Example for Configuring One-way Frame Delay Measurement in VPLS Networking
This section provides an example showing how to configure one-way frame delay measurement in VPLS networking.
Networking Requirements
As networks rapidly develop and applications diversify, various value-added services, such as Internet Protocol television (IPTV), video conferencing, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), are more widely used than ever before. Any link connectivity fault or network performance deterioration directly affects service quality on a live network, making performance monitoring on the pipes that transmit these services absolutely essential.
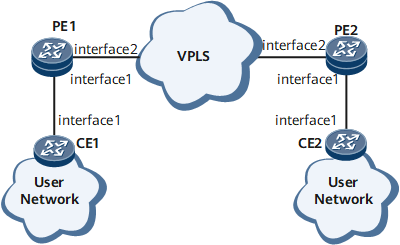
As shown in Figure 1, CFM is configured between each CE and PE and between PEs. To provide high-quality video services, providers hope to monitor the unidirectional delay over mobile bearer links in real time, while monitoring link connectivity. Monitoring the unidirectional delay over mobile bearer links allows the providers to respond quickly to video service quality deterioration.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure on-demand one-way frame delay measurement for the PW between the PEs to periodically collect statistics about the delay in frame transmission.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Configure the name of a VSI and the IP address of the interface of a VPLS.
Configure the names of the MD and MA between PE1 and PE2 and between CE1 and PE1.
Configure the interval at which 1DM messages are sent and the number of times when 1DM messages are sent.
Procedure
- Configure on-demand one-way frame delay measurement for a PW between PEs.
Configure a VPLS connection.
Configure a VPLS connection between PE1 and PE2. The detailed configurations are not provided here. For details, see the chapter "VPLS Configuration" in the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F SeriesRouter Configuration Guide - VPN or configuration files in this example.
After completing the configuration, run the display vsi name vsi-name verbose command on each PE to view information about the related VSI and PW.
<PE1> display vsi name ldp1 verbose ***VSI Name : ldp1 Administrator VSI : no Isolate Spoken : disable VSI Index : 1 PW Signaling : ldp Member Discovery Style : static Bridge-domain Mode : disable PW MAC Learn Style : unqualify Encapsulation Type : vlan MTU : 1500 Diffserv Mode : uniform Service Class : -- Color : -- DomainId : 255 Domain Name : Ignore AcState : disable P2P VSI : disable Create Time : 0 days, 0 hours, 10 minutes, 10 seconds VSI State : up VSI ID : 1 *Peer Router ID : 1.1.1.1 primary or secondary : primary ignore-standby-state : no VC Label : 4187 Peer Type : dynamic Session : up Tunnel ID : 0x0000000001004c4b42 Broadcast Tunnel ID : -- Broad BackupTunnel ID : -- CKey : 1 NKey : 2281701546 Stp Enable : 0 PwIndex : 1 Control Word : enable Interface Name : GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 State : up Access Port : false Last Up Time : 2013/02/21 08:44:46 Total Up Time : 0 days, 0 hours, 0 minutes, 14 seconds **PW Information: *Peer Ip Address : 1.1.1.1 PW State : up Local VC Label : 4187 Remote VC Label : 4187 Remote Control Word : enable PW Type : label Tunnel ID : 0x0000000001004c4b42 Broadcast Tunnel ID : -- Broad BackupTunnel ID : -- Ckey : 1 Nkey : 2281701546 Main PW Token : 0x0 Slave PW Token : 0x0 Tnl Type : ldp OutInterface : LDP LSP Backup OutInterface : -- Stp Enable : 0 PW Last Up Time : 2013/02/21 08:44:46 PW Total Up Time : 0 days, 0 hours, 0 minutes, 14 secondsConfigure basic Ethernet CFM functions and specify the MEP type as inward.
Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions on each PE. Specify the Ethernet CFM protocol in the version of IEEE Standard 802.1ag-2007. Create an MD named md1 and an MA named ma1, and bind the MA to the VSI.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] cfm enable [*PE1] cfm md md1 [*PE1-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] map vsi ldp1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 1 interface gigabitethernet0/1/1.1 inward [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 2 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [*PE1-md-md1] quit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] cfm enable [*PE2] cfm md md1 [*PE2-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] map vsi ldp1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 2 interface gigabitethernet0/1/1.1 inward [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send mep-id 2 enable [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 1 enable [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [*PE2-md-md1] quit
Configure the test instance.
# Configure PE1.
[*PE1] cfm md md1 [*PE1-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] test-id 1 mep 1 remote-mep 2 peer-ip 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] cfm md md1 [*PE2-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] test-id 1 mep 2 remote-mep 1 peer-ip 2.2.2.2 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] commit
Configure the DMM reception function on PE2.
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] delay-measure one-way receive test-id 1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] commit [~PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [~PE2-md-md1] quit
Enable on-demand one-way frame delay measurement for the PW on the VPLS network.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] delay-measure one-way send test-id 1 interval 1000 count 20 [~PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [~PE1-md-md1] quit
Verify the configuration.
Run the display y1731 statistic-type command on PE2 to view the statistics about the delay in unidirectional frame transmission.
<PE2> display y1731 statistic-type oneway-delay test-id 1 Latest one-way delay statistics of test-id 1: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Index Delay(usec) Delay variation(usec) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 531 - 2 423 108 3 527 104 4 327 200 5 456 129 6 481 25 7 342 139 8 463 121 9 642 179 10 677 35 11 507 170 12 511 4 13 510 1 14 557 47 15 489 68 16 403 86 17 498 95 18 508 10 19 513 5 20 591 78 21 490 101 22 468 22 23 514 46 24 393 121 25 509 116 26 516 7 27 662 146 28 571 91 29 383 188 30 545 162 31 421 124 32 612 191 33 645 33 34 75642 74997 35 594 75048 36 500 94 37 394 106 38 499 105 39 330 169 40 420 90 41 513 93 42 560 47 43 564 4 44 647 83 45 549 98 46 372 177 47 473 101 48 452 21 49 617 165 50 589 28 51 496 93 52 386 110 53 499 113 54 374 125 55 540 166 56 531 9 57 75535 75004 58 637 74898 59 360 277 60 75524 75164 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Average delay(usec) : 4254 Average delay variation(usec) : 6446 Maximum delay(usec) : 75642 Maximum delay variation(usec) : 75164 Minimum delay(usec) : 327 Minimum delay variation(usec) : 1
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # cfm version standard cfm enable # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 mpls # mpls l2vpn # mpls ldp # vsi ldp1 static pwsignal ldp vsi-id 1 peer 1.1.1.1 # mpls ldp #interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 vlan-type dot1q 2 l2 binding vsi ldp1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # cfm md md1 ma ma1 map vsi ldp1 mep mep-id 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable remote-mep mep-id 2 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable test-id 1 mep 1 remote-mep 2 peer-ip 1.1.1.1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # cfm enable # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi ldp1 static pwsignal ldp vsi-id 1 peer 2.2.2.2 # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 vlan-type dot1q 2 l2 binding vsi ldp1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # cfm md md1 ma ma1 map vsi ldp1 mep mep-id 2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 2 enable remote-mep mep-id 1 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 1 enable test-id 1 mep 2 remote-mep 1 peer-ip 2.2.2.2 delay-measure one-way receive test-id 1 # return