Example for Configuring SRLG Based on CR-LSP Hot Standby
Networking Requirements
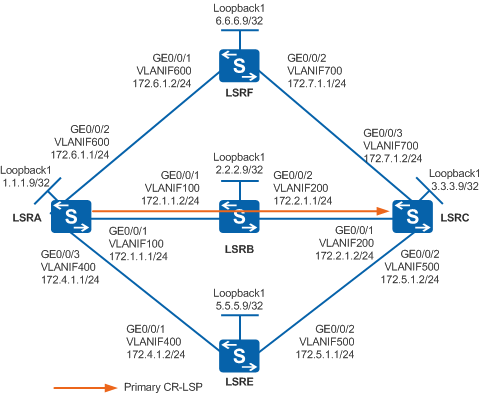
As shown in Figure 1, An MPLS TE tunnel is set up between LSRA and LSRC, with the path LSRA -> LSRB -> LSRC.
The link LSRA -> LSRB and the link LSRA -> LSRE are in the same SRLG (SRLG1 for example); the link LSRC -> LSRB and the link LSRC -> LSRE are in the same SLRG (SRLG2 for example).
To improve reliability, a hot-standby CR-LSP needs to be established and the links of the bypass CR-LSP and primary tunnel must be in different SRLGs.

In this scenario, to avoid loops, ensure that all connected interfaces have STP disabled and connected interfaces are removed from VLAN 1. If STP is enabled and VLANIF interfaces of switches are used to construct a Layer 3 ring network, an interface on the network will be blocked. As a result, Layer 3 services on the network cannot run normally.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to each interface and configure OSPF to ensure that there are reachable routes between LSRs.
Configure an ID for each LSR and globally enable MPLS, MPLS TE, RSVP-TE, CSPF on each node and interface, and enable OSPF TE.
On the ingress node of the primary tunnel, create a tunnel interface, and specify the IP address, tunneling protocol, destination IP address, tunnel ID, and dynamic signaling protocol RSVP-TE for the tunnel interface. The explicit path is LSRA -> LSRB -> LSRC.
Configure SRLG numbers for SRLG member interfaces.
Configure the SRLG path calculation mode on the ingress node of the primary tunnel.
Configure a hot-standby CR-LSP on the ingress node of the primary tunnel.
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface and configure OSPF.
# Configure LSRA. Configure IP addresses for interfaces of LSRB, LSRC, LSRE, and LSRF according to Figure 1. The configurations of LSRB, LSRC, LSRE, and LSRF are similar to the configuration of LSRA, and are not mentioned here.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname LSRA [LSRA] vlan batch 100 400 600 [LSRA] interface vlanif 100 [LSRA-Vlanif100] ip address 172.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [LSRA-Vlanif100] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 400 [LSRA-Vlanif400] ip address 172.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 [LSRA-Vlanif400] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 600 [LSRA-Vlanif600] ip address 172.6.1.1 255.255.255.0 [LSRA-Vlanif600] quit [LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 600 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type trunk [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit [LSRA] interface loopback 1 [LSRA-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 [LSRA-LoopBack1] quit [LSRA] ospf 1 [LSRA-ospf-1] area 0 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.6.1.0 0.0.0.255 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [LSRA-ospf-1] quit
After the configurations are complete, run the display ip routing-table command on each LSR. You can see that the LSRs learn the routes to Loopback1 of each other. The display on LSRA is used as an example.
[LSRA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 16 Routes : 18 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 172.1.1.2 Vlanif100 3.3.3.9/32 OSPF 10 2 D 172.1.1.2 Vlanif100 OSPF 10 2 D 172.4.1.2 Vlanif400 OSPF 10 2 D 172.6.1.2 Vlanif600 5.5.5.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 172.4.1.2 Vlanif400 6.6.6.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 172.6.1.2 Vlanif600 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.1.1.1 Vlanif100 172.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif100 172.2.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 172.1.1.2 Vlanif100 172.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.4.1.1 Vlanif400 172.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif400 172.5.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 172.4.1.2 Vlanif400 172.6.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.6.1.1 Vlanif600 172.6.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif600 172.7.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 172.6.1.2 Vlanif600 - Configure basic MPLS functions and enable MPLS TE, RSVP-TE,
and CSPF.
