PKI System Structure
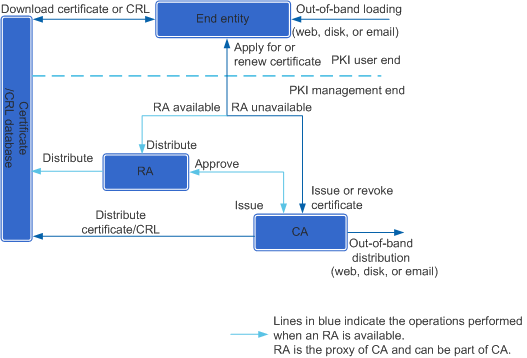
As shown in Figure 1, a PKI system consists of the end entity, certificate authority (CA), registration authority (RA), and certificate/certificate revocation list (CRL) storage database.
End entity
An end entity, or PKI entity, is the end user of PKI products or services. It can be an individual, an organization, a device (for example, a router or firewall), or process running on a computer.
-
The CA is the trusted entity that issues and manages digital certificates. The CA is an authoritative, trustable, and fair third-party organization. Generally, a CA is a server, for example, a server running Windows Server 2008.
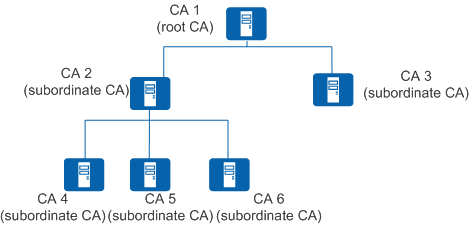
Figure 2 shows a hierarchical CA. The CA on the top of the hierarchy is the root CA and the others are subordinate CAs.
The root CA is the first CA (trustpoint) in the PKI system. It issues certificates to subordinate CAs, computers, users, and services. In most certificate-based applications, the root CA can be traced through the certificate chain. The root CA holds a self-signed certificate.
A subordinate CA can only obtain a certificate from its upper-level CA. The upper-level CA can be the root CA or another subordinate CA authorized by the root CA to issue certificates. The upper-level CA is responsible issuing and managing certificates of lower-level CAs, and the CAs at the bottom issue certificates to end entities. For example, CA 2 and CA 3 are subordinate CAs, holding the certificates issued by CA 1, and CA 4, CA 5, as well as CA 6 are also subordinate CAs, holding the certificates issued by CA 2.
When a PKI entity trusts a CA, the trust is derived along the certificate chain. A certificate chain is a set of certificates from the end entity to the root certificate. When a PKI entity in communication receives a certificate to be authenticated, the PKI entity verifies each issuer along the certificate chain.
Certificate management is the major function of CAs, including issuing, renewing, revoking, querying, and archiving certificates as well as distributing the Certificate Revocation List (CRL).
Registration Authority (RA)
An RA enrolls and approves digital certificates. It is a proxy for the CA and provides extended applications of certificate issuing and management. The RA processes the certification enrollment and revocation requests from users, verifies user identities, and decides whether to submit certificate issuing or revocation requests to the CA.
The RA may be part of the CA server, or independent of CA to share workload of CA and enhance CA system security.
Certificate/CRL database
A certificate may need to be revoked for the reasons such as entity name changing, private key leaking, or service interruption. Revoking a certificate is to unbind the public key from the PKI entity identity information. The PKI system uses a CRL to revoke certificates.
After a certificate is revoked, the CA issues a CRL to declare that the certificate is invalid and lists the serial numbers of revoked certificates. The CRL provides a method to verify certificate validity.
The certificate/CRL database stores and manages information about certificates and CRLs and allows information query. The certificate/CRL database can be built using a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) server, or database.
PKI manages the entire lifecycle of local certificates, including application, issue, storage, download, installation, authentication, renewal, and revocation.
Certificate Application
Certificate application is certificate enrollment. It is a process in which an entity registers with a CA and obtains a certificate from the CA. Generally, a PKI entity generates a pair of public and private keys. The public key and entity's identity information (included in certificate enrollment request) are sent to the CA to generate a local certificate. The private key is stored by the PKI entity to perform digital signature and decrypt the ciphertext sent from the peer.
A PKI entity can use either of the following methods to apply for a local certificate from CA:
Online
The PKI entity sends certificate enrollment requests to the CA by using the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) or Certificate Management Protocol version 2 (CMPv2).
Offline (PKCS#10)
The PKI entity prints the local certificate enrollment request in PKCS#10 format and saves it as a file. Then the user transfers the file to the CA server in out-of-band mode (web, disk, or email).
In addition, a PKI entity can issue a self-signed or local certificate to itself.
Certificate Issue
If an RA is available, the RA verifies the PKI entity's identity information when the PKI entity applies for a local certificate from CA. After the PKI entity passes verification, the RA sends the request to CA. The CA generates a local certificate based on the public key and identity information of the PKI entity, and then returns the local certificate information to the RA. If no RA is available, the CA verifies the PKI entity.
Certificate Storage
After the CA generates a local certificate, the CA or RA distributes the certificate to the certificate/CRL database. Users can download or browse directory of the certificates in the database.
Certificate Downloading
A PKI entity can download a local certificate, a CA/RA certificate, or a local certificate of another PKI entity from the CA server using SCEP, CMPv2, HTTP, or out-of-band mode.
Certificate Installation
A downloaded certificate (a local certificate, CA/RA certificate, or certificate of another PKI entity) must be installed on the device, that is, imported to the device memory; otherwise, the certificate does not take effect.
Certificate Authentication
Before a PKI entity uses a certificate obtained from the peer, for example, for the purposes of setting up a security tunnel or connection, the PKI entity authenticates the certificate and CA (whether the certificate is valid and issued by the expected CA). If the certificate is invalid, the PKI considers all certificates issued by this CA invalid. This seldom occurs because a device renews the CA certificate before expiration in normal situations.
The PKI entity uses CRL or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to authenticate certificates. In CRL mode, the PKI entity searches for the certificate in the CRL stored in local memory. If the certificate is included in the CRL, it indicates that the certificate has been revoked. If no CRL is available in local memory, a CRL needs to be downloaded and installed. In OCSP mode, the PKI entity sends a certificate status query message to the OCSP server, and the OCSP server returns the certificate state, including valid (not revoked), expired (revoked), and unknown (OCSP server cannot find the certificate status).
Certificate Renewal
When a certificate expires or the private key is leaked, the PKI entity must replace the certificate. The PKI entity can apply for a new certificate or use SCEP or CMPv2 to renew the existing certificate.
When a certificate is about to expire, the device applies for a shadow certificate. When the certificate expires, the shadow certificate becomes active.
The shadow certificate application process is the enrollment process for the new certificate.
Certificate Revocation
When the user identity, user information, or public key is modified or user service needs to be interrupted, a certificate revocation is required. Certificate revocation unbinds a public key from the PKI entity's identity information. The CA uses CRL or OCSP to revoke certificates for PKI entities, whereas a PKI entity revokes its own certificate in out-of-band mode.