DCI Scenarios
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) is a solution for communication between virtual machines (VMs) in different data centers (DCs). DCI runs on carriers' networks. It uses technologies such as Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network (VXLAN), Ethernet virtual private network (EVPN), and BGP/MPLS IP VPN to ensure secure and reliable transmission of packets from DCs, implementing communication between VMs in different DCs.
Concept |
Description |
|---|---|
Overlay network |
|
Underlay network |
An underlay network carries an overlay network and is usually a physical network at the underlying layer. |
Individual deployment of DC-GWs and DCI-PEs |
A DC-GW and a DCI-PE are different devices. |
Integrated deployment of DCI-PEs and DC-GWs |
A DC-GW and a DCI-PE are a single device, which applies to scenarios where carriers build their own DCs. |
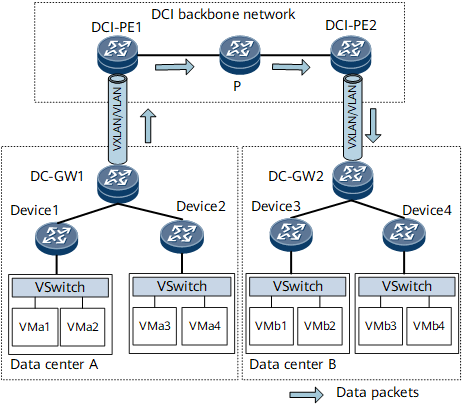
On the network shown in Figure 1, gateways in the DCs (DC-GW1 and DC-GW2) can access the carrier's network edge devices (DCI-PE1 and DCI-PE2) in EVPN-VXLAN or VLAN mode. The L3VPN or EVPN-MPLS function can be deployed on the DCI backbone network to transmit Layer 2 or Layer 3 service traffic. When DC A and DC B exchange their tenant host IP addresses or MAC addresses, EVPN integrated routing and bridging (IRB) routes, EVPN IP prefix routes, BGP VPNv4 routes, EVPN MAC routes, or ARP routes are used. For details about these routes, see Table 2.
Route |
Function |
Fields Carried in a Route |
|---|---|---|
EVPN IRB route |
Used to transmit a tenant's host IP address and MAC address on an EVPN. |
|
EVPN IP prefix route |
Used to transmit a tenant's host IP address or the address of the network segment to which the host IP address belongs on an EVPN. |
|
VPNv4 route |
Used to transmit a tenant's host IP address or the address of the network segment to which the host IP address belongs on an L3VPN. |
|
EVPN MAC route or ARP route |
Used to transmit a tenant's host MAC address or ARP information on an EVPN. |
|
DCI Control Plane
During Layer 3 route advertisement, a DC sends an IRB route or IP prefix route carrying a tenant's host IP address to a DCI-PE through the EVPN protocol. Upon receipt, the DCI-PE re-encapsulates the routing information into a BGP VPNv4 route if an L3VPN is deployed on the backbone network. Alternatively, if EVPN-MPLS is deployed on the backbone network, the DCI-PE re-encapsulates the received route into an IRB or IP prefix route. The re-encapsulated routes carry the VM's IP route and are transmitted to the remote DCI-PE through the backbone network.
The process of Layer 2 route advertisement is that a DC uses EVPN to send packets carrying the host's MAC address or ARP entries to the local DCI-PE. The local DCI-PE then re-generates the EVPN MAC/ARP routes that carry the MPLS encapsulation attribute. The regenerated routes that carry the VM's MAC address or ARP entries are transmitted to the remote DCI-PE.
Table 3 describes Layer 3 route advertisement and Layer 2 route advertisement.
Deployment Mode |
Services |
Advertisement Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
DC-GW1 to DCI-PE1 |
DCI-PE1 to DCI-PE2 |
DCI-PE2 to DC-GW2 |
||
L3VPN (VXLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW1 sends a tenant's host IP address to DCI-PE1 through an IRB route or IP prefix route. DCI-PE1 parses the tenant's host IP route from the received EVPN route. Then the system imports the tenant's route into the IP VPN instance based on RT matching between the EVPN route and the IP VPN instance and delivers information about VXLAN tunnel recursion to the VPN forwarding table. |
DCI-PE1 re-encapsulates the EVPN route received
from DC-GW1 into a BGP VPNv4 route, applying the following changes:
After re-encapsulation, DCI-PE1 sends the route to DCI-PE2. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE2 imports the BGP VPNv4
route into the local IP VPN instance based on the route RT and delivers
information about MPLS tunnel recursion to the VPN forwarding table.
