Example for Configuring Dual-Stack Static User Access (CPE Working in Routing Mode)
This section describes how to configure dual-stack static user access on a network where a CPE works in routing mode. A networking diagram is provided to help you understand the configuration procedure. The example provides the networking requirements, configuration roadmap, configuration procedure, and configuration files.
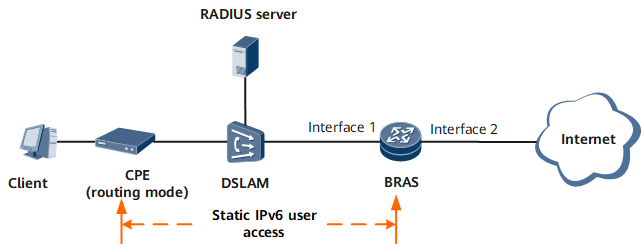
Networking Requirements
Figure 1 shows a dual-stack static user access network where a CPE works in routing mode. Configure a static IPv6 address, PD prefix, and IPv6 DNS server address for the client. Allow the client to be triggered to go online by sending NS/NA or IPv6 packets. Configure the client to use DHCPv6 or ND to obtain the PD prefix.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure AAA schemes, a RADIUS server group, a username generation mode, and a user password.
- Configure address pools.
- Configure a local IPv4 address pool. Configure the device to exclude the IP address segment of the user's IPv4 address during automatic address assignment.
- Configure a local IPv6 prefix pool and an IPv6 delegation prefix pool.
- Configure a local IPv6 address pool. Bind the local IPv6 prefix pool and the IPv6 delegation prefix pool to this local IPv6 address pool.
Configure an AAA domain. Apply the RADIUS server group, authentication and accounting schemes, and address pools to the AAA domain.
- Configure the BRAS to generate DUIDs in DUID-LLT mode.
- Configure interfaces.
- Configure IS-IS and BGP.
- Configure a static user.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- RADIUS server group name, and IP addresses and port numbers of the RADIUS authentication and accounting servers
Authentication scheme name and authentication mode
Accounting scheme name and accounting mode
- Local IPv4 address pool-related parameters, including the gateway address and address range
Names of the local IPv6 prefix pool and IPv6 delegation prefix pool, address prefix, and assignable prefix length
- AAA domain name
- Interface IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
- BGP peer addresses and passwords
Procedure
- # Set a host name, such as Device, for the BRAS.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname Device [*HUAWEI] commit
- Configure AAA schemes.
- Configure a RADIUS server group.
[~Device] radius-server group radius [*Device-radius-radius] radius-server authentication 192.168.7.249 1812 [*Device-radius-radius] radius-server accounting 192.168.7.249 1813 [*Device-radius-radius] radius-server shared-key-cipher huawei_123 [*Device-radius-radius] quit [*Device] commit
- Configure a username generation mode and a user password.
[~Device] aaa [~Device] default-user-name include ip-address [~Device-aaa] default-password cipher Huawei_123 [~Device-aaa] commit [~Device-aaa] quit
- Configure address pools.
- Configure an AAA domain. Bind the configured authentication and accounting schemes, RADIUS server group, and IPv4 and IPv6 address pools to the AAA domain.
[~Device] aaa [~Device-aaa] domain dom1 [*Device-aaa-domain-dom1] authentication-scheme radius [*Device-aaa-domain-dom1] accounting-scheme radius [*Device-aaa-domain-dom1] radius-server group radius [*Device-aaa-domain-dom1] commit [~Device-aaa-domain-dom1] ip-pool pool1 [~Device-aaa-domain-dom1] ipv6-pool pool1 [~Device-aaa-domain-dom1] ipv6-pool pool2 [~Device-aaa-domain-dom1] quit [~Device-aaa] quit
- Configure the BRAS to generate DUIDs in DUID-LLT mode.
[~Device] dhcpv6 duid llt [*Device] commit
- Configure interfaces.
- Configure basic IS-IS functions.
- Configure basic BGP functions.
- Configure a static user. The VLAN configured here must be within the VLAN range configured for the BAS interface.
