Establishing VXLAN Tunnels
A virtual extensible LAN (VXLAN) tunnel is determined by a pair of VXLAN tunnel endpoint (VTEP) IP addresses. Packets are encapsulated on the VTEP device and then transmitted through the VXLAN tunnel over routes. After the VXLAN tunnel is configured, when the IP addresses of VTEP devices on both ends of the tunnel are reachable at Layer 3, the VXLAN tunnel can be successfully established.
Figure 1 VXLAN networking
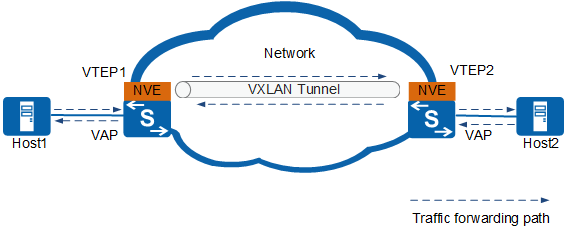

Based on tunnel creation modes, VXLAN tunnels can be divided into the following two types:
- Static VXLAN tunnels: completed by manually configuring local and remote VNIs, VTEP IP addresses, and headend replication lists. Static tunnel configuration is supported only for the VXLAN in centralized gateway mode. For details, see Centralized VXLAN Gateway Deployment in Static Mode.
- Dynamic VXLAN tunnels: dynamically created in BGP EVPN mode. Specifically, create BGP EVPN peers on VTEP devices on both ends and enable the peers to exchange VNI and VTEP IP address information over the BGP EVPN route to dynamically create VXLAN tunnels. Dynamic tunnel configuration through BGP EVPN is supported for the VXLAN in both centralized and distributed gateway modes. For details, see Centralized VXLAN Gateway Deployment Using BGP EVPN and Distributed VXLAN Gateway Deployment Using BGP EVPN.