WIDS Spoof SSID Profile
Context
WLAN services are available in public places, such as banks and airports. Users can connect to the WLANs after associating with corresponding SSIDs. If a rogue AP is deployed and provides spoofing SSIDs similar to authorized SSIDs, the users may be misled and connect to the rogue AP, which brings security risks. To address this problem, configure a fuzzy matching rule to identify spoofing SSIDs. The device compares a detected SSID with the matching rule. If the SSID matches the rule, the SSID is considered a spoofing SSID. The AP using the spoofing SSID is a rogue AP. The device then take countermeasures against the rogue AP, forcing users to disconnect from the AP.
Procedure
- Create an SSID profile.
- Modify an SSID profile.
- Choose . The WIDS Spoof SSID Profile List page is displayed.
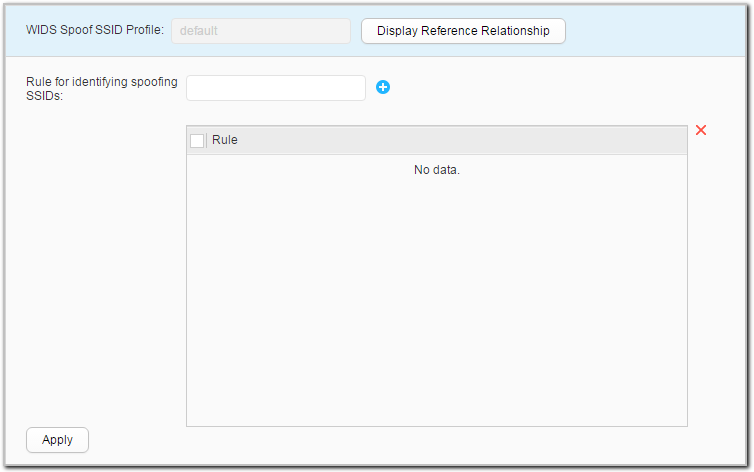
- Click the name of the WIDS spoof SSID profile that you want to modify. The WIDS spoof SSID profile configuration page is displayed.
- Set parameters for modifying a WIDS spoof SSID profile. Table 1 describes the parameters for modifying an SSID profile.
- Click Apply. In the Info dialog box that is displayed, click OK.
- Delete an SSID profile.
- Choose . The WIDS Spoof SSID Profile List page is displayed.
- Select the profile that you want to delete and click Delete. In the Confirm dialog box that is displayed, click OK.
- Display the profile reference relationship.