MPLS DiffServ Configuration Roadmap
BA and PHB
This section describes MPLS DiffServ configurations, which involves BA and PHB definitions. For details about BA and PHB definitions, see BA and PHB.
BA and PHB Implementations in an MPLS DiffServ Scenario
Three modes are defined in MPLS DiffServ scenarios: Uniform, Pipe, and Short Pipe.
- In Uniform mode, the original priorities of packets are used for QoS implementation on an MPLS network. The original priorities of packets are reset when the packets are leaving the MPLS network.
- In Pipe or Short Pipe mode, packets are allocated a desired priority on the MPLS network, regardless of their original priorities. After leaving the backbone network, the original priorities of packets remain unchanged.
- In Pipe mode, the egress on the MPLS network processes a packet based on its re-allocated priorities.
- In Short Pipe mode, the egress on the MPLS network processes a packet based on its original priorities.
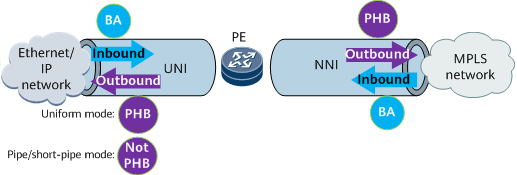
Both BA and PHB implementations are required on the network-side interface (NNI) of a PE. Therefore, run the trust upstream command on the network-side interface.
- In Uniform mode, PHB is required. To be specific, in Uniform mode, both BA and PHB implementations are required on the PE. Therefore, run the trust upstream command on the UNI too.
In Pipe or Short Pipe mode, the UNI of the PE requires BA but not PHB. Note that the diffserv-mode command is mutually exclusive with the trust upstream command.
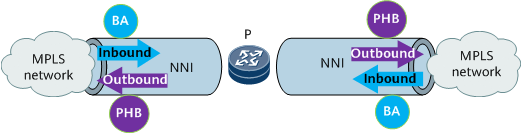
Both BA and PHB implementations are required on the network-side interface and user-side interface (UNI) of a P. Therefore, run the trust upstream command on both the network-side and user-side interfaces.