Configuring BGP RPD
RPD provides a new method of distributing route-policies and allows the NCE to efficiently and dynamically deploy route-policies.
Usage Scenario
In a MAN ingress or IGW scenario, uneven link resource usage or link faults may cause link congestion. To make full use of network bandwidth, you can deploy an inbound traffic optimization solution to adjust route priorities so that traffic is diverted to idle links. In such a scenario, the router functions as a forwarder, and RPD needs to be deployed on it.
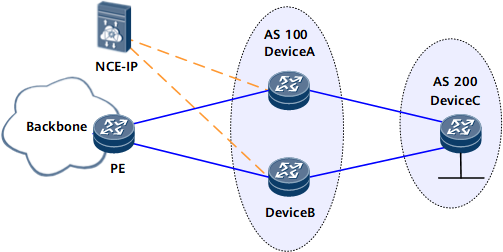
In Figure 1, an inbound traffic optimization solution is deployed so that traffic from AS 200 to the backbone network is monitored and scheduled in real time. If the link from Device C to Device A is congested, the traffic enters AS 100 through Device B and reaches the backbone network by path of the PE.
In this scenario, forwarders receive RPD policies delivered by the NCE and adjust route attributes and advertise routes based on the policies. The traffic optimization policy is configured on the NCE based on the traffic application. The following section describes relevant configurations on the forwarders. For details about how to configure the NCE, see the NCE manual.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring BGP RPD, complete the following tasks:
Configure basic BGP functions on a device, and establish a connection between the device and NCE to ensure routing reachability between them.
Procedure
- Configure basic RPD functions.
- (Optional) Configure GR to prevent the traffic interruption caused by a protocol restart.
- (Optional) Configure router ID-based filtering on non-RRs in the RR scenario so that the non-RRs only accept the RPD routes that match the router ID of the local BGP process. If a large number of RPD routes are accepted, a large number of policy nodes are generated accordingly, which reduces the performance.
- (Optional) Configure a delay for protocols to apply an updated RPD route-policy if the original policy changes.
Verifying the Configuration
Run the display bgp peer ipv4-address rpd export-policy command to check RPD route-policies.
Run the display bgp rpd routing-table command to check information about RPD routes.