loss rate on links is lower than 5%. If the packet loss rate is higher than 10%, the voice quality will deteriorate significantly.
- Real-time services, such as VoIP, online games, and video conferencing, require a delay lower than 100 ms, or even 50 ms. As the delay increases, user experience worsens.
To meet users' service quality requirements, carriers need to promptly measure the packet loss rate and delay so that they can quickly respond to resolve network issues if service quality deteriorates.
Feature Deployment
On the IP RAN shown in Figure 1, various carriers may operate the transport network between CSG1 and RSGs and the wireless networks between NodeBs/eNodeBs and CSG1 and between RSGs and RNC. The transport network quality, as indicated by the packet loss rate, delay, and jitter, also affect the wireless service quality. This requires that the transport network carrier use reliable performance measurement measures to monitor the transport network. When the wireless service quality deteriorates, the transport network carrier can promptly identify whether the fault has occurred on the transport network or wireless network using the transport network performance data.
IP Flow Performance Measurement (FPM) can be deployed on the transport network to monitor performance and locate faults. Table 1 lists the IP FPM deployments for various IP RAN solutions.
Table 1 IP FPM deploymentIP RAN Solution
|
IP FPM Deployment
|
|---|
E2E virtual private network (VPN) solution
|
Deploy a Measurement Control Point (MCP): - If routes are reachable over the entire transport network, deploy an MCP on any of CSG1, PE-AGG1/PE-AGG2, or RSG1/RSG2. Deploying an MCP on RSG1/RSG2 is recommended.
- If routes are reachable only within areas on the transport network, CSG1 does not have a route to RSG1/RSG2. Deploy an MCP on PE-AGG1/PE-AGG2.
Deploy a Data Collecting Point (DCP): - When performance measurement is implemented for end-to-end services, IP FPM runs on edge devices of the transport network. Deploy DCPs on CSG1, RSG1, and RSG2.
- When performance measurement is implemented for local switching services, deploy a DCP on CSG1 that is directly connected to NodeBs/eNodeBs.
Deploy a Target Logical Port (TLP): - When performance measurement is implemented for end-to-end services, IP FPM runs on edge devices of the transport network. Perform the following operations:
- Deploy a TLP on CSG1 and bind the TLP to the user-side interface on CSG1.
- Deploy TLPs on RSG1 and RSG2 and bind the TLPs to user-side interfaces on RSG1 and RSG2.
- When performance measurement is implemented for local switching services, deploy TLPs on CSG1 that is directly connected to NodeBs/eNodeBs and bind the TLPs to the user-side interfaces on CSG1. Perform the following operations:
|
Hierarchical VPN (HVPN) solution
|
Native IP+L3VPN solution
|
Mixed VPN solution
|
Deploy an MCP: If routes are reachable only within areas on the transport network, CSG1 does not have a route to RSG1/RSG2. Deploy an MCP on PE-AGG1/PE-AGG2.
Deploy a DCP: - When performance measurement is implemented for end-to-end services, IP FPM runs on edge devices of the transport network. Deploy DCPs on CSG1, RSG1, and RSG2.
- When performance measurement is implemented for local switching services, deploy a DCP on CSG1 that is directly connected to NodeBs/eNodeBs.
Deploy a TLP: - When performance measurement is implemented for end-to-end services, IP FPM runs on edge devices of the transport network. Deploy a TLP on CSG1 and bind the TLP to the user-side interface on CSG1. Then, deploy TLPs on RSG1 and RSG2 and bind the TLPs to user-side interfaces on RSG1 and RSG2.
- When performance measurement is implemented for local switching services, deploy TLPs on CSG1 that is directly connected to NodeBs/eNodeBs and bind the TLPs to the user-side interfaces on CSG1.
|
In addition, you can configure the following IP FPM functions:
Description for an IP FPM instance on an MCP and its associated DCPs to enhance maintainability
Authentication function on an MCP and its associated DCPs to enhance security
NTP clock synchronization in delay measurement on an MCP and its associated DCPs to ensure measurement accuracy
Conditions for triggering IP FPM alarms on an MCP so that the MCP can report alarms to the NMS based on packet loss and delay performance statistics
