Authentication Algorithm
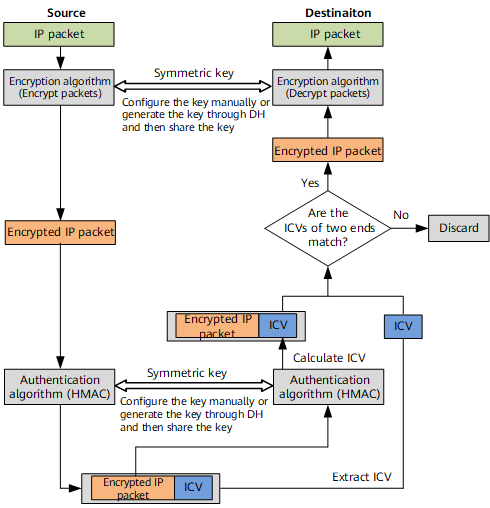
IPsec uses the Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) function to check data integrity and authenticity. HMAC is a combination of the hash function and the message authentication code (MAC). HMAC uses the hash function, with the symmetric key and data packet as the hash input. The hash output is a fixed-length digital signature called Integrity Check Value (ICV). The receiver compares the ICV digital signature generated on the local end with that sent by the peer end to check the integrity and authenticity of the data.
Authentication contains data source check and data integrity authentication because the two security services are provided as a suite. Data integrity authentication is implemented on the basis of each IP packet, in which the data integrity authentication key sent from the peer end is calculated to provide data source check indirectly.
Although the encrypted data can be decrypted only by using the key used for encryption, the authenticity of the decrypted data still cannot be verified. Besides, the encryption and decryption processes consume much CPU resources. Malicious users may take advantage to send spoofed packets to overload CPU resources. The HMAC function checks the data integrity and authenticity by comparing the digital signatures. The whole process is efficient and occupies few CPU resources.
Therefore, encryption and authentication are used together in devices that initiate IPsec VPN connections. The encrypted packet is processed through HMAC to generate a digital signature. Then the packet and digital signature are sent to the peer end (the digital signature is in the ICV field of the AH and ESP packet header. For details, see Security Protocol). The responder device compares the digital signature to check data integrity and authenticity. Packets that fail to pass the authentication are discarded, and those that pass the authentication are decrypted.
The symmetric key can be manually configured, or generated through the DH algorithm and shared by both devices.
MD5: generates a 128-bit message summary for an input message of any length.
SHA-1: generates a 160-bit message summary for an input message of less than 264 bits.
SHA2-256: generates a 256-bit message summary for an input message of less than 264 bits.
SHA2-384: generates a 384-bit message summary for an input message of less than 2128 bits.
SHA2-512: generates a 512-bit message summary for an input message of less than 2128 bits.
The message summary generated by SHA-2 and SHA-1 is longer than that of MD5, and therefore provides a more secure service.