Access Configuration
Context
The device supports two configuration modes. By default, the unified mode is used. You can run the undo authentication unified-mode command to switch the configuration mode to common mode.
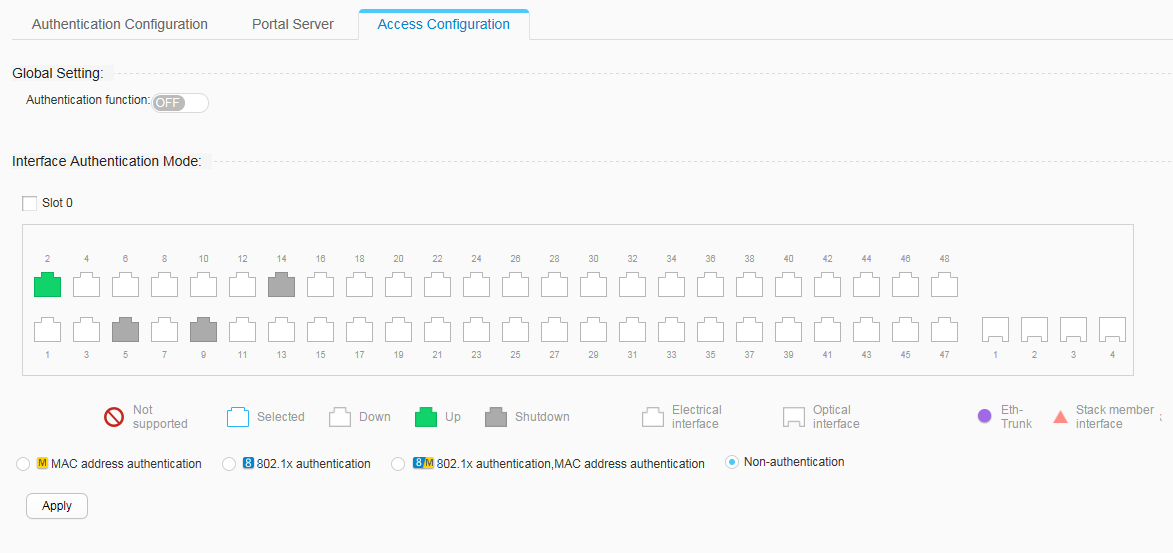
In the common mode, access configuration includes No-authentication, 802.1X authentication, MAC address authentication, MAC address bypass authentication. The last authentication mode is combinations of 802.1X authentication and MAC address authentication.
No-authentication: Users are allowed to access the network without authentication.
802.1X authentication: a Layer 2 authentication mode based on the 802.1X protocol. In this mode, the 802.1X client software must be installed on user terminals, and user identity authentication is performed between clients and servers using the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
MAC address authentication: uses MAC addresses of users as identity information. In this mode, the 802.1X client software does not need to be installed on user terminals.
MAC address bypass authentication: In this mode, 802.1X authentication is performed first and the delay timer for MAC address bypass authentication is enabled at the same time. If the 802.1X authentication still fails when the delay time expires, MAC address authentication is triggered.
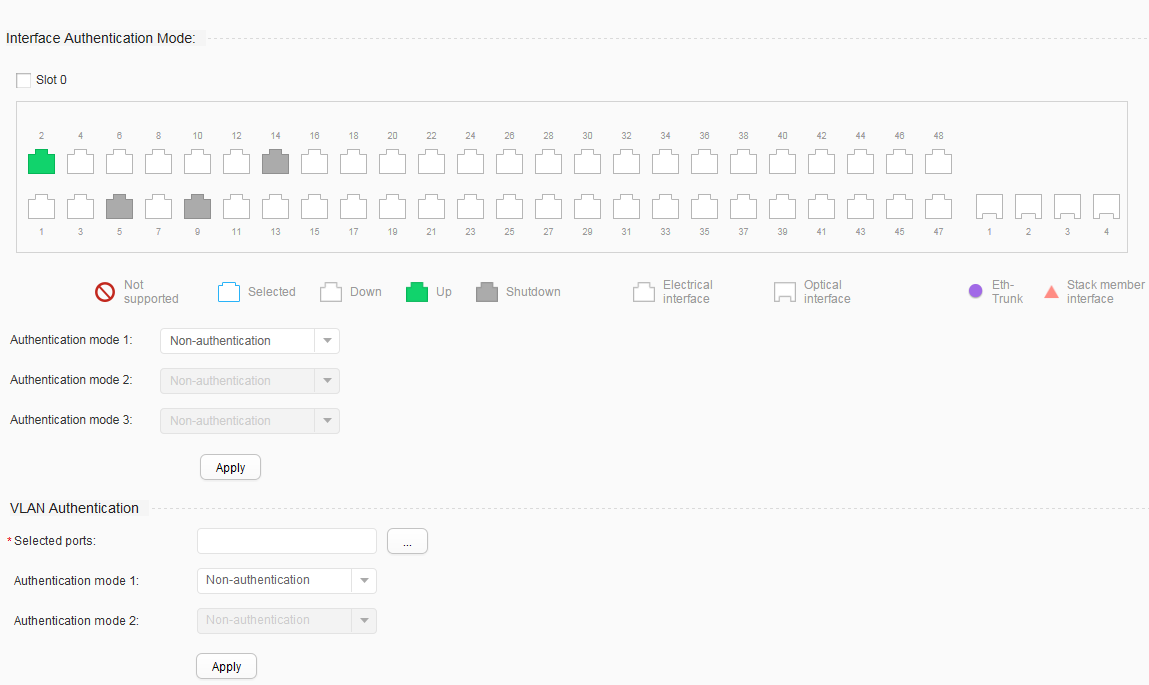
When performing access configuration, you must enable the authentication function first, and then select the interface to which the access configuration applies and select an authentication mode.
In the unified mode, access configuration includes No-authentication, 802.1X authentication, MAC address authentication, and Portal authentication.

After performing access configuration, perform the Authentication Configuration. The two functions implement user authentication together.
If non-authentication is configured, a user passes the authentication using any user name or password. Therefore, to protect the device or network security, you are advised to enable authentication, allowing only the authenticated users to access the device or network.