Overview of MVPN over BIERv6
Definition
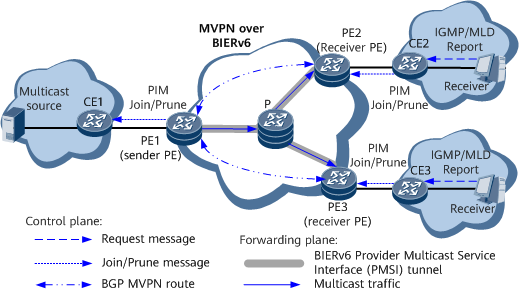
Multicast VPN (MVPN) offers advantages such as bandwidth saving, service isolation, high reliability, and good scalability, making it the option of choice as networks carry more and more video services. MVPN over BIERv6 uses BIERv6 as a transport tunnel to forward VPN IP multicast traffic across the VPN. MVPN over BIERv6 applies to both IPv4 and IPv6 networks, and is known as MVPNv4 over BIERv6 and MVPNv6 over BIERv6, respectively.
Figure 1 shows the typical MVPN over BIERv6 networking, in which PIM must be enabled on the sender PE and the network where the multicast source resides for interworking. Due to the service deployment and to facilitate subsequent descriptions, this document refers to the networks where CEs reside as VPNs, and the network where PEs and the P reside as a public network.
Network Architecture
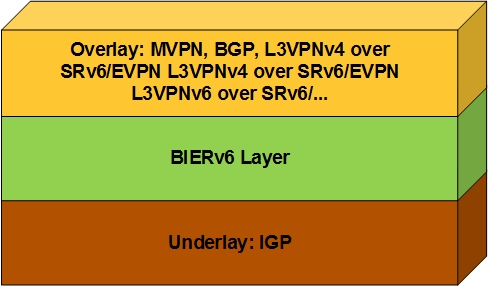
An MVPN over BIERv6 network consists of three layers, as shown in Figure 2.
- Underlay: It uses an IGP to establish adjacencies between BFRs and generate BIFTs to implement network interworking. Similar to a BIERv6 network, the MVPN over BIERv6 network also uses the TLVs defined in IS-ISv6 for BIERv6.
- BIERv6 layer: The BFIR encapsulates a BIERv6 packet header containing a BitString for each multicast packet. According to the BitString, transit BFRs forward the packets. Upon receipt of such packets, BFERs remove the BIERv6 packet header and send the packets to the overlay module for processing.
- Overlay: A VPN instance is created and bound to an interface on each PE, and BGP MVPN peer relationships are established using BGP MVPN Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI). Based on MVPN A-D routes, the sender PE calculates the set ID and BitString to be encapsulated in the BIERv6 packet header. In this manner, multicast forwarding paths are established between the sender PE and receiver PEs. In addition, a receiver PE constructs a BGP MVPN C-multicast (C is short for customer) route based on the PIM Join/Prune message received from a VPN and sends the C-multicast route to the sender PE, which then converts the route into a PIM Join/Prune message and sends the message to the corresponding CE.
BIERv6 PMSI Tunnel
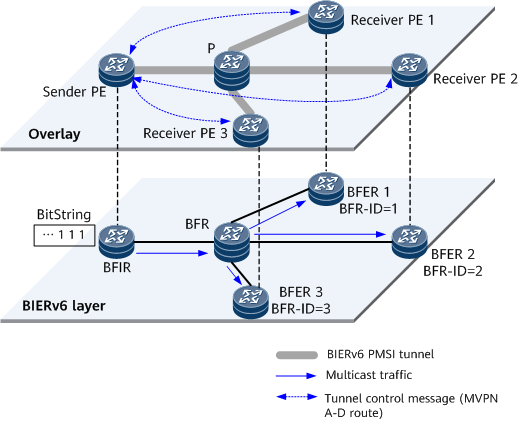
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, a sender PE needs to forward the multicast data it receives from a CE in a VPN to all or some receiver PEs in the same VPN. Each receiver PE forwards the multicast data it receives to the connected CE, which then forwards the data to VPN users. PEs in the same VPN need to establish a tunnel between themselves to transmit C-multicast services. This type of tunnel, which is established between PEs and is used to transmit C-multicast data over the public network, is called a Provider Multicast Service Interface (PMSI) tunnel.
As shown in Figure 3, a BIERv6 PMSI tunnel is established between the sender PE and multiple receiver PEs using MVPN NLRI. The sender PE functions as a BFIR, inserts a BIERv6 packet header (in which the bit positions of receiver PEs are set to 1 in the BitString) into the packet, and performs the BIERv6 forwarding process. The packet is then forwarded until it reaches each receiver PE.
PMSI tunnels are classified into the following types:
- Inclusive-PMSI (I-PMSI) tunnel: connects all PEs in the same MVPN. An I-PMSI tunnel is typically used as the default tunnel for data forwarding.
- Selective-PMSI (S-PMSI) tunnel: connects to some PEs in the same MVPN. An S-PMSI tunnel is used to transmit VPN data to PEs that require the data. If no multicast user requests multicast data from the corresponding (S, G) in the VPN connected to a receiver PE, the receiver PE will not receive such data. Compared with an I-PMSI tunnel, an S-PMSI tunnel prevents redundant data from being forwarded, thereby conserving network bandwidth.
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, both an I-PMSI tunnel and an S-PMSI tunnel can exist. The I-PMSI tunnel is used for data forwarding by default, and the S-PMSI tunnel automatically generates one or more tunnels based on the (S, G) information of different multicast services. For details about how PMSI tunnels are established, see BIERv6 PMSI Tunnel Establishment.