AP Online Process
The process in which a central AP goes online on an AC is similar to that of a common AP.
IP Address Allocation
- Static mode: An IP address is manually configured for the AP.
- DHCP mode: The AP functions as a DHCP client and requests an IP address from a DHCP server.
CAPWAP Tunnel Establishment
- Maintain the running status of APs and the AC.
- Help the AC manage APs and deliver configurations to APs.
- Transmit service data to the AC for centralized forwarding.
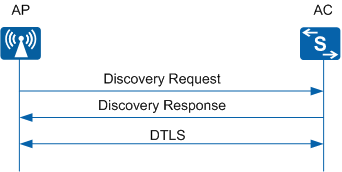
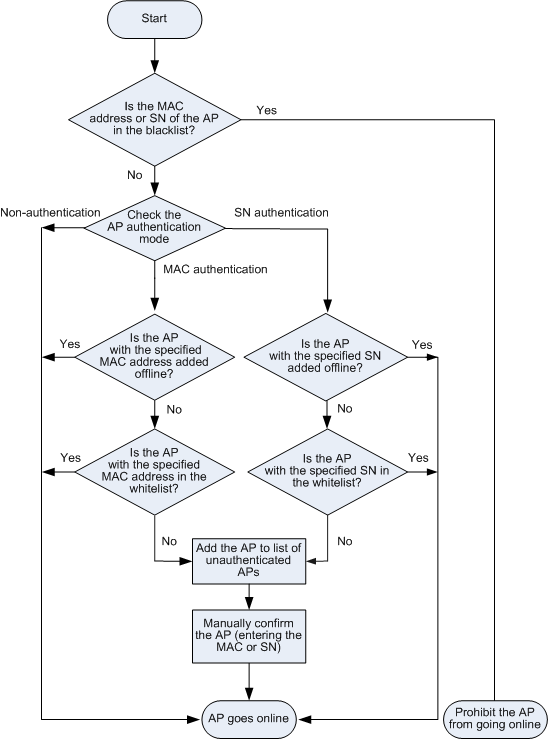
An AP sends a Discovery Request packet to find an available AC. (Discovery Phase) The AC determines whether to allow the AP. This process is similar to that in AP access and control phase. For details, see Figure 2. The AC does not respond to Discovery Request packets sent by the AP that is not allowed.
An AP can discover an AC in static or dynamic mode.Static mode
An AC IP address list is preconfigured on the AP. When the AP goes online, the AP unicasts a Discovery Request packet to each AC whose IP address is specified in the preconfigured AC IP address list. After receiving the Discovery Request packet, the ACs send Discovery Response packets to the AP. The AP then selects an AC to establish a CAPWAP tunnel according to the received Discovery Response packets.
Dynamic mode
An AP can dynamically discover an AC in DHCP, DNS, or broadcast mode. Details on each of the modes are as follows:
DHCP mode: An AP obtains the AC IP address through DHCP (by configuring a DHCP response packet to carry Option 43 containing the AC IP address list on the DHCP server), and sends a Discovery Request unicast packet to the AC. The AC then sends a Discovery Response packet to the AP.
DNS mode: An AP obtains the AC domain name and DNS server IP address through the DHCP service (by configuring a DHCP response packet to carry Option 15 containing the AC domain name on the DHCP server), and sends a request to the DNS server to obtain the IP address corresponding to the AC domain name. After obtaining the AC IP address, the AP unicasts a Discovery Request packet to the AC. The AC then sends a Discovery Response packet to the AP.
After receiving the DHCP Response packet, the AP obtains the AC domain name carried in Option 15. The AP then automatically adds the prefix huawei-wlan-controller to the obtained domain name and sends it to the DNS server to obtain the IP address corresponding to the AC domain name. For example, after obtaining the AC domain name ac.test.com configured on the DHCP server, the AP adds the prefix huawei-wlan-controller to ac.test.com and sends the huawei-wlan-controller.ac.test.com to the DNS server for resolution. The IP address corresponding to huawei-wlan-controller.ac.test.com must be configured on the DNS server.
- Broadcast mode: The AP broadcasts a Discovery Request packet to automatically discover ACs in the same network segment. The AP then selects an AC to establish a CAPWAP tunnel based on the Discovery Response packets received from available ACs. The broadcast mode is used in the following cases:
- When the AP fails to obtain the IP address of an AC, it broadcasts packets. If no AC responds to the broadcast packet for two times, a failure to discover an AC is determined.
- After obtaining the IP address of an AC, the AP sends unicast packets to the AC. If the AC does not respond to the unicast packets for 10 times, the AP sends a broadcast packet. If no AC responds to the broadcast packet, the AP repeats the process of sending unicast and broadcast packets. If there is still no response, a failure to discover an AC is determined.
The AP establishes CAPWAP tunnels with an AC.
CAPWAP tunnels include data tunnels and control tunnels.- Data tunnel: transmits service data packets from the AP to the AC for centralized forwarding.
- Control tunnel: transmits control packets between the AP and AC. You can also enable Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) encryption over the control tunnel to ensure security of CAPWAP control packets. Subsequently, CAPWAP control packets will be encrypted and decrypted using DTLS.

For details about the setup of active and standby CAPWAP links, see Understanding Dual-Link Cold Backup.
AP Access Control
The AP sends a Join Request packet to an AC. The AC then determines whether to allow the AP access and sends a Join Response packet to the AP. The Join Response packet carries the AP software upgrade mode and AP version information.
Figure 2 shows a flowchart depicting the process for AP access control.
AP Software Upgrade
The AP determines whether its system software version is the same as that specified on the AC according to parameters in the received Join Response packet. If the two versions are different, the AP updates its software version in AC, FTP, or SFTP mode.
After the software version is updated, the AP restarts and repeats steps 1 to 3.