Zero Touch Device Deployment Using the Commander
Zero touch devices can obtain file information from the Commander for deployment.
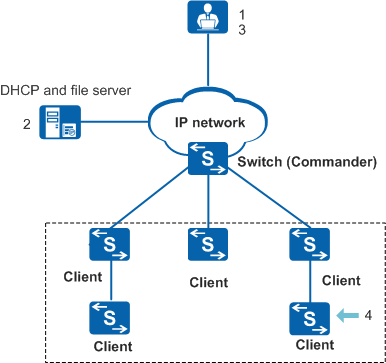
On the network shown in Figure 1, the clients are newly deployed switches without configuration files. The following uses one of these clients as an example to describe how the zero touch devices are configured through the Commander.
The network administrator selects a device as the Commander, plans the physical location, management IP address, management VLAN, and service parameters for the client, and makes a configuration file for the client.

Record the Commander IP address in the configuration file to facilitate client management and maintenance after the zero touch device deployment is complete.
The administrator configures the file server and DHCP server (only Option 148 is required), and saves the files required by the client to the working directory of the file server.
If the client and the DHCP server are located on different network segments, a DHCP relay agent must be deployed between them.
The administrator configures the file server IP address, user name, and password on the Commander and specifies files to be downloaded to the client based on the client MAC address or ESN reported by the hardware installation engineer.
If the network topology collection function is enabled on the Commander, the Commander can collect topology information automatically and specify information of files to be downloaded based on the collected topology information. Therefore, the network administrator does not need to obtain client MAC addresses or ESNs from the hardware installation engineer.
After the administrator completes the configuration, the client starts the zero touch device deployment process.
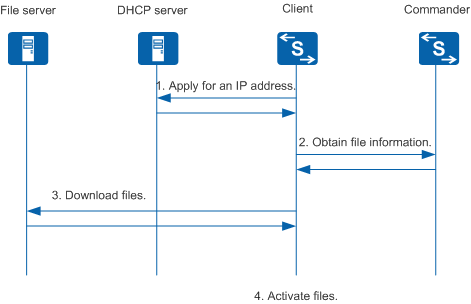
Figure 2 shows the interaction between network devices during the zero touch device deployment process.
The zero touch device deployment process goes through four stages:
Apply for an IP address.
The client sends a DHCP request to apply for an IP address. The DHCP server replies with a DHCP response that carries the allocated IP address and Commander IP address.
Obtain file information.
The client obtains file information from the Commander.
Download files.
The client downloads the required files from the file server according to the obtained information.
The client downloads required files in the following sequence:
- System software package
- Patch file
- Web page file
- Configuration file
- User-defined file
License files cannot be downloaded in the zero touch device deployment scenario.
-
The client activates the downloaded files according to the configured file activation policy.
If the client is a stack, the downloaded files are copied from the master switch to slave switches when the file activation time is reached. After the file copy is complete, the client activates the files and then starts to operate normally.
During the zero touch device deployment process, if a zero touch device cannot obtain an IP address, the device remains in the IP address application stage and periodically sends requests to apply for an IP address. The IP address application stage continues until the device obtains an IP address or the deployment process is stopped manually.
If an error occurs (for example, the server information is incorrect) after the device obtains an IP address, the device changes to the initial state and restarts the deployment process. If an error occurs again, the device returns to the initial state. This process repeats until it is stopped manually.
If the device fails to download a file in the file downloading stage, it tries again 1 minute later. If the download still fails after five retries, the device changes to the initial state 5 minutes later and restarts the DHCP process to obtain the file information and download the file again.