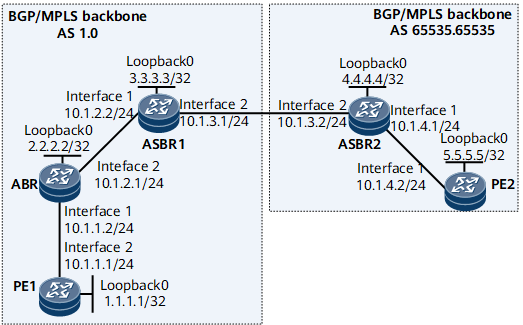
Example for Configuring an Inter-AS Seamless MPLS NG MVPN Option C
This example describes how to configure inter-AS seamless MPLS NG MVPN in Option C mode to implement E2E service connectivity, when the devices are in different ASs.
Networking Requirements
As shown in the Figure 1, PE1, the ABR, and ASBR1 are located in different ASs from PE2 and ASBR2. To enable PEs at both ends to communicate and provide VPN services, deploy inter-AS seamless MPLS NG MVPN.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure IGP protocols at each network to implement network connectivity at each network.
Set up an MPLS LDP LSP in each network.
Establish IBGP peer relationships at each AS and enable devices to exchange labeled routes.
Configure an EBGP peer relationship between ASBRs and enable these devices to exchange labeled routes across ASs.
Configure the ABR as an RR, so that PE2's loopback route advertised by ASBR2 to ASBR1 is reflected to PE1 through the ABR. The ABR reflects PE1's loopback route obtained from PE1 to ASBR1, and ASBR1 advertises the route to ASBR2 and PE2. PE1 and PE2 can then obtain each other's loopback routes.
Configure a routing policy to control label distribution for a BGP LSP to be established on each device. The egress of the BGP LSP to be established needs to assign an MPLS label to the route advertised to an upstream node. If a transit node receives a labeled IPv4 route from downstream, the downstream node must re-assign an MPLS label to the transit node.
Configure BGP peers.
Configure a P2MP LSP to carry multicast traffic.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of the devices (1.1.1.1, 2.2.2.2, 3.3.3.3, 4.4.4.4, and 5.5.5.5)
Route policy configured on each device (policy1)
The IP address of Loopback 1 on PE1's private network side is 6.6.6.6.
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface.
Assign an IP address and its mask to every physical interface; configure a loopback interface address as an LSR ID on every device shown in Figure 1; configure OSPF and IS-IS to advertise the route to the network segment of each interface and a host route to each loopback interface address (LSR ID). For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS and LDP globally on each device.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure ABR.
<ABR> system-view [~ABR] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*ABR] mpls [*ABR-mpls] quit [*ABR] mpls ldp [*ABR-mpls-ldp] quit [*ABR] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*ABR] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*ABR-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*ABR] commit
# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*ASBR1] mpls [*ASBR1-mpls] quit [*ASBR1] mpls ldp [*ASBR1-mpls-ldp] quit [*ASBR1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*ASBR1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*ASBR1] commit
# Configure ASBR2.
[~ASBR2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 [*ASBR2] mpls [*ASBR2-mpls] quit [*ASBR2] mpls ldp [*ASBR2-mpls-ldp] quit [*ASBR2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*ABSR2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [*ABSR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*ABSR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*ABSR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*ASBR2] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure automatic mLDP P2MP tunnel.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp [~PE1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] mldp recursive-fec [*PE1-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp] quit
The configuration of PE2 is similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure ABR.
[~ABR] mpls ldp [~ABR-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*ABR-mpls-ldp] mldp recursive-fec [*ABR-mpls-ldp] commit [~ABR-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] mpls ldp [~ASBR1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*ASBR1-mpls-ldp] mldp recursive-fec [*ASBR1-mpls-ldp] commit [~ASBR1-mpls-ldp] quit
The configuration of ASBR2 is similar to the configuration of ASBR1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish IBGP peer relationships at each AS, establish EBGP peer relationships between PEs and between ASBRs in different ASs, and enable these devices to exchange labeled routes.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 1.0 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 1.0 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*PE1-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 65535.65535 [*PE1-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE1-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 5.5.5.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] network 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] policy vpn-target [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 5.5.5.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] policy vpn-target [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 5.5.5.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the ABR.
