MVPN over BIERv6 Control Messages
MVPN over BIERv6 control messages are used to implement functions such as automatic MVPN member discovery, establish and maintain PMSI tunnels, and advertise C-multicast routes for MVPN members to join or leave multicast groups. Each MVPN over BIERv6 control message is carried in the NLRI field in a BGP Update message.
BGP MVPN NLRI
Figure 1 shows the format of BGP MVPN NLRI (referred to as MVPN NLRI for short), and Table 1 describes the fields in it.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Route Type |
Type of a BGP MVPN route (MVPN route for short). MVPN routes have seven types. For details, see Table 2. |
Length |
Length of the Route type specific field in MVPN NLRI. |
Route Type Specific |
MVPN route information. Different types of MVPN routes contain different information. Therefore, the length of this field is variable. |
Table 2 describes the types and functions of MVPN routes. C-S refers to the IP address (C-Source IP) of a C-multicast source, and C-G refers to the IP address (C-Group IP) of a C-multicast group. (C-S, C-G) multicast traffic is sent to all hosts that have joined the C-G multicast group and request data sent from the multicast source address C-S. (C-*, C-G) multicast traffic is sent to all hosts that have joined the C-G multicast group and have no requirements for a specific multicast source address.
Type |
Function |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1: Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route |
It is used for intra-AS MVPN member auto-discovery and is advertised by each PE with MVPN enabled. |
The two types of routes are called MVPN auto-discovery (A-D) routes and are used to automatically discover MVPN members and establish PMSI tunnels. |
2: Inter-AS I-PMSI A-D route |
It is used for inter-AS MVPN member auto-discovery and is advertised by each ASBR with MVPN enabled. This type of route is currently not supported (the inter-AS static traversal solution is used instead). |
|
3: S-PMSI A-D route |
It is used by a sender PE to send a notification of establishing a selective P-tunnel for a particular (C-S, C-G). |
|
4: Leaf A-D route |
It is used to respond to a Type 1 Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route with the flags field in the PMSI attribute being 1 or a Type 3 S-PMSI A-D route. If a receiver PE has a request for establishing an S-PMSI tunnel, it sends a Leaf A-D route to help the sender PE collect tunnel information. |
|
5: Source Active A-D route |
It is used by the sender PE to advertise C-multicast source information to other PEs in the same MVPN when the sender PE is aware of a new C-multicast source. |
|
6: Shared Tree Join route |
It is used in (C-*, C-G) scenarios. When a receiver PE receives a PIM (C-*, C-G) Join or Prune message, it converts the message into a Shared Tree Join route and sends the route to the sender PE through the BGP peer relationship. |
The two types of routes are called C-multicast routes. They are used to initiate the join or leave of VPN users and guide the transmission of C-multicast traffic. |
7: Source Tree Join route |
It is used in (C-S, C-G) scenarios. When a receiver PE receives a PIM (C-S, C-G) Join or Prune message, it converts the message into a Source Tree Join route and sends the route to the sender PE through the BGP peer relationship. |
Table 3 describes the fields of the Route type specific field in different route types.
Route Type |
Field |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1: Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route |
RT |
Used to filter the routing entries that can be added to the local routing table. |
PMSI Tunnel Attribute |
PMSI tunnel attribute. For details, see Table 4. |
|
Next Hop |
Next-hop IP address. |
|
RD |
VPN route distinguisher (RD). |
|
Prefix-SID |
In BIERv6 mode, this field carries the Src.DTX SID (IPv6 address for forwarding BIERv6 packets). In G-BIER mode, the MSID field carries the Src.DTX SID information. By default, a device uses the Prefix-SID attribute to carry the information. You can configure the device to use a Multicast Service Identifier (MSID) to carry the information. |
|
Origination Router's IP Addr |
IP address of the route originator. |
|
3: S-PMSI A-D route |
RT |
Used to filter the routing entries that can be added to the local routing table. |
PMSI Tunnel Attribute |
PMSI tunnel attribute. For details, see Table 4. |
|
Next Hop |
Next-hop IP address. |
|
RD |
VPN RD. |
|
Multicast Source Length |
Length of a C-multicast source IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Source |
IP address of a C-multicast source. |
|
Multicast Group Length |
Length of a C-multicast group IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Group |
IP address of a C-multicast group. |
|
Prefix-SID |
This field carries the Src.DTX SID. In G-BIER mode, the MSID field carries the Src.DTX SID information. By default, a device uses the Prefix-SID attribute to carry the information. You can configure the device to use an MSID to carry the information. |
|
Origination Router's IP Addr |
IP address of the route originator. |
|
4: Leaf A-D route |
RT |
Used to filter the routing entries that can be added to the local routing table. |
Route Key |
Route key. |
|
PMSI Tunnel Attribute |
PMSI tunnel attribute. For details, see Table 4. |
|
Origination Router's IP Addr |
IP address of the route originator. |
|
5: Source Active A-D route |
RD |
VPN RD. |
Multicast Source Length |
Length of a C-multicast source IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Source |
IP address of a C-multicast source. |
|
Multicast Group Length |
Length of a C-multicast group IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Group |
IP address of a C-multicast group. |
|
6: Shared Tree Join route, 7: Source Tree Join route |
RT |
Used to filter the routing entries that can be added to the local routing table. |
Next Hop |
Next-hop IP address. |
|
RD |
VPN RD. |
|
Source AS |
Number of the AS to which the route originator belongs. |
|
Multicast Source Length |
Length of a C-multicast source IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Source |
IP address of a C-multicast source. |
|
Multicast Group Length |
Length of a C-multicast group IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Multicast Group |
IP address of a C-multicast group. |
Format of the PMSI Tunnel Attribute in MVPN NLRI
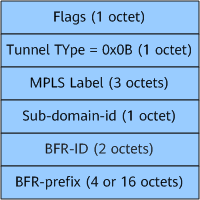
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, the PMSI tunnel attribute (PTA) carries information required for tunnel establishment. The PTA is carried in MVPN NLRI Type 1 and Type 3 routes that are advertised by a sender PE to a receiver PE, and in MVPN NLRI Type 4 routes that are advertised by a receiver PE to a sender PE.
