BIER I-PMSI Tunnel Establishment
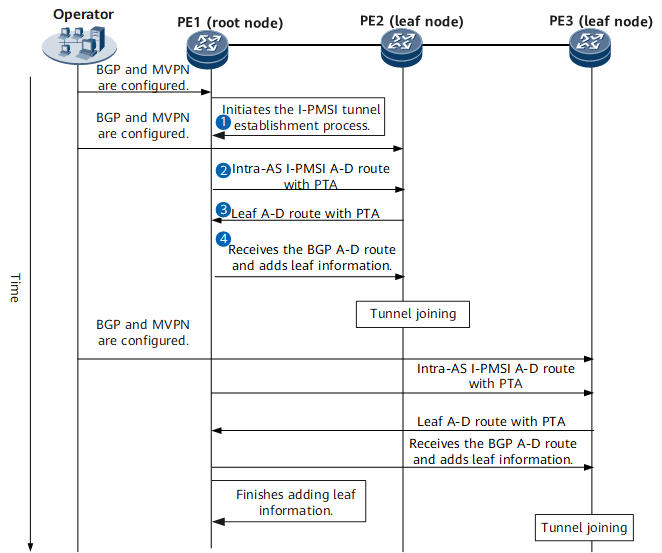
Provider Multicast Service Interface (PMSI) tunnels are logical channels for transmitting MVPN traffic on the public network. When BIER is used to create a PMSI tunnel, the receiver PE searches for the BFR-ID and BFR-prefix configured on the local end based on the Sub-domain-id value carried in the Intra-AS PMSI A-D route sent by the sender PE. In addition, the receiver PE replies with a Leaf A-D route. After receiving the BGP Leaf A-D route from the receiver PE, the sender PE matches the export MVPN target in the route against the local import MVPN target. If the two targets match, the sender PE accepts the route and records the receiver PE as an MVPN member. The sender PE records information about all MVPN members (receiver PEs) and combines the neighbor information into a BIER BitString to establish a BIER tunnel.
Step |
Device Name |
Prerequisites |
Key Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
PE1, PE2, and PE3 |
Basic functions of the public network and BIER have been configured on PE1, PE2, and PE3. |
N/A |
PE1 |
BGP and MVPN have been configured on PE1. PE1 has been configured as a sender PE. The I-PMSI tunnel type has been set to BIER. |
As a sender PE, PE1 initiates the I-PMSI tunnel establishment process. |
|
|
PE1 |
BGP and MVPN have been configured on PE2. PE1 has established a BGP MVPN peer relationship with PE2. |
PE1 sends a Type 1 BGP A-D route to PE2. This route carries the following information:
|
|
PE2 |
- |
1. After PE2 receives the BGP A-D route from PE1, PE2 matches the export MVPN target in the route against its local import MVPN target. The two targets match. Therefore, PE2 accepts this route. 2. PE2 replies with a Leaf A-D route carrying the following information:
|
|
PE1 |
- |
After PE1 receives the BGP Leaf A-D route from PE2, PE1 matches the export MVPN target in the route against its local import MVPN target. The two targets match. Therefore, PE1 accepts this route and records PE2 as an MVPN neighbor. |
PE1<->PE3 |
- |
PE1 completes the same interaction process with PE3 as with PE2. After receiving the Leaf A-D route from PE3, PE1 records PE3 as an MVPN neighbor. |
|
PE1 |
- |
1. Based on the BFR-IDs and BitStringLengths carried in received Leaf A-D routes, PE1 calculates the SIs of other PEs. 2. PE1 combines information about all leaf nodes to generate the BIER BitString corresponding to the specified (S, G). |



