Example for Configuring Basic Ethernet CFM Functions Based on BGP VPLS
Configure a BGP VSI on two PEs, and configure CFM on the two PEs' access interfaces. The BGP VSI can use CFM to monitor VC connectivity.
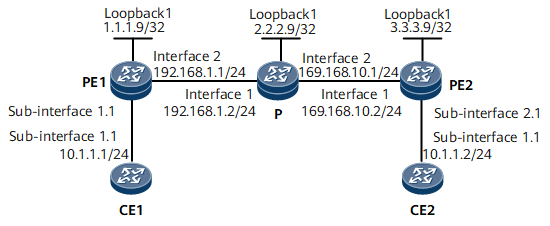
Networking Requirements
As shown in Figure 1, VPLS is enabled on PE1 and PE2. CE1 and CE2 are connected to PE1 and PE2, respectively. CE1 and CE2 belong to the same VPLS network. Configure a BGP VSI on PE1 and PE2. The VSI is Up. Configure CFM on the access interfaces of PE1 and PE2. Th remote MEP is Up. If the VC in the VSI fails, the remote MEP goes Down.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP and basic MPLS functions on the backbone network.
Establish LSPs between PEs.
Enable MPLS L2VPN on each PE.
Enable BGP peers to exchange VPLS information between PEs.
Create a VSI on each PE, specify BGP as the signaling protocol, and specify the RD, VPN target, and site ID.
Bind AC interfaces to VSIs.
Associate an MA with a VPLS on each PE.
Configure Ethernet CFM on each PE.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Peer IP address
VSI names on PE1 and PE2
BGP AS numbers on PE1 and PE2
Signaling protocol of a VSI (BGP in this example)
RD, VPN target, and site ID of the VSI on each PE
Interfaces to which VSIs are bound and VLAN IDs of the interfaces
MA and MD names on CE1 and CE2
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each device interface on the backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-Loopback1] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [*PE1-Loopback1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 192.168.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P [*HUAWEI] commit [~P] interface loopback1 [*P-Loopback1] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [*P-Loopback1] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 192.168.1.2 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 192.168.10.1 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface loopback1 [*PE2-Loopback1] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [*PE2-Loopback1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] 192.168.10.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure an IGP. In this example, OSPF is used.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ospf 1 [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE1-ospf-1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
[~P] ospf 1 [*P-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*P-ospf-1] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] ospf 1 [*PE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE2-ospf-1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure basic MPLS functions and establish LSPs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the P.
[~P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [*P] mpls [*P-mpls] quit [*P] mpls ldp [*P-mpls-ldp] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] commit
- Enable BGP peers to exchange VPLS information.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-ad-family [*PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] peer 3.3.3.9 signaling vpls [*PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback1 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-ad-family [*PE2-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] peer 1.1.1.9 signaling vpls [*PE2-bgp-af-l2vpn-ad] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
- Enable MPLS L2VPN on the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls l2vpn [*PE1-l2vpn] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls l2vpn [*PE2-l2vpn] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure a VSI on PEs.

The site IDs on both ends of a VPLS PW must be different.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] vsi bgp1 [*PE1-vsi-bgp1] pwsignal bgp [*PE1-vsi-bgp1-bgp] route-distinguisher 192.168.1.1:1 [*PE1-vsi-bgp1-bgp] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity [*PE1-vsi-bgp1-bgp] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [*PE1-vsi-bgp1-bgp] site 1 range 5 default-offset 0 [*PE1-vsi-bgp1-bgp] quit [*PE1-vsi-bgp1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] vsi bgp1 [*PE2-vsi-bgp1] pwsignal bgp [*PE2-vsi-bgp1-bgp] route-distinguisher 192.168.10.2:1 [*PE2-vsi-bgp1-bgp] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity [*PE2-vsi-bgp1-bgp] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [*PE2-vsi-bgp1-bgp] site 2 range 5 default-offset 0 [*PE2-vsi-bgp1-bgp] quit [*PE2-vsi-bgp1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Bind AC interfaces to VSIs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] l2 binding vsi bgp1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] l2 binding vsi bgp1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure CEs.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0.1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0.1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1] quit [*CE2] commit
- Configure Ethernet CFM on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] cfm enable [*PE1] cfm md md1 [*PE1-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] ccm-interval 100 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] map vsi bgp1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 1 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0.1 inward [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 2 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [*PE1-md-md1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] cfm enable [*PE2] cfm md md1 [*PE2-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] ccm-interval 100 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] map vsi bgp1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 2 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0.1 inward [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 1 [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send enable [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive enable [*PE2-md-md1-ma-ma1] quit [*PE2-md-md1] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the preceding configuration, run the display cfm remote-mep command on PE1 to check that the remote MEP is Up.
[*PE1]display cfm remote-mep The total number of RMEPs is : 1 The status of RMEPs : 1 up, 0 down, 0 disable -------------------------------------------------- MD Name : md1 Level : 0 MA Name : ma1 RMEP ID : 2 VLAN ID : 10 VSI Name : bgp1 L2VC ID : -- L2VPN Name : -- CE ID : -- CE Offset : -- L2TPV3 Tunnel Name : -- L2TPV3 Local Connection Name : -- MAC : 00e0-fc12-7890 CCM Receive : enabled Trigger-If-Down : enabled CFM Status : up Alarm Status : none Interface TLV : -- Port Status TLV : --
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 undo shutdown vlan-type dot1q 10 # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 undo shutdown vlan-type dot1q 10 # returnPE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi bgp1 pwsignal bgp route-distinguisher 192.168.1.1:1 vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity site 1 range 5 default-offset 0 # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 undo shutdown vlan-type dot1q 10 l2 binding vsi bgp1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 l2vpn-ad-family policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable peer 3.3.3.9 signaling vpls # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 # ma ma1 map vsi bgp1 ccm-interval 100 mep mep-id 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable remote-mep mep-id 2 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi bgp1 pwsignal bgp route-distinguisher 192.168.10.2:1 vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity site 2 range 5 default-offset 0 # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1 undo shutdown vlan-type dot1q 10 l2 binding vsi bgp1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 l2vpn-ad-family policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 1.1.1.9 signaling vpls # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 # ma ma1 map vsi bgp1 ccm-interval 100 mep mep-id 2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 2 enable remote-mep mep-id 1 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 1 enable # return