Encryption Algorithm
Encryption is a process in which plain text data is transformed into unreadable cipher text. The responder can decrypt the data only by using the correct key. In this way, encryption ensures the data confidentiality.
There are two types of encryption in IPsec VPN, data encryption (IP packet encryption) and protocol message encryption (ISAKMP message encryption).
Data Encryption
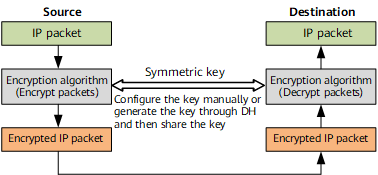
ESP can encapsulate content of IP packets to protect them during transmission. IPsec uses symmetric encryption algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data. When a symmetric encryption algorithm is used, the initiator and responder use the same key to encrypt and decrypt the data.
The symmetric key can be manually configured, or generated through the DH algorithm and shared by both devices.
IPsec uses the following encryption algorithms:
Data Encryption Standard (DES): uses a 64-bit key to encrypt a 64-bit IP packet in plaintext.
Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES): uses three 64-bit keys (in effect, a 192-bit key) to encrypt an IP packet in plaintext.
Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher Block Chaining 128 (AES-CBC-128): uses 128-bit AES-CBC encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher Block Chaining 192 (AES-CBC-192): uses 192-bit AES-CBC encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
Advanced Encryption Standard Cipher Block Chaining 256 (AES-CBC-256): uses 256-bit AES-CBC encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
- Advanced Encryption Standard with 128-bit keys and 16-octet Integrity Check Value in Galois/Counter Mode (AES-GCM-128): uses 128-bit AES-GCM encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
- Advanced Encryption Standard with 192-bit keys and 16-octet Integrity Check Value in Galois/Counter Mode (AES-GCM-192): uses 192-bit AES-GCM encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
- Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit keys and 16-octet Integrity Check Value in Galois/Counter Mode (AES-GCM-256): uses 256-bit AES-GCM encryption algorithm to encrypt IP packets.
3DES encrypts protocol packets more slowly than DES, but provides a more secure service. AES is more secure than 3DES.
Protocol Message Encryption
Protocol message encryption is used in IKE negotiation. Protocol message encryption also uses DES, 3DES, and AES. The symmetric key used for encryption is generated through the DH algorithm.