Identifying Types of Terminals Accessing the Network on Huawei Agile Controller-Campus
Context
As an increasing number of smart terminals are used, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), a new working style for enterprises, has become a trend. When an enterprise uses the BYOD solution, the administrator must determine the users and terminals that can connect to the enterprise network, where users can connect to the enterprise network, and access rights of different terminals. All these require terminal type identification.
Two terminal type identification methods are available:
Local identification
A switch identifies terminal types by analyzing MAC addresses, DHCP option information, and user agent (UA) information of terminals and then controls terminal access and grants access rights to terminals accordingly. The switch can also send identified terminal type information to a server, which then controls terminal access and grants access rights to terminals accordingly.
Remote identification
A switch obtains MAC addresses, DHCP option information, and UA information of terminals and sends the information to a server, which then controls terminal access and grants access rights to terminals accordingly.
Networking Requirements
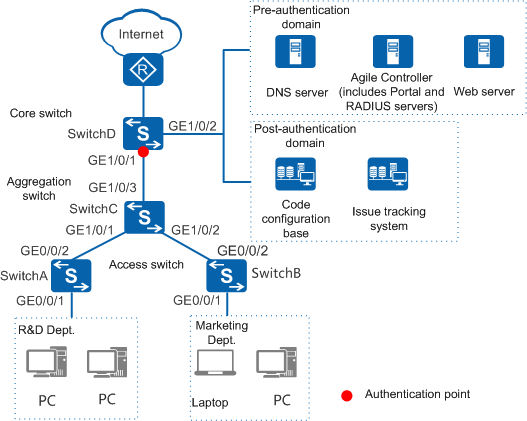
In Figure 1, to meet service requirements, an enterprise needs to deploy an identity authentication system to implement access control on users who attempt to access the enterprise network. Only authorized users can access the enterprise network.
- The authentication operations should be simple. The authentication system only performs access authorization and does not require any client software on user terminals.
- To facilitate future network reconstruction and save investment, the authentication control point must be deployed on a core switch.
- A unified identity authentication mechanism is used to authenticate all terminals accessing the campus network and deny accesses from unauthorized terminals. This mechanism identifies the terminals, records information about devices accessing the network, and automatically groups the devices by the device type to facilitate tracing of accidental information disclosure.
- R&D employees can only access public servers (such as the public web and DNS servers) of the company before authentication, and can access both the intranet (code base and issue tracking system) and Internet after passing authentication.
- Marketing employees can only access public servers (such as the public web and DNS servers) of the company before authentication, and can only access the Internet after passing authentication.
Configuration Logic
- Perform Portal authentication configuration. For details, see Configuring Portal Authentication for Access Users on Huawei Agile Controller-Campus (Authentication Point on Core Switch).
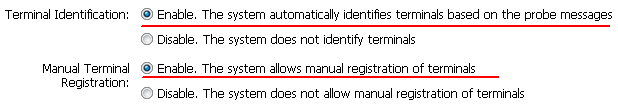
- Configure the terminal type awareness function so that the switch can identify terminal types based on the packets sent by terminals.
- Enable the UA function so that the switch can obtain UA information from the packets sent by terminals.
Configuration Notes
The authentication control point in this example must be deployed on the S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731S-H, S5731-S, S5731S-S, S6720-HI, S5732-H, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, or S6730S-S fixed switch or X series card of modular switch running V200R009C00 or a later version.
Huawei Agile Controller-Campus in V100R001 functions as the Portal server and RADIUS server in this example. For the Agile Controller-Campus, the version required is V100R001, V100R002, V100R003.
The RADIUS authentication and accounting shared keys and Portal shared key on the switch must be the same as those on the Agile Controller-Campus server.
By default, the switch allows the packets from RADIUS and Portal servers to pass. You do not need to configure authentication-free rules for the two servers on the switch.
Data Plan
This example provides only the configuration of terminal type identification. For details about VLAN planning, network data planning, and service data planning, see Configuring Portal Authentication for Access Users on Huawei Agile Controller-Campus (Authentication Point on Core Switch).
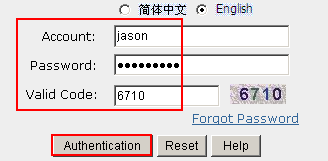
In this example, the administrator user name and password are admin and Admin_123, and the user name and password of Portal users are Jason and Admin_1234.
Procedure
- Configure the core switch.
# Configure the core switch to send DHCP option and UA information to the Agile Controller-Campus, which then uses the information as original information to identify terminals.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchD [SwitchD] dhcp enable [SwitchD] dhcp snooping enable [SwitchD] device-sensor dhcp option 12 55 60 [SwitchD] http parse user-agent enable

For wireless users, you can configure attributes for APs when the switch works as an AC. In versions earlier than V200R011C10, the configurations are not delivered to APs in real time, and are delivered to APs only after you run the commit command in the WLAN view. In V200R011C10 and later versions, the commit command is deleted, the switch delivers the configurations to APs every 5 seconds.
- Configure the Agile Controller-Campus.
- Check the configuration.
Check terminal type identification results.
- Choose .
Check whether the terminal is in the device list.
If the terminal is in the device list, its terminal type has been identified.