Example for Configuring Static BFD for CR-LSPs
Networking Requirements
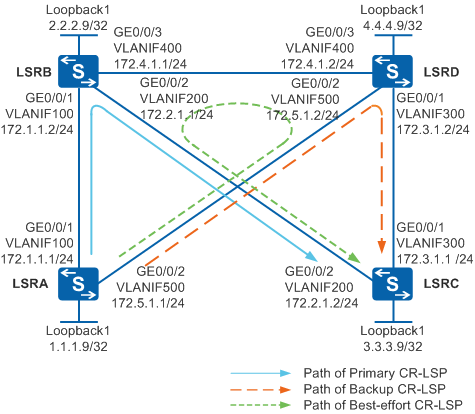
The path of the primary CR-LSP is LSRA -> LSRB -> LSRC.
The path of the backup CR-LSP is LSRA -> LSRD -> LSRC.
When the primary CR-LSP fails, traffic switches to the backup CR-LSP. After the primary CR-LSP recovers, traffic switches back to the primary CR-LSP in 15 seconds. If both the primary CR-LSP and backup CR-LSP fail, traffic switches to the best-effort path. Explicit paths can be configured for the primary and backup CR-LSPs. A best-effort path can be generated automatically. In this example, the best-effort path is LSRA -> LSRD -> LSRB -> LSRC. The calculated best-effort path varies according to the faulty node.
Two static BFD sessions need to be configured to detect primary and backup CR-LSPs:
When the primary CR-LSP fails, traffic fast switches to the backup CR-LSP.
When the backup CR-LSP fails within 15 seconds after the primary CR-LSP recovers, traffic switches back to the primary CR-LSP.

In this scenario, to avoid loops, ensure that all connected interfaces have STP disabled and connected interfaces are removed from VLAN 1. If STP is enabled and VLANIF interfaces of switches are used to construct a Layer 3 ring network, an interface on the network will be blocked. As a result, Layer 3 services on the network cannot run normally.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure a hot-standby CR-LSP and best-effort path.
Create two BFD sessions on the ingress node and bind them to CR-LSPs to detect primary and backup CR-LSPs. Configure two BFD sessions on the egress node and bind them to IP addresses (ensure that the route from LSRC to LSRA is reachable).
Procedure
- Configure a hot-standby CR-LSP and best-effort path.
Configure the primary CR-LSP, backup CR-LSP, and best-effort path according to Example for Configuring CR-LSP Hot Standby.
- Configure static BFD for CR-LSPs.
Establish BFD sessions between LSRA and LSRC to detect faults on primary and backup CR-LSPs. Bind the BFD session on LSRA to the CR-LSP and BFD session on LSRC to the IP address. Set the intervals for sending and receiving BFD packets to 500 ms and the local detection multiplier of BFD to 3.
# Configure LSRA.
[LSRA] bfd [LSRA-bfd] quit [LSRA] bfd prilsp2lsrc bind mpls-te interface tunnel 1 te-lsp [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] discriminator local 139 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] discriminator remote 239 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] min-tx-interval 500 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] min-rx-interval 500 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] detect-multiplier 3 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] process-pst [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] notify neighbor-down [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] commit [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-prilsp2lsrc] quit [LSRA] bfd backuplsp2lsrc bind mpls-te interface tunnel 1 te-lsp backup [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] discriminator local 339 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] discriminator remote 439 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] min-tx-interval 500 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] min-rx-interval 500 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] detect-multiplier 3 [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] process-pst [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] notify neighbor-down [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] commit [LSRA-bfd-lsp-session-backuplsp2lsrc] quit
# Configure LSRC.
[LSRC] bfd [LSRC-bfd] quit [LSRC] bfd reversepri2lsra bind peer-ip 1.1.1.9 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] discriminator local 239 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] discriminator remote 139 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] min-tx-interval 500 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] min-rx-interval 500 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] detect-multiplier 3 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] commit [LSRC-bfd-session-reversepri2lsra] quit [LSRC] bfd reversebac2lsra bind peer-ip 1.1.1.9 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] discriminator local 439 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] discriminator remote 339 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] min-tx-interval 500 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] min-rx-interval 500 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] detect-multiplier 3 [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] commit [LSRC-bfd-session-reversebac2lsra] quit
After the configurations are complete, run the display bfd session discriminator command on LSRA and LSRC. You can see that the BFD session status is Up.
The display on LSRA is used as an example.
[LSRA] display bfd session discriminator 139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type InterfaceName -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 139 239 3.3.3.9 Up S_TE_LSP Tunnel1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- [LSRA] display bfd session discriminator 339 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type InterfaceName -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 339 439 3.3.3.9 Up S_TE_LSP Tunnel1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Verify the configuration.
Connect two interfaces, Port 1 and Port 2, on a tester to LSRA and LSRC respectively. On Port 1, inject MPLS traffic and send traffic to Port 2. After the cable attached to GE0/0/1 on LSRA or LSRB is removed, traffic fast switches to the backup CR-LSP at the millisecond level.
After the cable is inserted into GE0/0/1, run the display mpls te tunnel-interface tunnel 1 command to view tunnel information until the primary CR-LSP is set up. Then remove the cable from GE0/0/2 on LSRA or LSRD within 15s. You can see that traffic switches back to the primary CR-LSP at the millisecond level.
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # vlan batch 100 500 # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # explicit-path backup-path next hop 172.5.1.2 next hop 172.3.1.1 next hop 3.3.3.9 # explicit-path pri-path next hop 172.1.1.2 next hop 172.2.1.2 next hop 3.3.3.9 # interface Vlanif100 ip address 172.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif500 ip address 172.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 500 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel1 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.9 mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te record-route mpls te path explicit-path pri-path mpls te path explicit-path backup-path secondary mpls te backup hot-standby mode revertive wtr 15 mpls te backup ordinary best-effort mpls te commit # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.5.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # bfd backuplsp2lsrc bind mpls-te interface Tunnel1 te-lsp backup discriminator local 339 discriminator remote 439 min-tx-interval 500 min-rx-interval 500 process-pst notify neighbor-down commit # bfd prilsp2lsrc bind mpls-te interface Tunnel1 te-lsp discriminator local 139 discriminator remote 239 min-tx-interval 500 min-rx-interval 500 process-pst notify neighbor-down commit # return
LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # vlan batch 100 200 400 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif100 ip address 172.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif200 ip address 172.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif400 ip address 172.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # vlan batch 200 300 # bfd # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif200 ip address 172.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif300 ip address 172.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 300 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # bfd reversebac2lsra bind peer-ip 1.1.1.9 discriminator local 439 discriminator remote 339 min-tx-interval 500 min-rx-interval 500 commit # bfd reversepri2lsra bind peer-ip 1.1.1.9 discriminator local 239 discriminator remote 139 min-tx-interval 500 min-rx-interval 500 commit # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return
LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # vlan batch 300 400 500 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif300 ip address 172.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif400 ip address 172.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface Vlanif500 ip address 172.5.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 300 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 500 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 400 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.5.1.0 0.0.0.255 mpls-te enable # return