Example for Configuring Dynamic BFD for a Multi-hop PW
Networking Requirements
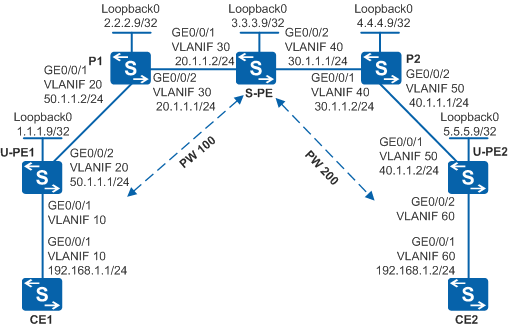
As shown in Figure 1, UPE1 and UPE2 are connected through the MPLS backbone network. A dynamic multi-hop PW is set up between UPE1 and UPE2 through the LSP tunnel, with SPE functioning as the switching node.
A dynamic BFD session is required to check connectivity of the multi-hop PW between UPE1 and UPE2, protecting services on the link.

By default, LNP is enabled globally on the device. If a VLANIF interface is used as an AC-side interface for L2VPN, the configuration conflicts with LNP. In this case, run the lnp disable command in the system view to disable LNP.
The lnp disable command has no impact on services before the device restarts. After the device restarts, the device can only forward packets from the VLANs specified by the port default vlan command at Layer 2. The port default vlan 1 command is configured by default, so only packets of VLAN 1 can be forwarded at Layer 2.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP protocol on the backbone network so that backbone network devices can communicate.
Configure basic MPLS functions and establish LSP tunnels on the backbone network. Establish remote MPLS LDP peer relationships between UPE1 and SPE, and between UPE2 and SPE.
Create a PW template and enable the control word function.
Set up an MPLS L2VC between U-PEs.
Configure PW switching on SPE.
Configure basic BFD functions and dynamic BFD for PWs on U-PEs.
Procedure
- Configure VLANs that each interface belongs to and assign an IP address to each VLANIF interface according to Figure 1.
# Configure CE1. The configuration on UPE1, UPE2, P1, P2, SPE, and CE2 is similar to the CE1, and is not mentioned here.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [CE1] vlan batch 10 [CE1] interface vlanif 10 [CE1-Vlanif10] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 [CE1-Vlanif10] quit [CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Configure an IGP protocol on the MPLS backbone network.
Configure an IGP protocol on the MPLS backbone network. This example uses OSPF.
When configuring OSPF, advertise 32-bit IP addresses of loopback interfaces on UPE1, SPE, and UPE2.
# Configure UPE1.
[UPE1] interface loopback 0 [UPE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [UPE1-LoopBack0] quit [UPE1] interface vlanif 20 [UPE1-Vlanif20] ip address 50.1.1.1 24 [UPE1-Vlanif20] quit [UPE1] ospf 1 [UPE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 50.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [UPE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure P1.
[P1] interface loopback 0 [P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [P1-LoopBack0] quit [P1] interface vlanif 20 [P1-Vlanif20] ip address 50.1.1.2 24 [P1-Vlanif20] quit [P1] interface vlanif 30 [P1-Vlanif30] ip address 20.1.1.1 24 [P1-Vlanif30] quit [P1] ospf 1 [P1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 50.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [P1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure SPE.
[SPE] interface loopback 0 [SPE-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [SPE-LoopBack0] quit [SPE] interface vlanif 30 [SPE-Vlanif30] ip address 20.1.1.2 24 [SPE-Vlanif30] quit [SPE] interface vlanif 40 [SPE-Vlanif40] ip address 30.1.1.1 24 [SPE-Vlanif40] quit [SPE] ospf 1 [SPE-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [SPE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 [SPE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [SPE-ospf-1] quit
