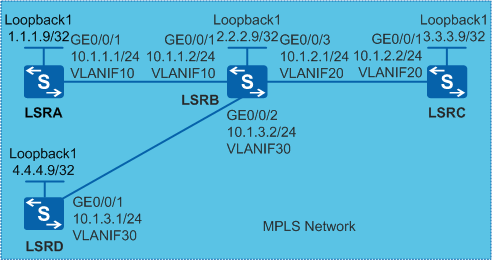
Example for Configuring an LDP Inbound Policy
Networking Requirements
On a network shown in Figure 1, MPLS LDP is deployed. LSRD functions as the access device and has low performance. If the number of received labels on LSRD is not controlled, many LSPs are established, which occupy memory resources and cause LSRD overload. Therefore, LSRD establishes LDP LSPs with only LSRC. The number of LSPs needs to be reduced to save LSRD memory resources.
Configuration Roadmap
To meet the preceding requirements, configure an LDP inbound policy. The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure OSPF on LSRs to implement IP connectivity on the backbone network.
- Configure local LDP sessions on the LSR so that LDP LSPs can be set up.
- Configure an LDP inbound policy so that the LSRD receives only Label Mapping messages from LSRB to LSRC. This setting saves the memory of the LSRD and saves resources.
Procedure
- Create VLANs and VLANIF interfaces on the switch, and configure IP addresses for the VLANIF interfaces.
# Configure LSRA. The configurations of LSRB, LSRC, and LSRD are similar to the configuration of LSRA, and are not mentioned here.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname LSRA [LSRA] interface loopback 1 [LSRA-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [LSRA-LoopBack1] quit [LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [LSRA] vlan 10 [LSRA-vlan10] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 10 [LSRA-Vlanif10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [LSRA-Vlanif10] quit
- Configure OSPF to advertise the network segments connecting to interfaces on each node and to advertise the routes of hosts with LSR IDs.
# Configure LSRA. The configurations of LSRB, LSRC, and LSRD are similar to the configuration of LSRA, and are not mentioned here.
[LSRA] ospf 1 [LSRA-ospf-1] area 0 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [LSRA-ospf-1] quit
- Configure local LDP sessions.
# Configure LSRA.
[LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [LSRA] mpls [LSRA-mpls] quit [LSRA] mpls ldp [LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 10 [LSRA-Vlanif10] mpls [LSRA-Vlanif10] mpls ldp [LSRA-Vlanif10] quit
# Configure LSRB.
[LSRB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [LSRB] mpls [LSRB-mpls] quit [LSRB] mpls ldp [LSRB-mpls-ldp] quit [LSRB] interface vlanif 10 [LSRB-Vlanif10] mpls [LSRB-Vlanif10] mpls ldp [LSRB-Vlanif10] quit [LSRB] interface vlanif 20 [LSRB-Vlanif20] mpls [LSRB-Vlanif20] mpls ldp [LSRB-Vlanif20] quit [LSRB] interface vlanif 30 [LSRB-Vlanif30] mpls [LSRB-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [LSRB-Vlanif30] quit
# Configure LSRC.
[LSRC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [LSRC] mpls [LSRC-mpls] quit [LSRC] mpls ldp [LSRC-mpls-ldp] quit [LSRC] interface vlanif 20 [LSRC-Vlanif20] mpls [LSRC-Vlanif20] mpls ldp [LSRC-Vlanif20] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[LSRD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [LSRD] mpls [LSRD-mpls] quit [LSRD] mpls ldp [LSRD-mpls-ldp] quit [LSRD] interface vlanif 30 [LSRD-Vlanif30] mpls [LSRD-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [LSRD-Vlanif30] quit
# After the configuration is complete, run the display mpls lsp command on LSRD to view the established LSP.
[LSRD] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - LSP Is Only Iterated by RLFA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.9/32 NULL/1024 -/Vlanif30 1.1.1.9/32 1024/1024 -/Vlanif30 2.2.2.9/32 NULL/3 -/Vlanif30 2.2.2.9/32 1025/3 -/Vlanif30 3.3.3.9/32 NULL/1025 -/Vlanif30 3.3.3.9/32 1026/1025 -/Vlanif30 4.4.4.9/32 3/NULL -/-The command output shows that the LSPs from LSRD to LSRA, LSRB, and LSRC are established.
- Configure an LDP inbound policy.
# Configure an IP prefix list on LSRD to allow only routes to LSRC to pass.
[LSRD] ip ip-prefix prefix1 permit 3.3.3.9 32
# Configure the LDP inbound policy on LSRD so that LSRC accepts only Label Mapping messages from LSRD.
[LSRD] mpls ldp [LSRD-mpls-ldp] inbound peer 2.2.2.9 fec ip-prefix prefix1 [LSRD-mpls-ldp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display mpls lsp command on LSRD to view the established LSP to LSRC.
[LSRD] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - LSP Is Only Iterated by RLFA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 3.3.3.9/32 NULL/1025 -/Vlanif30 3.3.3.9/32 1026/1025 -/Vlanif30 4.4.4.9/32 3/NULL -/-
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # vlan batch 10 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # returnLSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # vlan batch 10 20 30 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif30 ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # vlan batch 20 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # returnLSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # vlan batch 30 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls # mpls ldp inbound peer 2.2.2.9 fec ip-prefix prefix1 # interface Vlanif30 ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # ip ip-prefix prefix1 index 10 permit 3.3.3.9 32 # return