Example for Configuring OSPF-BGP Synchronization
Networking Requirements
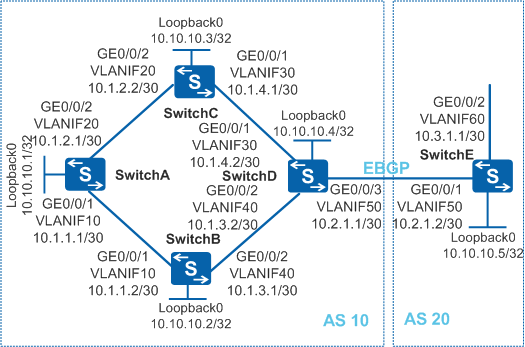
As shown in Figure 1, an EBGP connection is established between SwitchD and SwitchE. IBGP connections are established between switches in AS 10, and OSPF is used as an IGP protocol. OSPF-BGP synchronization needs to be enabled on SwitchB so that the traffic from SwitchA to AS 20 will not be interrupted when SwitchB restarts.

In this scenario, ensure that all connected interfaces have STP disabled. If STP is enabled and VLANIF interfaces of switches are used to construct a Layer 3 ring network, an interface on the network will be blocked. As a result, Layer 3 services on the network cannot run normally.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure VLANs for interfaces, VLANIF interfaces for the VLANs, and IP addresses for each VLANIF interface to implement communication within network segments.
Configure basic OSPF functions and IBGP connections on SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD (excluding 10.2.1.1/30) to implement device connections within AS 10.
Configure EBGP connections between SwitchD and SwitchE, and import direct routes and OSPF routes to implement communication between AS 10 and AS 20.
Set the OSPF protocol cost to 2 on SwitchC so that SwitchA selects only SwitchB as the intermediate router to the network segment 10.2.1.0 and SwitchC becomes the backup of SwitchB.
Enable OSPF-BGP synchronization on SwitchB so that the traffic from SwitchA to AS 20 will not be interrupted when SwitchB restarts.
Procedure
- Configure VLANs for interfaces.
# Configure SwitchA. The configurations of SwitchB, SwitchC, SwitchD, and SwitchE are similar to the configuration of SwitchA.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchA [SwitchA] vlan batch 10 20 [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
- Assign IP addresses to the VLANIF interfaces and loopback interfaces.
# Configure SwitchA. The configurations of SwitchB, SwitchC, SwitchD, and SwitchE are similar to the configuration of SwitchA.
[SwitchA] interface vlanif 10 [SwitchA-Vlanif10] ip address 10.1.1.1 30 [SwitchA-Vlanif10] quit [SwitchA] interface vlanif 20 [SwitchA-Vlanif20] ip address 10.1.2.1 30 [SwitchA-Vlanif20] quit [SwitchA] interface loopback 0 [SwitchA-LoopBack0] ip address 10.10.10.1 32 [SwitchA-LoopBack0] quit
- Configure basic OSPF functions.
# Configure SwitchA. The configurations of SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD are similar to the configuration of SwitchA.
[SwitchA] router id 10.10.10.1 [SwitchA] ospf 1 [SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0 [SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.0 [SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 [SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 [SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [SwitchA-ospf-1] quit
- Configure IBGP fully meshed connections.
# Configure SwitchA.
[SwitchA] bgp 10 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 [SwitchA-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchA-bgp] quit
# Configure SwitchB.
[SwitchB] bgp 10 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 [SwitchB-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchB-bgp] quit
# Configure SwitchC.
[SwitchC] bgp 10 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 [SwitchC-bgp] peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchC-bgp] quit
# Configure SwitchD.
[SwitchD] bgp 10 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [SwitchD-bgp] quit
- Establish an EBGP connection.
# Configure SwitchD.
[SwitchD] bgp 10 [SwitchD-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 20 [SwitchD-bgp] import-route direct [SwitchD-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [SwitchD-bgp] quit
# Configure SwitchE.
[SwitchE] bgp 20 [SwitchE-bgp] router-id 10.10.10.5 [SwitchE-bgp] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 10 [SwitchE-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [SwitchE-bgp-af-ipv4] network 10.3.1.0 30 [SwitchE-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [SwitchE-bgp] quit
- Configure a cost for OSPF on SwitchC.
[SwitchC] interface vlanif 20 [SwitchC-Vlanif20] ospf cost 2 [SwitchC-Vlanif20] quit [SwitchC] interface vlanif 30 [SwitchC-Vlanif30] ospf cost 2 [SwitchC-Vlanif30] quit
# Check the routing table on SwitchA. The routing table shows that the route to the destination network segment 10.3.1.0 is learned through BGP and the outbound interface is Vlanif10.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 14 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif10 10.1.2.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 Vlanif20 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif20 10.1.3.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.1.4.0/30 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 Vlanif20 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.2.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.10.10.4 Vlanif10 10.3.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.2.1.2 Vlanif10 10.10.10.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.10.10.2/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.10.10.3/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.2.2 Vlanif20 10.10.10.4/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# Check the routing table on SwitchB.
