Example for Using STelnet to Log In to Other Devices (SM2 Authentication Mode)
In this example, local key pairs are generated on the STelnet client and secure shell (SSH) server, and an SM2 public key is generated on the SSH server and then bound to the STelnet client, implementing communication between the STelnet client and SSH server.
Networking Requirements
Large numbers of devices need to be managed and maintained on a network. You cannot connect each device to a terminal. When no reachable route exists between remote devices and a terminal, you can use Telnet to log in to the remote devices from the device that you have logged in to. Telnet provides no secure authentication mode, and data is transmitted in simple mode over TCP, which brings security risks.
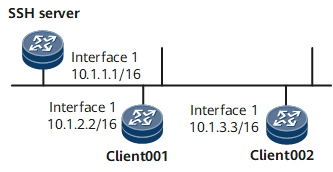
STelnet is a secure Telnet service over SSH connections. SSH provides encryption and authentication functions to protect devices against attacks, such as IP address spoofing. After the STelnet server function is enabled on the SSH server, the STelnet client can log in to the SSH server in password, ECC, password-ECC, DSA, password-DSA, RSA, password-RSA, SM2, password-SM2, or all authentication mode. On the network shown in Figure 1, users client001 and client002 are configured to log in to the SSH server in password and SM2 authentication modes, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure client001 and client002 to log in to the SSH server in different authentication modes.
Configure STelnet client002 and the SSH server to generate local key pairs, and bind the SM2 public key of the SSH client to client002 to authenticate the client when the client logs in to the server.
Enable the STelnet service on the SSH server.
Set the service type of client001 and client002 to STelnet.
Enable first authentication on the SSH client.
Configure client001 and client002 to log in to the SSH server using STelnet.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Password authentication for client001
client002 with the public key being sm2key001 and authentication mode being SM2 authentication
SSH server at IP address 10.1.1.1
Procedure
- Generate a local key pair on the SSH server.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname SSH Server [*HUAWEI] commit [~SSH Server] ssh server publickey sm2
- Create SSH users on the server.

There are several authentication modes for SSH users: password, RSA, password-RSA, DSA, password-DSA, ECC, password-ECC, SM2, password-SM2 and All.
If the authentication mode is password, password-ECC, password-DSA, password-sm2 or password-RSA, configure a local user on the server with the same user name.
If the authentication mode is RSA, password-RSA, DSA, password-DSA, SM2, password-SM2, ECC, password-ECC, or All, save the RSA, DSA, SM2, or ECC public key generated on the SSH client to the server.
# Configure the VTY user interface.
[*SSH Server] user-interface vty 0 4 [*SSH Server-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode aaa [*SSH Server-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh [*SSH Server-ui-vty0-4] user privilege level 3 [*SSH Server-ui-vty0-4] commit [~SSH Server-ui-vty0-4] quit
Create SSH user client001.
# Create SSH user client001 and configure password authentication for the user.
[~SSH Server] ssh user client001 [*SSH Server] ssh user client001 authentication-type password [*SSH Server] commit
# Set a password for client001.
[~SSH Server] aaa [*SSH Server-aaa] local-user client001 password Please configure the password (8-128) Enter Password: Confirm Password:

The password must meet the following requirements:
The password is entered in man-machine interaction mode. The system does not display the entered password.
A password is a string of 8 to 16 case-sensitive characters and must contain at least two types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters.
- Special characters exclude question marks (?) and spaces. However, spaces are allowed in the password if the password is enclosed in quotation marks.
- Double quotation marks cannot contain double quotation marks if spaces are used in a password.
- Double quotation marks can contain double quotation marks if no space is used in a password.
For example, the password "Aa123"45"" is valid, but the password "Aa 123"45"" is invalid.
The configured password is displayed in ciphertext in the configuration file.
[*SSH Server-aaa] local-user client001 service-type ssh [*SSH Server-aaa] commit [~SSH Server-aaa] quit
Create SSH user client002.
# Create SSH user client002 and configure SM2 authentication for the user.
[~SSH Server] ssh user client002 [*SSH Server] ssh user client002 authentication-type sm2 [*SSH Server] ssh authorization-type default root [*SSH Server] commit
- Assign an SM2 public key to the SSH server.
# Generate a local key pair on client002.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname client002 [*HUAWEI] commit [~client002] ssh client publickey sm2 [~client002] sm2 key-pair label sm2key001 Info: Key pair generation will take a short while. Please wait... Info: Creating the key pair succeeded. [~client002] ssh client assign sm2-host-key sm2key001 [*client002] commit
# Display the SM2 public key generated on client002.
[~client002] display sm2 key-pair ===================================== Label Name: sm2key001 Modulus: 521 Time of Key pair created: 2018-06-19 15:39:45 ===================================== Key : 0474F110 F90F131B B6F6D929 9A23A41E F1AB1666 AC4BE4EE EF2CD876 2B633F80 DD5CF42F 147A722F DE527F39 247F3744 C23296BE FE3BE502 EEF7D9EC BC28A576 7E =====================================# Send the SM2 public key generated on client002 to the server.
