Remote Attestation
Background
Communication devices and their system software may be maliciously replaced. Connecting such devices to networks compromises network security. Therefore, each device's identity must be attested before the device can access a network. This ensures that only trusted devices can access networks, thereby improving network security.
Definition
Remote attestation (RA) is used to check whether a device is trustworthy. It is a key technology of the trusted computing solution.
RA Fundamentals
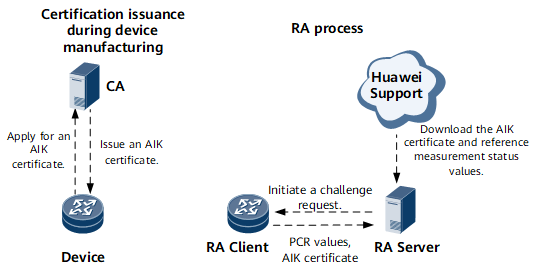
RA involves three components: RA server, RA client, and Certificate Authority (CA).
As the core component of RA, the RA server stores reference values (such as the BIOS, BootLoader, and OS kernel measurement status values) of the platform configuration register (PCR), receives the PCR values sent by an RA client, and checks whether the RA client is trustworthy.
The RA client is a device that is equipped with a trusted platform module (TPM) and supports trusted boot. It responds to the challenge request of the RA server and sends collected PCR values to the RA server.
The CA issues an attestation identity key (AIK) certificate (preset in the TPM) to prevent the RA client from being spoofed.
The RA process is as follows:
1. The RA server initiates a challenge request.
2. The RA client returns the AIK certificate, and the RA server verifies the certificate.
3. The RA client submits the PCR measurement status values.
4. The RA server downloads the reference measurement status values from https://support.huawei.com and updates the existing values.
5. The RA server checks whether the PCR measurement status values sent by the RA client are consistent with the downloaded values. If they are consistent, the RA client is verified successfully through RA.
Benefits
RA enables users to remotely check device trustworthiness.