# Configure P2.
[P2] interface loopback 0 [P2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.9 32 [P2-LoopBack0] quit [P2] interface vlanif 40 [P2-Vlanif40] ip address 30.1.1.2 24 [P2-Vlanif40] quit [P2] interface vlanif 50 [P2-Vlanif50] ip address 40.1.1.1 24 [P2-Vlanif50] quit [P2] ospf 1 [P2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 [P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [P2-ospf-1] quit
# Configure UPE2.
[UPE2] interface loopback 0 [UPE2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.9 32 [UPE2-LoopBack0] quit [UPE2] interface vlanif 50 [UPE2-Vlanif50] ip address 40.1.1.2 24 [UPE2-Vlanif50] quit [UPE2] ospf 1 [UPE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [UPE2-ospf-1] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip routing-table command on U-PEs, Ps, and SPE. You can see that these devices have learnt the routes of each other.
The U-PEs can ping each other. The display on UPE1 is used as an example.
[UPE1] ping 40.1.1.2 PING 40.1.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 40.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=252 time=160 ms Reply from 40.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=252 time=120 ms Reply from 40.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=252 time=150 ms Reply from 40.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=252 time=150 ms Reply from 40.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=252 time=160 ms --- 40.1.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 120/148/160 ms - Enable MPLS, and set up LSP tunnels and remote LDP sessions.
Configure basic MPLS functions on the MPLS backbone network, and set up LSP tunnels and remote LDP sessions between UPE1 and SPE, and between SPE and UPE2.
# Configure UPE1.
[UPE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [UPE1] mpls [UPE1-mpls] quit [UPE1] mpls ldp [UPE1-mpls-ldp] quit [UPE1] interface vlanif 20 [UPE1-Vlanif20] mpls [UPE1-Vlanif20] mpls ldp [UPE1-Vlanif20] quit [UPE1] mpls ldp remote-peer 3.3.3.9 [UPE1-mpls-ldp-remote-3.3.3.9] remote-ip 3.3.3.9 [UPE1-mpls-ldp-remote-3.3.3.9] quit
# Configure P1.
[P1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [P1] mpls [P1-mpls] quit [P1] mpls ldp [P1-mpls-ldp] quit [P1] interface vlanif 20 [P1-Vlanif20] mpls [P1-Vlanif20] mpls ldp [P1-Vlanif20] quit [P1] interface vlanif 30 [P1-Vlanif30] mpls [P1-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [P1-Vlanif30] quit
# Configure SPE.
[SPE] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [SPE] mpls [SPE-mpls] quit [SPE] mpls ldp [SPE-mpls-ldp] quit [SPE] interface vlanif 30 [SPE-Vlanif30] mpls [SPE-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [SPE-Vlanif30] quit [SPE] interface vlanif 40 [SPE-Vlanif40] mpls [SPE-Vlanif40] mpls ldp [SPE-Vlanif40] quit [SPE] mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.9 [SPE-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.9] remote-ip 1.1.1.9 [SPE-mpls-ldp-remote-1.1.1.9] quit [SPE] mpls ldp remote-peer 5.5.5.9 [SPE-mpls-ldp-remote-5.5.5.9] remote-ip 5.5.5.9 [SPE-mpls-ldp-remote-5.5.5.9] quit
# Configure P2.
[P2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [P2] mpls [P2-mpls] quit [P2] mpls ldp [P2-mpls-ldp] quit [P2] interface vlanif 40 [P2-Vlanif40] mpls [P2-Vlanif40] mpls ldp [P2-Vlanif40] quit [P2] interface vlanif 50 [P2-Vlanif50] mpls [P2-Vlanif50] mpls ldp [P2-Vlanif50] quit
# Configure UPE2.
[UPE2] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 [UPE2] mpls [UPE2-mpls] quit [UPE2] mpls ldp [UPE2-mpls-ldp] quit [UPE2] interface vlanif 50 [UPE2-Vlanif50] mpls [UPE2-Vlanif50] mpls ldp [UPE2-Vlanif50] quit [UPE2] mpls ldp remote-peer 3.3.3.9 [UPE2-mpls-ldp-remote-3.3.3.9] remote-ip 3.3.3.9 [UPE2-mpls-ldp-remote-3.3.3.9] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display mpls ldp session command on U-PEs, Ps, or SPE. You can see that the Status field is Operational. Run the display mpls ldp peer command. You can view the LDP peer status. Run the display mpls lsp command to view the LSP status. The display on SPE is used as an example.
