Link Aggregation in Stack Scenarios
Inter-chassis Eth-Trunk
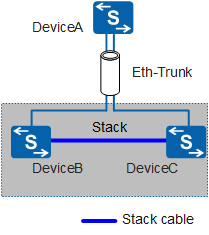
In Figure 1, DeviceB and DeviceC constitute a stack to form a logical device. An inter-chassis Eth-Trunk is composed of physical interfaces of devices in a stack. When there is a failure of the device in the stack or a physical interface of the Eth-Trunk, traffic can be transmitted between devices through stack cables. The inter-chassis Eth-Trunk ensures reliable transmission and implements device backup.
Preferential Forwarding of Local Traffic by an Inter-Chassis Eth-Trunk
In a stack, reliable transmission can be ensured by configuring an Eth-Trunk as the outbound interface. Member interfaces of the Eth-Trunk are located on different devices. When the stack forwards traffic, the Eth-Trunk may select an inter-chassis member interface based on the hash algorithm. This forwarding mode occupies bandwidth resources between devices in the stack and reduces traffic forwarding efficiency due to bandwidth limitations on the bandwidth of cables between devices. Preferential forwarding of local traffic can be used to address the issue.
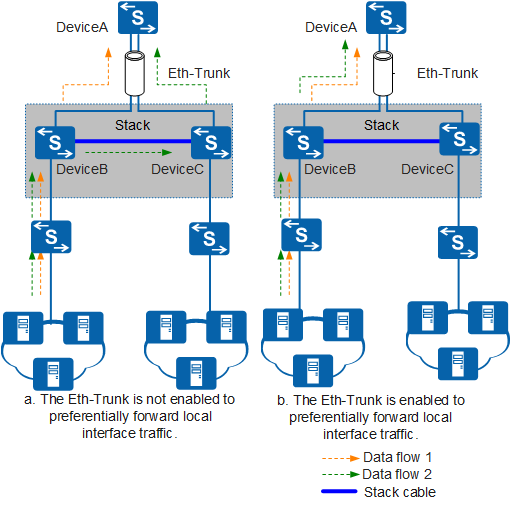
In Figure 2, DeviceB and DeviceC constitute a stack, which connects to DeviceA through an Eth-Trunk.
After the Eth-Trunk in the stack is configured to preferentially forward local traffic, the following functions are implemented:
Local device forwards traffic it receives
When there are outbound interfaces of the Eth-Trunk on DeviceB and these interfaces are functioning properly, the Eth-Trunk forwarding table of DeviceB contains only local member interfaces as outbound interfaces. The hash algorithm is used to select one of these local member interfaces, and traffic is only forwarded through DeviceB.
Another device forwards traffic received by local device
When there are no outbound interfaces of the Eth-Trunk on DeviceB or these interfaces are faulty, the Eth-Trunk forwarding table of DeviceB contains all available member interfaces (including those on other devices). The hash algorithm is used to select a member interface on DeviceC as the outbound interface, and traffic is forwarded through DeviceC.

- This function is only valid for known unicast packets, and is invalid for unknown unicast packets, broadcast packets, and multicast packets.
- Before configuring an Eth-Trunk to preferentially forward local traffic, ensure that member interfaces of the local Eth-Trunk have sufficient bandwidth to forward local traffic; otherwise, traffic may be discarded.