[~SSH Server] sm2 peer-public-key sm2key001 Enter "SM2 public key" view, return system view with "peer-public-key end". [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key] public-key-code begin Enter "SM2 public key" view, return system view with "peer-public-key end". [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key-sm2-key-code] 0474F110 F90F131B B6F6D929 9A23A41E F1AB1666 [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key-sm2-key-code] AC4BE4EE EF2CD876 2B633F80 DD5CF42F 147A722F [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key-sm2-key-code] DE527F39 247F3744 C23296BE FE3BE502 EEF7D9EC [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key-sm2-key-code] BC28A576 7E [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key-sm2-key-code] public-key-code end [*SSH Server-sm2-public-key] peer-public-key end [*SSH Server] commit
- Bind the SM2 public key to client002.
[~SSH Server] ssh user client002 assign sm2-key sm2key001 [*SSH Server] commit
- Enable the STelnet service on the SSH server.
# Enable the STelnet service.
[~SSH Server] stelnet server enable [*SSH Server] ssh server-source -i GigabitEthernet0/0/0 [*SSH Server] commit
- Set the service type of client001 and client002 to STelnet.
[*SSH Server] ssh user client001 service-type stelnet [*SSH Server] ssh user client002 service-type stelnet [*SSH Server] commit
- Connect STelnet clients to the SSH server.
# For the first login, enable first-time authentication on the clients.
Enable first-time authentication on client001.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname client001 [*HUAWEI] commit [~client001] ssh client first-time enable [*client001] commit
Enable first-time authentication on client002.
[~client002] ssh client first-time enable [*client002] commit
# Log in to the SSH server in password authentication mode on STelnet client001 by entering the username and password.
[~client001] stelnet 10.1.1.1 Trying 10.1.1.1 ... Press CTRL+K to abort Connected to 10.1.1.1 ... Please input the username:client001 Enter password:The following information indicates that the login is successful:
Info: The max number of VTY users is 20, and the number of current VTY users on line is 6. The current login time is 2018-07-16 11:42:42. First login successfully.# Connect client002 to the SSH server in SM2 authentication mode.
<~client002> stelnet 10.1.1.1 Trying 10.1.1.1 ... Press CTRL+K to abort Connected to 10.1.1.1 ... The server is not authenticated. Continue to access it?(Y/N):y Save the server's public key?(Y/N):y The server's public key will be saved with the name 10.1.1.1. Please wait... Please input the username: client002 Info: The max number of VTY users is 20, and the number of current VTY users on line is 6. The current login time is 2018-07-16 11:42:42.If the login succeeds, the user view is displayed. If the login fails, a Session is disconnected message is displayed.
- Verify the configuration.
# Display the SSH status.
[~SSH Server] display ssh server status SSH Version : 2.0 SSH authentication timeout (Seconds) : 60 SSH authentication retries (Times) : 3 SSH server key generating interval (Hours) : 0 SSH version 1.x compatibility : Enable SSH server keepalive : Disable SFTP IPv4 server : Enable SFTP IPv6 server : Enable STELNET IPv4 server : Enable STELNET IPv6 server : Enable SNETCONF IPv4 server : Enable SNETCONF IPv6 server : Enable SNETCONF IPv4 server port(830) : Disable SNETCONF IPv6 server port(830) : Disable SCP IPv4 server : Enable SCP IPv6 server : Enable SSH IPv4 server port : 22 SSH IPv6 server port : 22 SSH server source address : 10.1.1.1 SSH ipv6 server source address : 0::0 SSH ipv6 server source vpnName : ACL name : ACL number : ACL6 name : ACL6 number : SSH server ip-block : Enable
# Display SSH user information.
[~SSH Server] display ssh user-information ---------------------------------------------------- Username : client001 Authentication-type : password User-public-key-name : User-public-key-type : - Sftp-directory : - Service-type : stelnet Username : client002 Authentication-type : sm2 User-public-key-name : sm2key001 User-public-key-type : SM2 Sftp-directory : - Service-type : stelnet ---------------------------------------------------- Total 2, 2 printed
Configuration Files
SSH server configuration file
# sysname SSH Server # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 # sm2 peer-public-key sm2key001 public-key-code begin 0474F110 F90F131B B6F6D929 9A23A41E F1AB1666 AC4BE4EE EF2CD876 2B633F80 DD5CF42F 147A722F DE527F39 247F3744 C23296BE FE3BE502 EEF7D9EC BC28A576 7E public-key-code end peer-public-key end # stelnet server enable ssh server-source -i GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ssh user client001 ssh user client001 authentication-type password ssh user client001 service-type stelnet ssh user client002 ssh user client002 assign sm2-key sm2key001 ssh user client002 authentication-type sm2 ssh authorization-type default root ssh user client002 service-type stelnet # aaa local-user client001 password cipher @%@%UyQs4,KTtSwJo(4QmW#K,LC:@%@% local-user client001 service-type ssh # user-interface vty 0 4 authentication-mode aaa protocol inbound ssh user privilege level 3 # return
client001 configuration file
# sysname client001 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.0.0 # ssh client first-time enable # returnclient002 configuration file
# sysname client002 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.3.3 255.255.0.0 # ssh client first-time enable # return