# Configure LSRA. The configurations of LSRB, LSRC, LSRE, and LSRF are similar to the configuration of LSRA, and are not mentioned here. CSPF only needs to be configured on the ingress node of the primary tunnel.
[LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [LSRA] mpls [LSRA-mpls] mpls te [LSRA-mpls] mpls rsvp-te [LSRA-mpls] mpls te cspf [LSRA-mpls] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 100 [LSRA-Vlanif100] mpls [LSRA-Vlanif100] mpls te [LSRA-Vlanif100] mpls rsvp-te [LSRA-Vlanif100] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 400 [LSRA-Vlanif400] mpls [LSRA-Vlanif400] mpls te [LSRA-Vlanif400] mpls rsvp-te [LSRA-Vlanif400] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 600 [LSRA-Vlanif600] mpls [LSRA-Vlanif600] mpls te [LSRA-Vlanif600] mpls rsvp-te [LSRA-Vlanif600] quit
- Configure OSPF TE.
# Configure LSRA. The configurations of LSRB, LSRC, LSRE, and LSRF are similar to the configuration of LSRA, and are not mentioned here.
[LSRA] ospf [LSRA-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable [LSRA-ospf-1] area 0 [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls-te enable [LSRA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [LSRA-ospf-1] quit
- On LSRA, create an MPLS TE tunnel for the primary CR-LSP.
# Configure the explicit path of the primary CR-LSP.
[LSRA] explicit-path pri-path [LSRA-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 172.1.1.2 [LSRA-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 172.2.1.2 [LSRA-explicit-path-pri-path] next hop 3.3.3.9 [LSRA-explicit-path-pri-path] quit
# Configure the MPLS TE tunnel interface of the primary CR-LSP.
[LSRA] interface tunnel 1 [LSRA-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopBack 1 [LSRA-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol mpls te [LSRA-Tunnel1] destination 3.3.3.9 [LSRA-Tunnel1] mpls te tunnel-id 100 [LSRA-Tunnel1] mpls te path explicit-path pri-path [LSRA-Tunnel1] mpls te commit [LSRA-Tunnel1] quit
Run the display interface tunnel 1 command on LSRA. You can see that the tunnel status is Up.
[LSRA] display interface tunnel 1 Tunnel1 current state : UP Line protocol current state : UP Last line protocol up time : 2013-01-22 16:57:00 Description: ...
- Configure SRLG.
Configure SRLG1 for links LSRA -> LSRB and LSRA -> LSRE, and SRLG2 for links LSRC -> LSRB and LSRC -> LSRE. Configure the SRLG path calculation mode on the ingress node LSRA of the primary tunnel.
# Configure LSRA.
[LSRA] interface vlanif 100 [LSRA-Vlanif100] mpls te srlg 1 [LSRA-Vlanif100] quit [LSRA] interface vlanif 400 [LSRA-Vlanif400] mpls te srlg 1 [LSRA-Vlanif400] quit
# Configure LSRB.
[LSRB] interface vlanif 200 [LSRB-Vlanif200] mpls te srlg 2 [LSRB-Vlanif200] quit
# Configure LSRE.
[LSRE] interface vlanif 500 [LSRE-Vlanif500] mpls te srlg 2 [LSRE-Vlanif500] quit
# Configure the SRLG path calculation mode on LSRA.
[LSRA] mpls [LSRA-mpls] mpls te srlg path-calculation strict [LSRA-mpls] quit
Run the display mpls te srlg all command to view SRLG information and the interfaces that belong to the SRLG. The display on LSRA is used as an example.
[LSRA] display mpls te srlg all Total SRLG supported : 1024 Total SRLG configured : 2 SRLG 1: Vlanif100 Vlanif400Run the display mpls te link-administration srlg-information to view SRLGs to which the interfaces belong. The display on LSRA is used as an example.
[LSRA] display mpls te link-administration srlg-information SRLGs on Vlanif100 : 1 SRLGs on Vlanif400 : 1Run the display mpls te cspf tedb srlg command to view TEDB information of the specified SRLG.