[~ABR] bgp 1.0 [*ABR-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 1.0 [*ABR-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack 1 [*ABR-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 1.0 [*ABR-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack 1 [*ABR-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ABR-bgp] quit [*ABR] commit
# Configure ASBR1.
<ASBR1> system-view [~ASBR1] bgp 1.0 [*ASBR1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 1.0 [~ASBR1-bgp] peer 10.1.3.2 as-number 65535.65535 [*ASBR1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.3.2 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.3.2 label-route-capability [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ASBR1-bgp] quit [*ASBR1] commit
# Configure ASBR2.
<ASBR2> system-view [~ASBR2] bgp 65535.65535 [*ASBR2-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 65535.65535 [*ASBR2-bgp] peer 10.1.3.1 as-number 1.0 [*ASBR2-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*ASBR2-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.3.1 enable [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 5.5.5.5 enable [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.3.1 label-route-capability [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 5.5.5.5 label-route-capability [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] network 5.5.5.5 32 [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ASBR2-bgp] quit [*ASBR2] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 65535.65535 [*PE2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 65535.65535 [*PE2-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 1.0 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*PE2-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*PE2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 4.4.4.4 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 4.4.4.4 label-route-capability [*PE2-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] policy vpn-target [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] policy vpn-target [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure ABR as an RR to reflect the VPNv4 routes of PE1 and PE2 to each other.
# Configure ABR.
[~ABR] bgp 1.0 [*ABR-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ABR-bgp] quit [*ABR] commit
- Configure a route-policy on each device to establish a BGP LSP.
# Configure a route-policy on PE1, and apply it to the routes to be advertised to peers.
[~PE1] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*PE1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*PE1-route-policy] quit [*PE1] bgp 1.0 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy1 export [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
The configuration of PE2 is similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure a route policy on ABR, and apply it to the routes to be advertised to peers.
[~ABR] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*ABR-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*ABR-route-policy] quit [*ABR] bgp 1.0 [*ABR-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 route-policy policy1 export [*ABR-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ABR-bgp] quit [*ABR] commit
# Configure a route-policy on ASBR1, and apply it to the routes to be advertised to peers.
[~ASBR1] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*ASBR1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] quit [~ASBR1] route-policy policy2 permit node 1 [*ASBR1-route-policy] if-match mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] quit [*ASBR1] bgp 1.0 [*ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.1.3.2 route-policy policy1 export [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy2 export [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ASBR1-bgp] quit [*ASBR1] commit
Repeat this step for ASBR2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure unicast peers and BGP MVPN neighbors.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance ng [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 1.2.3.4:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 both [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng] quit [*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance ng [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface LoopBack1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance ng [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] bgp 1.0 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance ng [*PE1-bgp-af-vpn-ng] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-af-vpn-ng] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
The configuration of PE2 is similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure P2MP LSPs to carry multicast traffic on PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 [~PE1] ip vpn-instance ng [~PE1-vpn-instance-ng] ipv4-family [~PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] sender-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] rpt-spt mode [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] auto-discovery inter-as [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] ipmsi-tunnel [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] mldp [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-ng] commit [~PE1-vpn-instance-ng] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] multicast mvpn 5.5.5.5 [~PE2] ip vpn-instance ng [~PE2-vpn-instance-ng] ipv4-family [~PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [~PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] rpt-spt mode [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] auto-discovery inter-as [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-ng] commit [~PE2-vpn-instance-ng] quit
- Configure PIM.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] pim vpn-instance ng [~PE1-pim-vpn-instance-ng] static-rp 6.6.6.6 [*PE1-pim-vpn-instance-ng] commit [~PE1-pim-vpn-instance-ng] quit [*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] pim vpn-instance ng [*PE2-pim-ng] static-rp 6.6.6.6 [*PE2-pim-ng] commit [~PE2-pim-ng] quit [~PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] igmp enable [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, run the display ip routing-table command on PE1 or PE2 to display the routes to each other's loopback address.