[~Device] static-user 10.179.180.253 10.179.180.253 gateway 10.179.180.1 2001:db8:1::1 2001:db8:1::1 delegation-prefix 2001:db8:10:: 2001:db8:10:: 60 ipv6-gateway 2001:db8:1:: interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9.1 vlan 1 qinq 100 domain-name dom1 detect
- Verify the configurations.
# Run the display ip pool command on the router. Check whether the configurations are as planned.
<HUAWEI> display ip pool ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Pool-Name : 1 Pool-No : 0 Pool-constant-index: - Position : Local Status : Unlocked RUI-Flag : - Gateway : 10.179.180.1 Mask : 255.255.255.0 Vpn instance : -- Unnumbered gateway: - IP address Statistic Total :253 Used :0 Free :0 Conflicted :0 Disable :253 Designated :0 Gateway :0 Ratio :100%# Run the display ipv6 prefix command on the router. Check whether the configurations are as planned.
<HUAWEI> display ipv6 prefix ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Index Name Address/Length Type Constant-index ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 pre1 2001:db8:1::/48 LOCAL - 1 pre2 2001:db8:10::/44 DELEGATION - ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total created prefix pool(s): 2
Configuration Files
# sysname Device # dhcpv6 duid 0001000124fbc193dc99141ea1e9 # ipv6 prefix pre1 local prefix 2001:DB8:1::/48 # ipv6 prefix pre2 delegation prefix 2001:DB8:10::/44 # ipv6 pool pool1 bas local prefix pre1 # ipv6 pool pool2 bas delegation prefix pre2 # radius-server group radius radius-server shared-key-cipher %^%#glhJ;yPG#$=tC&(Is%q!S_";(k.Ef$:978$$e:TY%^% radius-server authentication 192.168.7.249 1812 weight 0 radius-server accounting 192.168.7.249 1813 weight 0 # ip pool pool1 bas local gateway 10.179.180.1 255.255.255.0 section 0 10.179.180.2 10.179.180.254 excluded-ip-address 10.179.180.2 10.179.180.254 # aaa default-user-name include ip-address default-password cipher $$e:TY%^%glhJ;yPG#$=tC&(Is%q!S_";(k.Ef$%^%#:978 authentication-scheme radius accounting-scheme radius # domain dom1 authentication-scheme radius accounting-scheme radius radius-server group radius ip-pool pool1 ipv6-pool pool1 ipv6-pool pool2 # isis 100 cost-style wide traffic-eng level-2 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 preference 105 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:200:2:2102:2205:1:1/127 ipv6 address auto link-local isis enable 100 isis ipv6 enable 100 isis ipv6 cost 500 level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9.1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address auto link-local statistic enable user-vlan 1 10 qinq 100 bas # access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication dom1 authentication-method bind authentication-method-ipv6 bind ip-trigger arp-trigger ipv6-trigger nd-trigger # # interface LoopBack0 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:200::2205/128 ipv6 address auto link-local isis enable 100 isis ipv6 enable 100 # bgp 64830 group IPv6-GROUP internal peer IPv6-GROUP password cipher %^%#rxKl0^%`n7zLXD<YQ,gFwwtzMEjGK!j}a`L;h(aU%^%# peer 2001:DB8:200::2101 as-number 64830 peer 2001:DB8:200::2101 group IPv6-GROUP group group2 external peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 101 peer 2.2.2.2 group group2 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 101 peer 3.3.3.3 group group2 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route unr peer group2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 group group2 peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 group group2 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization preference 20 230 230 import-route unr maximum load-balancing 6 peer IPv6-GROUP enable peer IPv6-GROUP advertise-community peer IPv6-GROUP keep-all-routes peer 2001:DB8:200::2101 enable peer 2001:DB8:200::2101 group IPv6-GROUP # static-user 10.179.180.253 10.179.180.253 gateway 10.179.180.1 2001:db8:1::1 2001:db8:1::1 ipv6-gateway 2001:db8:1:: interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9.1 vlan 1 qinq 100 domain-name dom1 detect # return