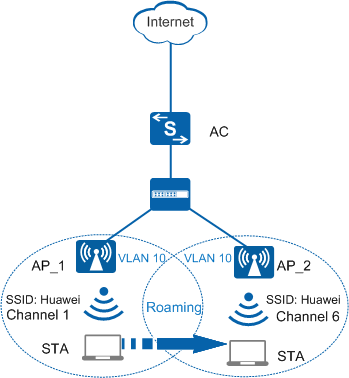
Roaming Between APs in the Same Service VLAN
As shown in Figure 1, a STA moves between two APs that connect to the same AC and belong to the same service VLAN, without service interruption.
Roaming between APs in the same service VLAN is classified into fast and non-fast roaming.
Non-Fast Roaming
Non-fast roaming technology is used when a STA uses a non-WPA2-802.1X security policy. If a STA uses WPA2-802.1X but does not support fast roaming, the STA still needs to complete 802.1X authentication before roaming between two APs.

If a STA needs to roam between two APs, the APs must have the same SSID and security policy profile. The names of security profiles can be different but configurations in the security profiles must be the same.
- The STA sends a Probe Request frame on each channel. After receiving this, the APs send Probe Response frames to the STA. After AP_2 receives the Probe Request frame on channel 6, it sends a Probe Response frame to the STA on channel 6. When the STA receives Probe Response frames, it selects an AP to associate with according to signal strength and quality. In this scenario, assume that the STA selects AP_2 to associate with, as shown in Figure 1.
- The STA sends AP_2 a Re-authentication Request packet on channel 6. After AP_2 authenticates the STA, it sends a Re-authentication Response packet to the STA.
- The STA sends a Re-association Request packet to AP_2, which then sends the packet to the AC. The AC sends a Re-association Response packet, allowing the STA to re-associate with AP_2.
The STA re-associates with AP_2 and then disassociates from AP_1. To do so, the STA sends a Disassociation frame to AP_1 on channel 1.
- If the STA uses the WEP security policy, the STA roaming process is complete.
- If the STA uses the WPA/WPA2-PSK or WPA/WPA2-802.1X security policies, the STA needs to perform access authentication and key negotiation again. For details about key negotiation, see Key Negotiation in WPA/WPA2.
Fast Roaming
When STAs use the WPA2-802.1X security policy and support fast roaming, they do not need to perform 802.1X authentication again during roaming. They only need to perform key negotiation. In this case, fast roaming reduces the roaming delay and improves WLAN services.
- The STA accesses the Internet through AP_1 for the first time. When the AC authenticates the STA and a PMK is generated, the STA and AC save the PMK information. Each PMK has a PMK-ID, which is calculated based on the PMK, SSID, STA MAC address, and BSSID.
- During roaming, the STA sends AP_2 a Re-association Request packet that carries the PMK-ID.
- After AP_2 receives this packet, it notifies the AC that the STA needs to roam from AP_1 to AP_2.
- The AC searches the PMK caching table for the PMK of the STA. It does so according to the PMK-ID carried in the Re-association Request packet. If the AC finds a matching PMK, the AC considers that 802.1X authentication has been performed on the STA and uses the cached PMK for key negotiation.