FlexE Functions
According to the mappings between FlexE clients and groups, FlexE can provide three main functions: bonding, channelization, and sub-rating. Through these functions, FlexE clients can flexibly provide bandwidth not constrained to the rates of Ethernet PHYs to upper-layer applications.
Based on these three functions, FlexE implements on-demand interface bandwidth allocation and hard pipe isolation, and can be used on IP networks to implement ultra-high bandwidth interfaces, 5G network slicing, and interconnection with optical transmission devices.
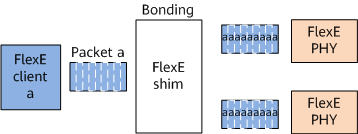
Bonding
As shown in Figure 1, bonding means that multiple PHYs are bonded to support a higher rate. For example, two 100GE PHYs can be bonded to provide a MAC rate of 200 Gbit/s.
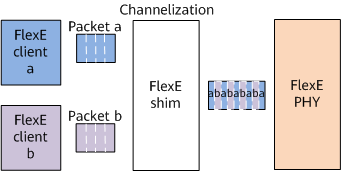
Channelization
As shown in Figure 2, channelization allows multiple low-rate MAC data streams to share one or more PHYs. For example, channelization allows four MAC data streams (35 Gbit/s, 25 Gbit/s, 20 Gbit/s, and 20 Gbit/s) to be carried over one 100GE PHY or allows three MAC data streams (150 Gbit/s, 125 Gbit/s, and 25 Gbit/s) to be carried over three 100GE PHYs.
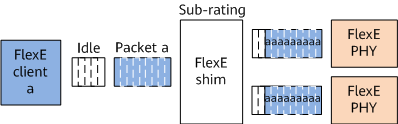
Sub-rating
As shown in Figure 3, sub-rating allows MAC data streams with a single low rate to share one or more PHYs, and uses a specially defined error control block to reduce the rate. For example, a 100GE PHY carries only 50 Gbit/s MAC data streams.
Sub-rating is a subset of channelization in a certain sense.