DCI-PE2 re-encapsulates the received BGP VPNv4 route into an IP prefix
route, applying the following changes:
After re-encapsulation, DCI-PE2 sends the IP prefix route to DC-GW2. |
EVPN-MPLS (VLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW1 sends routes destined for the network segment on which a tenant's host IP address resides to DCI-PE1 through an IGP or BGP route. Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 delivers these routes to the VPN forwarding table. |
DCI-PE1 re-encapsulates the VPN route into
an IP prefix route, applying the following changes:
After re-encapsulation, DCI-PE1 sends the route to DCI-PE2. |
After receiving the EVPN route, DCI-PE2 imports the route into the local IP VPN instance based on the RT of the EVPN route, generates a VPN route forwarding entry, and advertises the EVPN route to DC-GW2 through a VPN IGP or BGP peer relationship. |
Layer 2 services |
DCI-PE1 learns the source MAC address of service traffic received from DC-GW1. Then DCI-PE1 generates a local MAC forwarding entry and an EVPN MAC route. |
DCI-PE1 generates an EVPN MAC route, applying
the following changes:
After re-encapsulation, DCI-PE1 sends the route to DCI-PE2. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE2 imports the MAC/IP advertisement route into the local EVPN instance based on the route RT and generates a local Layer 2 forwarding entry accordingly. |
|
EVPN-MPLS (VXLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW1 sends a tenant's host IP address to DCI-PE1 through an IRB route or IP prefix route. DCI-PE1 parses the tenant's host IP route from the received EVPN route. Then the system imports the tenant's route into the IP VPN instance based on RT matching between the local EVPN instance and the IP VPN instance and delivers information about VXLAN tunnel recursion to the VPN forwarding table. |
DCI-PE1 re-encapsulates the route into an
IRB or IP prefix route. The encapsulation mode changes from VXLAN
to MPLS:
After re-encapsulation, DCI-PE1 sends the route to DCI-PE2. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE2 imports the IRB or IP prefix route into the IP VPN instance and delivers information about MPLS tunnel recursion to the VPN forwarding table. DCI-PE2 changes the L2 and L3 VPN labels in the route to L2 and L3 VNIs, re-encapsulates the route into an IRB or IP prefix route, and then sends the route to DC-GW2. |
Layer 2 services |
DC-GW1 sends a tenant's host MAC address to DCI-PE1 through a MAC/IP advertisement route. DCI-PE1 imports the MAC/IP advertisement route into the local EVPN instance based on RT matching and generates a MAC forwarding entry. |
DCI-PE1 re-encapsulates the EVPN routes and change the next-hop IP address to the IP address of the locally established EVPN peer. The RD and RT attributes in the EVPN routes that carry the VXLAN encapsulation attribute are replaced with the RD and RT of the local EVPN instance. The MPLS label is requested. The re-encapsulated MAC/IP Advertisement routes are then advertised to DCI-PE2. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE2 imports the MAC/IP advertisement route into the local EVPN instance based on RT matching. DCI-PE2 re-encapsulates the EVPN route by changing the next hop to its own VTEP address, replacing the RD and RT values of the EVPN route with those of the local EVPN instance and padding the route with an L2VNI. Then DCI-PE2 sends the re-encapsulated MAC address advertisement route to DC-GW2. |
|
DCI Data Plane
Table 4 describes Layer 2 traffic forwarding and Layer 3 traffic forwarding.
