Example for Configuring Routing Policies to Control BGP Route Advertisement and Acceptance
Routing policies can be configured to flexibly filter BGP routes, allowing only desired routes to be advertised and accepted so that these routes guide network traffic forwarding properly.
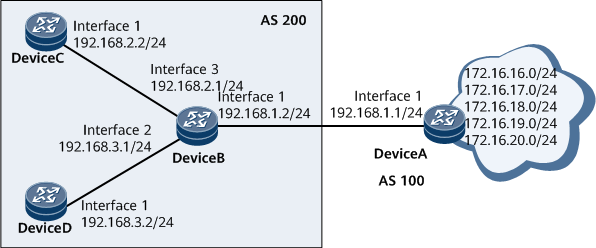
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceB, DeviceC, and DeviceD reside in AS 200 and run OSPF, whereas DeviceA resides in AS 100. DeviceA receives routes from the Internet. It is required that DeviceA provide only the routes 172.16.17.0/24, 172.16.18.0/24, and 172.16.19.0/24 for DeviceB, DeviceC accept only the route 172.16.18.0/24, and DeviceD accept all the routes provided by DeviceB.
Precautions
When configuring routing policies to control BGP route advertisement and acceptance, note the following:
When configuring an IP prefix list, specify a proper IP prefix range according to actual requirements.
Note that the name of a configured IP prefix list is case-sensitive.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure basic OSPF functions on DeviceB, DeviceC, and DeviceD.
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between DeviceA and DeviceB. Establish IBGP peer relationships between DeviceB and DeviceC, and between DeviceB and DeviceD.
Configure static routes on DeviceA and import them to the BGP routing table.
Configure an export routing policy for BGP routes on DeviceA and check the filtering result on DeviceB.
Configure an import routing policy for BGP routes on DeviceC and check the filtering result on DeviceC.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Five static routes configured and imported on DeviceA
OSPF backbone area (area 0) where DeviceB, DeviceC, and DeviceD reside
Names of IP prefix lists and routes to be filtered
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure OSPF in AS 100.
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] ospf [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
# Configure DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] ospf [*DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
# Configure DeviceD.
[~DeviceD] ospf [*DeviceD-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
- Configure basic BGP functions.
# Configure DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.3.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 192.168.2.1 as-number 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure DeviceD.
[~DeviceD] bgp 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 192.168.3.1 as-number 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] commit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
- Configure five static routes on DeviceA and import them to the BGP routing table.
[~DeviceA] ip route-static 172.16.16.0 24 NULL0 [*DeviceA] ip route-static 172.16.17.0 24 NULL0 [*DeviceA] ip route-static 172.16.18.0 24 NULL0 [*DeviceA] ip route-static 172.16.19.0 24 NULL0 [*DeviceA] ip route-static 172.16.20.0 24 NULL0 [*DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] import-route static [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Check the BGP routing table of DeviceB. The command output shows that DeviceB has learned the imported static routes.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 5 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 172.16.16.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.17.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.18.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.19.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.20.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100?
- Configure a routing policy to filter the BGP routes to be advertised.
# Configure an IP prefix list named a2b on DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] ip ip-prefix a2b index 10 permit 172.16.17.0 24 [*DeviceA] ip ip-prefix a2b index 20 permit 172.16.18.0 24 [*DeviceA] ip ip-prefix a2b index 30 permit 172.16.19.0 24 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure an export routing policy based on the IP prefix list a2b on DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] filter-policy ip-prefix a2b export static [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Check the BGP routing table of DeviceB. The command output shows that DeviceB has received only the three routes that match the IP prefix list a2b.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 3 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 172.16.17.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.18.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100? *> 172.16.19.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100?
- Configure a routing policy to filter the BGP routes to be accepted.
# Configure an IP prefix list named in on DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix in index 10 permit 172.16.18.0 24 [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure an import routing policy based on the IP prefix list in on DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] filter-policy ip-prefix in import [*DeviceC-bgp] commit
# Check the BGP routing table of DeviceC. The command output shows that DeviceC has accepted only the route that matches the IP prefix list in.
[~DeviceC] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 3.3.3.3 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 1 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 172.16.18.0/24 192.168.1.1 0 0 100?
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization filter-policy ip-prefix a2b export static import-route static peer 192.168.1.2 enable # ip ip-prefix a2b index 10 permit 172.16.17.0 24 ip ip-prefix a2b index 20 permit 172.16.18.0 24 ip ip-prefix a2b index 30 permit 172.16.19.0 24 # ip route-static 172.16.16.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 ip route-static 172.16.17.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 ip route-static 172.16.18.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 ip route-static 172.16.19.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 ip route-static 172.16.20.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 200 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 200 peer 192.168.2.2 as-number 200 peer 192.168.3.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 192.168.1.1 enable peer 192.168.2.2 enable peer 192.168.3.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 192.168.2.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization filter-policy ip-prefix in import peer 192.168.2.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ip ip-prefix in index 10 permit 172.16.18.0 24 # return
DeviceD configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 200 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 192.168.3.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 192.168.3.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return