Configuring NG MVPN Option B in an Inter-AS Seamless MPLS Scenario
This section describes how to configure NG MVPN Option B in an inter-AS seamless MPLS scenario, in which inter-ASBRs establish EBGP peer relationships over inter-AS BGP LSPs.
Usage Scenario
In NG MVPN Option B in an inter-AS seamless MPLS scenario, the devices belong to different ASs. An inter-AS BGP LSP needs to be established to implement E2E service connectivity.
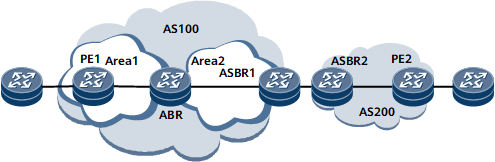
The local PE and ABR establish an IBGP peer relationship, the ABR and local ASBR establish an IBGP peer relationship, the local and remote ASBRs establish an EBGP peer relationship, and the remote ASBR and PE establish an IBGP peer relationship. The public network uses non-segmented inter-AS mLDP tunnels to carry multicast VPN traffic. The ABR functions as an RR to reflect MVPN routes. The MVPN address family needs to be enabled on the local and remote PEs, local and remote ASBRs, and ABR. Figure 1 shows NG MVPN Option B networking in an inter-AS seamless MPLS scenario.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring NG MVPN Option B in an inter-AS seamless MPLS scenario, complete the following tasks:
Configure an IGP for the MPLS backbone network of each AS to ensure IP connectivity on each backbone network.
Configure basic MPLS functions and MPLS LDP for the MPLS backbone network of each AS.
Establish an IBGP peer relationship between the PE and ABR/ASBR in the same AS.
Establish an IBGP peer relationship between the ABR and ASBR.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the local and remote ASBRs.
Configure a VPN instance on each PE connected to a CE and bind interfaces to VPN instances.
Assign an IP address to each CE interface that is connected to a PE.
- Configuring Global MPLS LDP Functions and Enabling MPLS LDP on Interfaces
- Global LDP must be enabled on each node before LDP services can be configured in an MPLS domain.
- Configuring an Automatic mLDP P2MP Tunnel
- Automatic mLDP P2MP tunnels are used to transmit NG MVPN traffic.
- Configuring a Static RP
- To use a static Rendezvous Point (RP) in a PIM-SM domain, configure the same RP address and same address range of multicast groups that the RP serves on all routers in the PIM-SM domain.
- Configuring MP-IBGP Among PEs, ABRs, and ASBRs in the Same AS
- By introducing extended community attributes into BGP, MP-IBGP can advertise VPNv4 routes among the PEs, ABRs, and ASBRs.
- Configuring MP-EBGP Between ASBRs in Different ASs
- After an MP-EBGP peer relationship is established between ASBRs, an ASBR can advertise the VPNv4 routes of its AS to the other ASBR.
- Configuring a Routing Policy to Control Label Distribution on ASBRs
- Configure a routing policy to control MPLS label allocation for each IPv4 route. The ASBR only allocates label to the routes that match the rules in the policy.
- Configuring Route Reflection on an ABR
- Route reflection on an ABR is used to reflect the VPNv4 routes advertised by the PE or ASBR to other devices in the same AS. As a result, PE does not need to set up BGP peer relationship with ASBR, which simplifies configurations.
- Configuring BGP MVPN Peers
- Establish a BGP MVPN peer relationship between devices belonging to the same MVPN, so that the devices can use BGP to exchange BGP A-D and BGP C-multicast routes.
- Configuring a P2MP LSP to Carry Multicast Traffic
- An NG MVPN uses P2MP LSPs to carry multicast traffic. Only mLDP P2MP LSPs are supported.