[SwitchB] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 14 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif10 10.1.2.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.1.3.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.3.1 Vlanif40 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif40 10.1.4.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.2.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.10.10.4 Vlanif40 10.3.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.2.1.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.1/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.10.10.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.10.10.3/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.4/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
The preceding command output shows that the route to the destination network segment 10.3.1.0 is learned by SwitchB through BGP and the outbound interface is Vlanif40. The routes to the network segments 10.1.2.0 and 10.1.4.0 are learned through OSPF, and the costs of the routes are both 2.
- Configure OSPF-BGP synchronization on SwitchB.
[SwitchB] ospf [SwitchB-ospf-1] stub-router on-startup [SwitchB-ospf-1] return
- Verify the configuration.
# Save the configurations.
<SwitchB> saveThe system displays a message asking whether you want to save the configurations. Enter y.
# Restart SwitchB.
<SwitchB> rebootThe system displays a message asking whether you want to continue with a system reboot. Enter y.
# Check the routing table on SwitchA. The routing table shows that the route to the destination network segment 10.3.1.0 is learned through BGP and the outbound interface is Vlanif20.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 10 Routes : 10 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.2.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 Vlanif20 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif20 10.1.4.0/30 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 Vlanif20 10.2.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.10.10.4 Vlanif20 10.3.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.2.1.2 Vlanif20 10.10.10.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.10.10.3/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.2.2 Vlanif20 10.10.10.4/32 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 Vlanif20 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# Check the routing table on SwitchB. The routing table shows that only OSPF routes exist in the routing table and their costs are at least 65535. This is because that OSPF (IGP) routes converge faster than BGP routes.
<SwitchB> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 12 Routes : 13 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif10 10.1.2.0/30 OSPF 10 65536 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.1.3.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.3.1 Vlanif40 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif40 10.1.4.0/30 OSPF 10 65536 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.1/32 OSPF 10 65535 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.10.10.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.10.10.3/32 OSPF 10 65536 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 OSPF 10 65536 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.4/32 OSPF 10 65535 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# After the network is stable, check the routing table of SwitchB again.
<SwitchB> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 14 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 Vlanif10 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif10 10.1.2.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.1.3.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.3.1 Vlanif40 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif40 10.1.4.0/30 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.2.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.10.10.4 Vlanif40 10.3.1.0/30 IBGP 255 0 RD 10.2.1.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.1/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 10.10.10.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0 10.10.10.3/32 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.1 Vlanif10 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 10.10.10.4/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.3.2 Vlanif40 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
The preceding command output shows that, after BGP routes on SwitchB converge, the routing information restores.
Configuration Files
SwitchA configuration file
# sysname SwitchA # router id 10.10.10.1 # vlan batch 10 20 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 10 peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.10.2 enable peer 10.10.10.3 enable peer 10.10.10.4 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.0 # return
SwitchB configuration file
# sysname SwitchB # router id 10.10.10.2 # vlan batch 10 40 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface Vlanif40 ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 10 peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.10.1 enable peer 10.10.10.3 enable peer 10.10.10.4 enable # ospf 1 stub-router on-startup area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.10.10.2 0.0.0.0 # return
SwitchC configuration file
# sysname SwitchC # router id 10.10.10.3 # vlan batch 20 30 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252 ospf cost 2 # interface Vlanif30 ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.252 ospf cost 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 10.10.10.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 10 peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.4 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.10.1 enable peer 10.10.10.2 enable peer 10.10.10.4 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.10.10.3 0.0.0.0 # return
SwitchD configuration file
# sysname SwitchD # router id 10.10.10.4 # vlan batch 30 40 50 # interface Vlanif30 ip address 10.1.4.2 255.255.255.252 # interface Vlanif40 ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.252 # interface Vlanif50 ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 10.10.10.4 255.255.255.255 # bgp 10 peer 10.10.10.1 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.2 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.10.10.3 as-number 10 peer 10.10.10.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 20 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct import-route ospf 1 peer 10.10.10.1 enable peer 10.10.10.2 enable peer 10.10.10.3 enable peer 10.2.1.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.10.10.4 0.0.0.0 # return
SwitchE configuration file
# sysname SwitchE # vlan batch 50 60 # interface Vlanif50 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface Vlanif60 ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 60 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 10.10.10.5 255.255.255.255 # bgp 20 router-id 10.10.10.5 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 10 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 10.3.1.0 255.255.255.252 peer 10.2.1.1 enable # return