[SPE] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) A '*' before a session means the session is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1.1.1.9:0 Operational DU Active 0000:00:14 57/57 2.2.2.9:0 Operational DU Active 0000:00:14 56/56 4.4.4.9:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:05 22/22 5.5.5.9:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:12 52/52 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 4 session(s) Found.
[SPE] display mpls ldp peer LDP Peer Information in Public network A '*' before a peer means the peer is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID TransportAddress DiscoverySource ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1.1.1.9:0 1.1.1.9 Remote Peer : 1.1.1.9 2.2.2.9:0 2.2.2.9 Vlanif30 4.4.4.9:0 4.4.4.9 Vlanif40 5.5.5.9:0 5.5.5.9 Remote Peer : 5.5.5.9 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 4 Peer(s) Found.
[SPE] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - LSP Is Only Iterated by RLFA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 3.3.3.9/32 3/NULL -/- 1.1.1.9/32 NULL/1024 -/Vlanif30 1.1.1.9/32 1024/1024 -/Vlanif30 2.2.2.9/32 NULL/3 -/Vlanif30 2.2.2.9/32 1025/3 -/Vlanif30 4.4.4.9/32 NULL/3 -/Vlanif40 4.4.4.9/32 1027/3 -/Vlanif40 5.5.5.9/32 NULL/1027 -/Vlanif40 5.5.5.9/32 1026/1027 -/Vlanif40 - Create and configure PW templates.
Create PW templates and enable the control word function.
# Configure UPE1.
[UPE1] mpls l2vpn [UPE1-l2vpn] quit [UPE1] pw-template pwt [UPE1-pw-template-pwt] peer-address 3.3.3.9 [UPE1-pw-template-pwt] control-word [UPE1-pw-template-pwt] quit
# Configure UPE2.
[UPE2] mpls l2vpn [UPE2-l2vpn] quit [UPE2] pw-template pwt [UPE2-pw-template-pwt] peer-address 3.3.3.9 [UPE2-pw-template-pwt] control-word [UPE2-pw-template-pwt] quit
- Create VCs.
Configure dynamic PWs on U-PEs, and configure PW switching on SPE.
# Configure UPE1.In this example, a VLANIF interface is used as the AC-side interface, so you need to run the lnp disable command in the system view before performing the following steps. If you cannot disable LNP on the live network, do not use a VLANIF interface as the AC-side interface.
[UPE1] interface vlanif 10 [UPE1-Vlanif10] mpls l2vc pw-template pwt 100 [UPE1-Vlanif10] quit
# Configure SPE.
[SPE] mpls l2vpn [SPE-l2vpn] quit [SPE] mpls switch-l2vc 1.1.1.9 100 between 5.5.5.9 200 encapsulation vlan
# Configure UPE2.In this example, a VLANIF interface is used as the AC-side interface, so you need to run the lnp disable command in the system view before performing the following steps. If you cannot disable LNP on the live network, do not use a VLANIF interface as the AC-side interface.
[UPE2] interface vlanif 60 [UPE2-Vlanif60] mpls l2vc pw-template pwt 200 [UPE2-Vlanif60] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display mpls l2vc interface command on U-PEs to check L2VPN connections. You can see that PWs are set up and in Active state. In addition, BFD for PWs is disabled on the PWs.
The display on UPE1 is used as an example.