Figure 2 shows the format of the PTA. Table 4 describes the values of the fields in the PTA on the ingress and egress.
Field |
Field Value on the Ingress |
Field Value on the Egress |
|---|---|---|
Flags |
1 |
0 |
Tunnel Type |
0x0B |
0x0B |
MPLS Label |
VPN label allocated by the upstream node |
0 |
Sub-domain-id |
Set by the ingress based on the service carried over a tunnel |
Sub-domain ID in the BIER tunnel information carried in the PMSI A-D route received from the ingress |
BFR-ID |
BFR-ID configured for the corresponding sub-domain on the ingress |
BFR-ID configured for the corresponding sub-domain on the egress |
BFR-prefix |
BFR-prefix configured for the corresponding sub-domain on the ingress |
BFR-prefix configured for the corresponding sub-domain on the egress |
Description of the BGP Prefix-SID Attribute
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, the Prefix-SID attribute carries Src.DTx information. Figure 3 shows the format of this attribute.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
TLV Type |
The value 5 indicates SRv6 L3 Service TLV. The value 6 indicates SRv6 L2 Service TLV. |
Length |
Length of the TLV value. |
Reserved |
Reserved field. |
Route type specific(variable) |
SRv6 service information. The length of this field is variable. For detailed format of this field, see the format of SRv6 Service Sub-TLVs. |
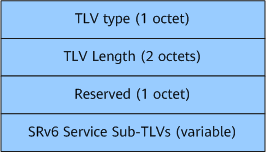
Format of SRv6 Service Sub-TLV
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV is used to advertise SRv6 service information. Figure 4 shows the format.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Type |
SRv6 service information type. |
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Length |
Length of an SRv6 Service Sub-TLV. |
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV (variable) |
The length of this field is variable, and this field contains data specific to SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Type. |
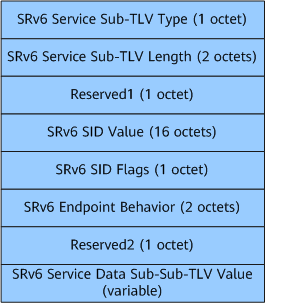
Format of SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV
SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV is used to advertise SRv6 SIDs. Figure 5 shows the format.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Type |
The value is fixed at 1, indicating SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV. |
SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Length |
Length of the SRv6 SID Value field. |
Reserved1 |
Reserved field. For the transmit end, the value is 0. This field must be ignored on the receive end. |
SRv6 SID Value |
SRv6 SID. |
SRv6 SID Flags |
SRv6 SID flag. For the transmit end, the value is 0. This field must be ignored on the receive end. |
SRv6 Endpoint Behavior |
SRv6 endpoint behavior. |
Reserved2 |
Reserved field. For the transmit end, the value is 0. This field must be ignored on the receive end. |
SRv6 Service Data Sub-Sub-TLV Value |
Used to advertise SRv6 SID attributes. The length is variable. |
Description of the BGP MSID Attribute
In G-BIER, a new BGP attribute (MSID) is used to carry the source IPv6 address.
The BGP MSID attribute and its content comply with the format requirements defined for BGP attributes. This attribute uses the design of the sub-TLV without fixed fields. Figure 6 shows the encoding format of the BGP MSID attribute, and Table 8 describes each field in it.
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Type. The value is 1. |
Sub-TLV Length |
Length. If there is one sub-sub-TLV, the value is 25. If there is no sub-sub-TLV, the value is 17. |
Reserved |
Reserved field. The value is 0. |
IPv6 Address |
Source IPv6 address. |
In G-BIER, the sub-TLV can carry one or no sub-sub-TLV. Figure 7 shows the format of the sub-sub-TLV, and Table 9 describes the fields in the sub-sub-TLV.
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Type. The value is 1. |
Sub-TLV Length |
The value is 5. |
Flags |
Currently, the value is 0. |
Prefix Length |
Length of the prefix in an IPv6 address. |
MSID Length |
Length of the MSID. It is recommended that the maximum value be less than or equal to 20. |
Reserved |
Reserved field. The value is 0. |