Configuring EVC VPLS Accessing L3VPN
This section describes how to create a VBDIF interface to implement EVC VPLS accessing L3VPN.
Usage Scenario
EVC interfaces are Layer 2 interfaces that do not support IP addresses. If EVC L2VPN accessing L3VPN is required, you must create a BD-based interface, or VBDIF interface. A VBDIF interface is a Layer 3 interface that supports IP address configuration. The VBDIF interface allows communication with the L3VPN.
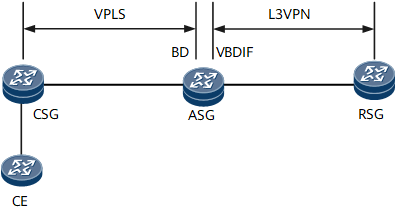
As shown in Figure 1, on the access network, the CSG provides a BD for user site access and connects to the ASG over a VPLS PW; on the bearer network, the ASG uses the VBDIF interface to terminate the VPLS PW and establishes an L3VPN with the RSG.
Pre-configuration tasks
Before configuring EVC VPLS accessing L3VPN, complete the following task:
Procedure
- Configure EVC VPLS on the CSG and ASG. For configuration details, see Configuring the EVC Model to Carry VPLS Services.
- Create VPN instances on the ASG and RSG and establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship. For configuration details, see Configuring Basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN.
- Create a VBDIF interface on the ASG and bind the VBDIF interface to the L3VPN.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.