[UPE1] display mpls l2vc interface vlanif 10 *client interface : Vlanif10 is up Administrator PW : no session state : up AC status : up Ignore AC state : disable VC state : up Label state : 0 Token state : 0 VC ID : 100 VC type : VLAN destination : 3.3.3.9 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 8195 remote VC label : 8195 local AC OAM State : up local PSN OAM State : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN OAM state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote status code : 0x0 ignore standby state : no BFD for PW : unavailable VCCV State : up manual fault : not set active state : active forwarding entry : exist link state : up local VC MTU : 1500 remote VC MTU : 1500 local VCCV : cw alert ttl lsp-ping bfd remote VCCV : cw alert ttl lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- PW template name : pwt primary or secondary : primary load balance type : flow Access-port : false Switchover Flag : false VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x4800200f Backup TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x0 create time : 0 days, 0 hours, 2 minutes, 40 seconds up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 12 minutes, 59 seconds last change time : 0 days, 0 hours, 12 minutes, 59 seconds VC last up time : 2010/11/26 08:25:38 VC total up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 12 minutes, 59 seconds CKey : 16 NKey : 15 PW redundancy mode : frr AdminPw interface : -- AdminPw link state : -- Diffserv Mode : uniform Service Class : be Color : -- DomainId : -- Domain Name : --
- Configure dynamic BFD for a multi-hop PW on PEs.
# Configure UPE1.
[UPE1] bfd [UPE1-bfd] quit [UPE1] bfd for pw enable [UPE1] interface vlanif 10 [UPE1-Vlanif10] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 remote-vcid 200 [UPE1-Vlanif10] quit
# Configure UPE2.
[UPE2] bfd [UPE2-bfd] quit [UPE2] bfd for pw enable [UPE2] interface vlanif 60 [UPE2-Vlanif60] mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 remote-vcid 100 [UPE2-Vlanif60] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# CE1 and CE2 can ping each other successfully.
<CE1> ping 192.168.1.2 PING 192.168.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=600 ms Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=160 ms Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=220 ms Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=210 ms Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=220 ms --- 192.168.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 160/282/600 ms# Run the display mpls l2vc interface command on U-PEs to view the PW status. You can see that dynamic BFD for PWs is enabled and the BFD session is Up.
The display on UPE1 is used as an example.
[UPE1] display mpls l2vc interface vlanif 10 *client interface : Vlanif10 is up Administrator PW : no session state : up AC status : up Ignore AC state : disable VC state : up Label state : 0 Token state : 0 VC ID : 100 VC type : VLAN destination : 3.3.3.9 local group ID : 0 remote group ID : 0 local VC label : 8195 remote VC label : 8195 local AC OAM State : up local PSN OAM State : up local forwarding state : forwarding local status code : 0x0 remote AC OAM state : up remote PSN OAM state : up remote forwarding state: forwarding remote status code : 0x0 ignore standby state : no Dynamic BFD for PW : enable Detect Multipier : 3 Min Transit Interval : 100 Max Receive Interval : 100 Dynamic BFD Session : built BFD for PW : available BFD sessionIndex : 256 BFD state : up VCCV State : up manual fault : not set active state : active forwarding entry : exist link state : up local VC MTU : 4470 remote VC MTU : 4470 local VCCV : cw alert ttl lsp-ping bfd remote VCCV : cw alert ttl lsp-ping bfd local control word : enable remote control word : enable tunnel policy name : -- PW template name : pwt primary or secondary : primary load balance type : flow Access-port : false Switchover Flag : false VC tunnel/token info : 1 tunnels/tokens NO.0 TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x4800200f Backup TNL type : lsp , TNL ID : 0x0 create time : 0 days, 0 hours, 24 minutes, 0 seconds up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 15 minutes, 0 seconds last change time : 0 days, 0 hours, 15 minutes, 0 seconds VC last up time : 2010/11/26 08:25:38 VC total up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 15 minutes, 0 seconds CKey : 16 NKey : 15 PW redundancy mode : frr AdminPw interface : -- AdminPw link state : -- Diffserv Mode : uniform Service Class : be Color : -- DomainId : -- Domain Name : --
# Run the display bfd session all verbose command on U-PEs to view the BFD session status. You can see that the BFD session is Up, the BFD session is bound to a PW, and the type of the BFD session is dynamic.