Deployment Mode |
Services |
Forwarding Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
DC-GW2 to DCI-PE2 |
DCI-PE2 to DCI-PE1 |
DCI-PE1 to DC-GW1 |
||
L3VPN (VXLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW2 sends a data packet to DCI-PE2 through the VXLAN tunnel. |
DCI-PE2 parses the VXLAN data packet to obtain the VNI and data packet. Based on the VNI, DCI-PE2 finds the corresponding VPN instance and, based on the tenant's host IP address for the MPLS tunnel to DCI-PE1, searches the corresponding VPN instance forwarding table. After encapsulating a VPN label and a public MPLS tunnel label into the data packet, DCI-PE2 sends the packet to DCI-PE1 through the MPLS tunnel. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 removes the public MPLS tunnel label, and, based on the VPN label, finds the corresponding VPN instance. Then, based on the tenant's host IP address for the VXLAN tunnel to DC-GW1, DCI-PE1 searches the corresponding VPN instance forwarding table. DCI-PE1 encapsulates the data packet with a VXLAN header and then sends the VXLAN packet to DC-GW1. |
EVPN-MPLS (VLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW2 sends a data packet to DCI-PE2 through VPN forwarding. |
DCI-PE2 searches the forwarding table of the VPN instance bound to the interface that receives the data packet and, based on the destination address of the data packet, finds the MPLS tunnel to DCI-PE1. After encapsulating a VPN label and a public MPLS tunnel label into the data packet, DCI-PE2 sends the packet to DCI-PE1 through the MPLS tunnel. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 removes the public MPLS tunnel label, and, based on the VPN label, finds the corresponding VPN instance. Based on the tenant's host IP address, DC-PE1 searches the corresponding VPN instance forwarding table for the outbound interface to DC-GW1. Then, DC-PE1 sends the data packet to DC-GW1 through the outbound interface. |
Layer 2 services |
DC-GW2 sends a data packet to DCI-PE2 through Layer 2 forwarding on the data plane. |
DCI-PE2 searches the forwarding table of the EVPN instance bound to the interface that receives the data packet and, based on the destination address of the data packet, finds the MPLS tunnel to DCI-PE1. After encapsulating a VPN label and a public MPLS tunnel label into the data packet, DCI-PE2 sends the packet to DCI-PE1 through the MPLS tunnel. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 removes the public MPLS tunnel label, and, based on the VPN label, finds the corresponding EVPN instance. Based on the MAC forwarding entry for the broadcast domain bound to the EVPN instance, DC-PE1 finds the corresponding outbound interface and sends the data packet to DC-GW1 through the outbound interface. |
|
EVPN-MPLS (VXLAN access) |
Layer 3 services |
DC-GW2 sends a data packet to DCI-PE2 through the VXLAN tunnel. |
DCI-PE2 parses the VXLAN data packet to obtain the VNI and data packet. Based on the VNI, DCI-PE2 finds the corresponding VPN instance and, based on the tenant's host IP address for the MPLS tunnel to DCI-PE1, searches the corresponding VPN instance forwarding table. After encapsulating a VPN label and a public MPLS tunnel label into the data packet, DCI-PE2 sends the packet to DCI-PE1 through the MPLS tunnel. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 removes the public MPLS tunnel label, and, based on the VPN label, finds the corresponding VPN instance. Then, based on the tenant's host IP address for the VXLAN tunnel to DC-GW1, DCI-PE1 searches the corresponding VPN instance forwarding table. DCI-PE1 encapsulates the data packet with a VXLAN header and then sends the VXLAN packet to DC-GW1. |
Layer 2 services |
DC-GW2 sends a data packet to DCI-PE2 through the VXLAN tunnel. |
DCI-PE2 parses the VXLAN data packet to obtain the VNI and data packet. Based on the VNI, DCI-PE2 finds the corresponding broadcast domain. Based on the broadcast domain, DCI-PE2 finds the forwarding table of the corresponding EVPN instance. DCI-PE2 searches for the forwarding information corresponding to the destination address of the data packet, that is, information about the MPLS tunnel to DCI-PE1. After encapsulating a VPN label and a public MPLS tunnel label into the data packet, DCI-PE2 sends the packet to DCI-PE1 through the MPLS tunnel. |
Upon receipt, DCI-PE1 removes the public MPLS tunnel label and, based on the VPN label and BD ID, finds the corresponding broadcast domain, and then, based on the tenant's host destination MAC address, searches the broadcast domain for the VXLAN tunnel to DC-GW1. DCI-PE1 encapsulates the data packet with a VXLAN header and then sends the VXLAN packet to DC-GW1. |
|