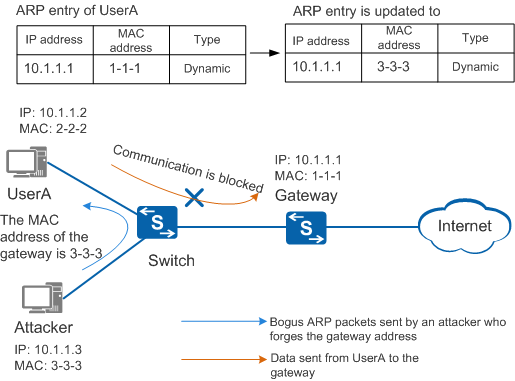
Gratuitous ARP Packet Sending
As shown in Figure 1, an attacker forges the gateway address to send a bogus ARP packet to UserA. UserA then records an incorrect ARP entry for the gateway. As a result, the gateway cannot receive packets from UserA.
To avoid the preceding problem, configure gratuitous ARP packet sending on the gateway. Then the gateway sends gratuitous ARP packets at intervals to update the ARP entries of authorized users so that the ARP entries contain the correct MAC address of the gateway.