Carrier Scenario
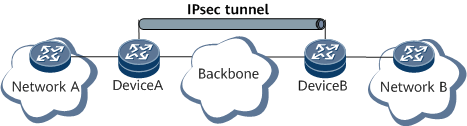
Site-to-Site VPN
IPsec provides security protection for any IP-based communications. It is applicable to both the traditional fixed network and the mobile network such as Long Term Evolution (LTE). Regardless of the fixed network or mobile network, most IPsec applications in the carrier scenario are site-to-site VPN and GRE over IPsec.
The site-to-site VPN can be flexibly deployed. When a NAT device exists between two IPsec gateways, the IPsec NAT traversal is supported.
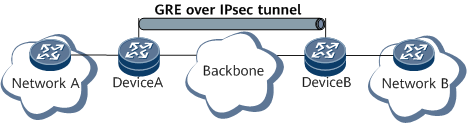
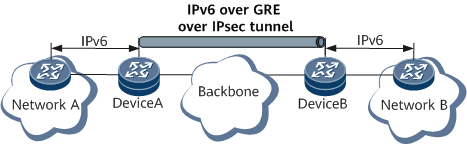
GRE over IPsec
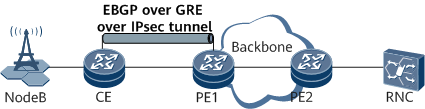
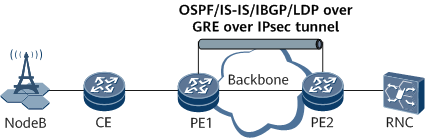
Various applications are based on GRE over IPsec, for example, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Label Distribution Protocol (LDP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS), and IPv6. Based on the same principle, these applications encapsulate packets as IP packets using GRE and then transmit the packets over IPsec tunnels, as shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, and Figure 5.