MVPN over BIERv6 Forwarding Process
Ingress IP Address on an MVPN over BIERv6 Network
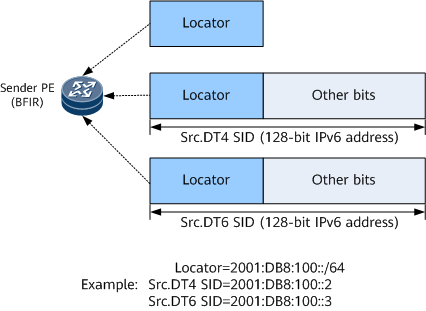
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, SRv6 must be enabled on internal nodes. The ingress (sender PE) needs to be configured with an IPv6 address for forwarding BIERv6 packets. This IPv6 address is called a Src.DT4 SID on an MVPNv4 over BIERv6 network, and called a Src.DT6 SID on an MVPNv6 over BIERv6 network. Src.DT4 is short for Source Address for Decapsulation and IPv4 Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB) Table Lookup, and Src.DT6 is short for Source Address for Decapsulation and IPv6 MFIB Table Lookup. The BIERv6 mode can be switched to the G-BIER mode. In G-BIER mode, the MSID attribute carries Src.DT information.
Figure 1 shows Src.DT4 SID and Src.DT6 SID structures.
On the MVPN over BIERv6 network, the ingress encapsulates the Src.DT4 SID or Src.DT6 SID as the outer source IPv6 address of each BIERv6 packet. This source IPv6 address remains unchanged during transmission from the BFIR to BFERs on the MVPN over BIERv6 network.
On an MVPN over G-BIER network, the egress PE needs to perform RPF check based on the selected upstream multicast hop (UMH). Therefore, the egress PE needs to know not only the ingress from which the IPv6 G-BIER packet came but also the MVPN instance to which the packet belongs. A source IPv6 address can contain the two parts of information. Specifically, the locator part of the source IPv6 address identifies the ingress from which the packet came, and the bits except the locator in the source IPv6 address, together with information about an upstream node, determine the MVPN instance to which the packet belongs.
Packet Forwarding Process
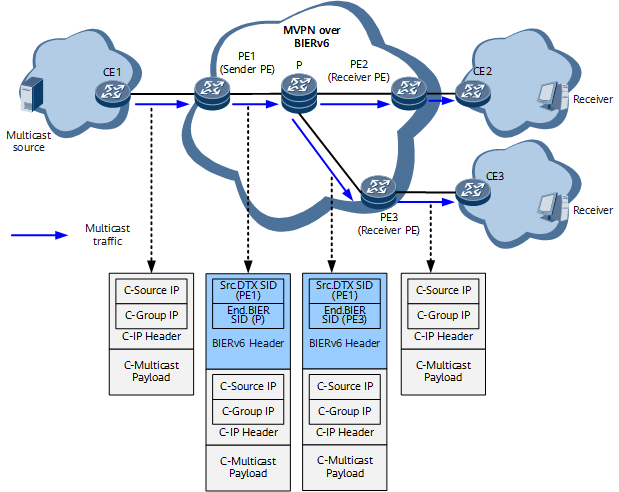
Figure 2 shows the packet forwarding process on an MVPN over BIERv6 network. In the figure, Src.DTX SID refers to a Src.DT4 SID on an MVPNv4 over BIERv6 network or a Src.DT6 SID on an MVPNv6 over BIERv6 network. In addition, C is short for customer in C-Group IP, C-Source IP, C-IP Header, and C-Multicast Payload, which represent the IP address of a C-multicast group, IP address of a C-multicast source, IP header of a C-multicast packet, and payload of a C-multicast packet, respectively.
- After receiving a C-multicast packet, the sender PE selects a PMSI tunnel based on the C-Source IP and C-Group IP in the C-IP Header of the packet. This PE then inserts the outer BIERv6 packet header (including a set ID and BitString) into the packet based on the tunnel attribute, and sets its Src.DT4 SID or Src.DT6 SID as the outer source IPv6 address.
- According to the BIERv6 forwarding process, the sender PE queries the BIFT, sets the destination address of the packet to the End.BIER SID of the next-hop node, and forwards the multicast packet through one or more matched outbound interfaces. For details about the BIERv6 forwarding process, see BIERv6 Forwarding Plane Fundamentals.
- Transit nodes on the MVPN over BIERv6 network forward the packet according to the BIERv6 forwarding process.
- After receiving the multicast packet, a receiver PE determines that it is a destination node of the BIERv6 packet according to the BitString. This PE removes the BIERv6 header and then forwards the packet out of the MVPN over BIERv6 network and into the VPN for forwarding.