The following example uses the command output on PE1:
<PE1> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 10 Routes : 10 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.2/32 OSPF 10 1 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 5.5.5.5/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 2.2.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/2 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display mpls lsp command on PE1 or PE2 to display the LSP information.
The following example uses the command output on PE1:
<PE1> display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 3/NULL -/- 2.2.2.2/32 NULL/3 -/GigabitEthernet0/1/2 2.2.2.2/32 32828/3 -/GigabitEthernet0/1/2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: BGP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 32830/NULL -/- 5.5.5.5/32 NULL/32835 -/-Run the ping lsp command on PE1 or PE2 to check the connectivity of BGP LSP.
The following example uses the command output on PE1:
<PE1> ping lsp bgp 5.5.5.5 32 LSP PING FEC: IPV4 PREFIX 5.5.5.5/32/ : 100 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 5.5.5.5: bytes=100 Sequence=1 time=94 ms Reply from 5.5.5.5: bytes=100 Sequence=2 time=4 ms Reply from 5.5.5.5: bytes=100 Sequence=3 time=4 ms Reply from 5.5.5.5: bytes=100 Sequence=4 time=4 ms Reply from 5.5.5.5: bytes=100 Sequence=5 time=4 ms --- FEC: BGP LABLED IPV4 PREFIX 5.5.5.5/32 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4/22/94 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 # ip vpn-instance ng ipv4-family route-distinguisher 1.2.3.4:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp rpt-spt mode auto-discovery inter-as ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec ipv4-family # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance ng ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Virtual-Template0 ppp authentication-mode auto # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface LoopBack1 ip binding vpn-instance ng ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 # interface NULL0 # bgp 1.0 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 1.0 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 65535.65535 peer 5.5.5.5 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability peer 5.5.5.5 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 5.5.5.5 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 5.5.5.5 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance ng import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # pim vpn-instance ng static-rp 6.6.6.6 # returnABR configuration file
# sysname ABR # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000c.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface Virtual-Template0 ppp authentication-mode auto # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface NULL0 # bgp 1.0 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 1.0 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 1.0 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 route-policy policy1 export peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # return
ASBR1 configuration file
# sysname ABR1 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000a.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Virtual-Template0 ppp authentication-mode auto # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface NULL0 # bgp 1.0 peer 10.1.3.2 as-number 65535.65535 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 1.0 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.1.3.2 enable peer 10.1.3.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.1.3.2 label-route-capability peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy2 export peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # route-policy policy2 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 10.1.3.2 # return
ASBR2 configuration file
# sysname ASBR2 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000b.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Virtual-Template0 ppp authentication-mode auto # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface NULL0 # bgp 65535.65535 peer 10.1.3.1 as-number 1.0 peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 65535.65535 peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.3.1 enable peer 10.1.3.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.1.3.1 label-route-capability peer 5.5.5.5 enable peer 5.5.5.5 route-policy policy2 export peer 5.5.5.5 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # route-policy policy2 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 10.1.3.1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # multicast mvpn 5.5.5.5 # ip vpn-instance ng ipv4-family route-distinguisher 2.3:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn c-multicast signaling bgp rpt-spt mode auto-discovery inter-as ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec # ipv4-family # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000d.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance ng ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable # interface Virtual-Template0 ppp authentication-mode auto # interface LoopBack0 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface NULL0 # bgp 65535.65535 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 1.0 peer 1.1.1.1 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 65535.65535 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 4.4.4.4 label-route-capability # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance ng import-route direct # pim vpn-instance ng static-rp 6.6.6.6 # return