The display on UPE1 is used as an example.
[UPE1] display bfd session all verbose -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Session MIndex : 256 State : Up Name : dyn_8192 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Discriminator : 8192 Remote Discriminator : 8192 Session Detect Mode : Asynchronous Mode Without Echo Function BFD Bind Type : PW(Master) Bind Session Type : Dynamic Bind Peer IP Address : -.-.-.- NextHop Ip Address : -.-.-.- Bind Interface : Vlanif10 PW TTL Mode : - PW TTL : - Node : UPE Encapsulation Type : - Vc Id : - Track Interface : - Local Vc Label : 1027 Remote Vc Label : 1027 Swap Vc Label : - FSM Board Id : 1 TOS-EXP : 6 Min Tx Interval (ms) : 100 Min Rx Interval (ms) : 100 Actual Tx Interval (ms): 2800 Actual Rx Interval (ms): 2800 Local Detect Multi : 3 Detect Interval (ms) : - Echo Passive : Disable Acl Number : - Destination Port : 3784 TTL : 1 Proc Interface Status : Disable Process PST : Enable WTR Interval (ms) : - Active Multi : 3 DSCP : - Last Local Diagnostic : No Diagnostic Bind Application : L2VPN | OAM_MANAGER | MPLSFW Session TX TmrID : - Session Detect TmrID : - Session Init TmrID : - Session WTR TmrID : - Session Echo Tx TmrID : - PDT Index : FSM-0 | RCV-0 | IF-0 | TOKEN-0 Session Description : - -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total UP/DOWN Session Number : 1/0
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 10 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # return
UPE1 configuration file

The lnp disable command has no impact on services before the device restarts. After the device restarts, the device can only forward packets from the VLANs specified by the port default vlan command at Layer 2. The port default vlan 1 command is configured by default, so only packets of VLAN 1 can be forwarded at Layer 2.
# sysname UPE1 # vlan batch 10 20 # lnp disable #bfd for pw enable # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls l2vpn # pw-template pwt peer-address 3.3.3.9 control-word # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 3.3.3.9 remote-ip 3.3.3.9 # interface Vlanif10 mpls l2vc pw-template pwt 100 mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 remote-vcid 200 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 50.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 50.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # vlan batch 20 30 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif20 ip address 50.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif30 ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 50.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
SPE configuration file
# sysname SPE # vlan batch 30 40 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls l2vpn # mpls switch-l2vc 1.1.1.9 100 between 5.5.5.9 200 encapsulation vlan # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 1.1.1.9 remote-ip 1.1.1.9 # mpls ldp remote-peer 5.5.5.9 remote-ip 5.5.5.9 # interface Vlanif30 ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif40 ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # vlan batch 40 50 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif40 ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif50 ip address 40.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
UPE2 configuration file

The lnp disable command has no impact on services before the device restarts. After the device restarts, the device can only forward packets from the VLANs specified by the port default vlan command at Layer 2. The port default vlan 1 command is configured by default, so only packets of VLAN 1 can be forwarded at Layer 2.
# sysname UPE2 # vlan batch 50 60 # lnp disable #bfd for pw enable # bfd # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 mpls # mpls l2vpn # pw-template pwt peer-address 3.3.3.9 control-word # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer 3.3.3.9 remote-ip 3.3.3.9 # interface Vlanif50 ip address 40.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif60 mpls l2vc pw-template pwt 200 mpls l2vpn pw bfd min-rx-interval 100 min-tx-interval 100 remote-vcid 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 60 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 5.5.5.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 60 # interface Vlanif60 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 60 # return