Inter-AS EVPN Option C
Inter-AS EVPN Option C implements Layer 2 interconnection between networks in different ASs.
Background
With the wide application of MPLS VPN solutions, different MANs of a service provider or collaborative backbone networks of different service providers often span multiple ASs. Similar to L3VPN services, EVPN services running on an MPLS network must also have the capability of spanning ASs.
Implementation
By advertisement of labeled routes between PEs, end-to-end BGP LSPs can be established to carry Layer 2 traffic in BGP ASs (including inter-IGP areas) and inter-BGP ASs that only support Option C.
- Ethernet auto-discovery routes
- MAC and IP routes
- Inclusive multicast routes
- Ethernet segment routes
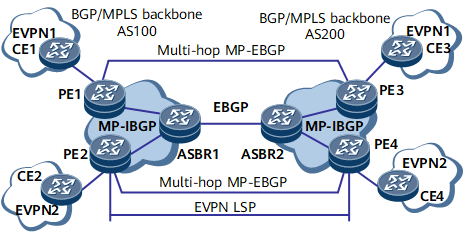
- ASBRs advertise labeled IPv4 routes to PEs in their respective ASs through MP-IBGP, and advertise labeled IPv4 routes received on PEs in the local AS to the ASBR peers in other ASs. ASBRs in the transit AS also advertise labeled IPv4 routes. Therefore, a BGP LSP can be established between the ingress PE and egress PE.
- PEs in different ASs establish multi-hop EBGP connections with each other and exchange EVPN routes.
- ASBRs do not store EVPN routes or advertise EVPN routes to each other.
To improve expansibility, you can specify a route reflector (RR) in each AS. An RR stores all EVPN routes and exchanges EVPN routes with PEs in the AS. RRs in two ASs establish MP-EBGP connections with each other and advertise EVPN routes.
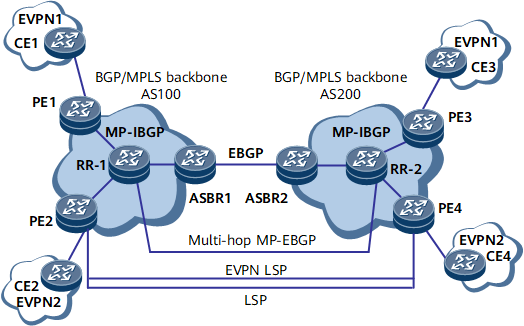
- A local ASBR learns a labeled public network BGP route from the peer ASBR, assigns a label to this route based on a matching policy, and advertises this route to its IBGP peer. Then, a complete public network LSP is established.
- The IBGP peer relationship between a PE and ASBR in the same AS is not required. In this solution, a local ASBR learns a labeled public network BGP route from the peer ASBR and imports this route to an IGP to trigger LDP LSP establishment. Then, a complete LSP is established between the ingress and egress on the public network.
Benefits
EVPN routes are directly exchanged between an ingress PE and egress PE. The routes do not have to be stored and forwarded by intermediate devices.
Only PEs exchange EVPN routing information. Ps and ASBRs forward packets only. The intermediate devices need to support only MPLS forwarding rather than MPLS VPN services. In such a case, ASBRs are no longer the performance bottlenecks. Inter-AS EVPN Option C, therefore, is suitable for an EVPN that spans multiple ASs.