[LSRA] display mpls te cspf tedb srlg 1 Interface-Address IGP-Type Area 172.1.1.1 OSPF 0 172.4.1.1 OSPF 0
[LSRA] display mpls te cspf tedb srlg 2 Interface-Address IGP-Type Area 172.2.1.1 OSPF 0 172.5.1.1 OSPF 0
- Configure a hot-standby CR-LSP on the ingress node.
# Configure LSRA.
[LSRA] interface tunnel 1 [LSRA-Tunnel1] mpls te backup hot-standby [LSRA-Tunnel1] mpls te commit [LSRA-Tunnel1] quit
Run the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on LSRA. You can see that the hot-standby CR-LSP has been established.
[LSRA] display mpls te tunnel-interface ---------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel1 ---------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel State Desc : UP Active LSP : Primary LSP Session ID : 100 Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.9 Egress LSR ID: 3.3.3.9 Admin State : UP Oper State : UP Primary LSP State : UP Main LSP State : READY LSP ID : 54 Hot-Standby LSP State : UP Main LSP State : READY LSP ID : 32780Run the display mpls te hot-standby state interface tunnel 1 command on LSRA to view the hot-standby CR-LSP.
[LSRA] display mpls te hot-standby state interface tunnel 1 (s): same path --------------------------------------------------------------------- Verbose information about the Tunnel1 hot-standby state --------------------------------------------------------------------- session id : 100 main LSP token : 0x51 hot-standby LSP token : 0x4f HSB switch result : Primary LSP HSB switch reason : - WTR config time : 10s WTR remain time : - using overlapped path : no
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, run the display mpls te tunnel path command on LSRA to view nodes that the primary CR-LSP and backup CR-LSP pass.
[LSRA] display mpls te tunnel path Tunnel Interface Name : Tunnel1 Lsp ID : 1.1.1.9 :100 :54 Hop Information Hop 0 172.1.1.1 Hop 1 172.1.1.2 Hop 2 2.2.2.9 Hop 3 172.2.1.1 Hop 4 172.2.1.2 Hop 5 3.3.3.9 Tunnel Interface Name : Tunnel1 Lsp ID : 1.1.1.9 :100 :32780 Hop Information Hop 0 172.6.1.1 Hop 1 172.6.1.2 Hop 2 6.6.6.9 Hop 3 172.7.1.1 Hop 4 172.7.1.2 Hop 5 3.3.3.9
# Run the shutdown command on GE0/0/2 of LSRA.
[LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] shutdown [LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Run the display mpls te hot-standby state interface tunnel 1 command on LSRA. You can see that the hot-standby LSP token is 0x0. This means that the hot-standby LSP is not set up even though there are paths for setting up the hot-standby LSP.
[LSRA] display mpls te hot-standby state interface tunnel 1 (s): same path --------------------------------------------------------------------- Verbose information about the Tunnel1 hot-standby state --------------------------------------------------------------------- session id : 100 main LSP token : 0x51 hot-standby LSP token : 0x0 HSB switch result : Primary LSP HSB switch reason : - WTR config time : 10s WTR remain time : - using overlapped path : -
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # vlan batch 100 400 600 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls mpls te mpls te srlg path-calculation strict mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # explicit-path pri-path next hop 172.1.1.2 next hop 172.2.1.2 next hop 3.3.3.9 # interface Vlanif100 ip address 172.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te srlg 1 mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif400 ip address 172.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te srlg 1 mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif600 ip address 172.6.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 600 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.9 mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te record-route mpls te path explicit-path pri-path mpls te backup hot-standby mpls te commit # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.6.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # vlan batch 100 200 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif100 ip address 172.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif200 ip address 172.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te srlg 2 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # vlan batch 200 500 700 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif200 ip address 172.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif500 ip address 172.5.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif700 ip address 172.7.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 500 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 700 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.5.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.7.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRE configuration file
# sysname LSRE # vlan batch 400 500 # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif400 ip address 172.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif500 ip address 172.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te srlg 2 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 500 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.5.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRF configuration file
# sysname LSRF # vlan batch 600 700 # mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif600 ip address 172.6.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif700 ip address 172.7.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 600 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 700 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 6.6.6.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 6.6.6.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.6.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.7.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return