Example for Configuring MPLS EVPN L3VPN E-LAN Option B
This section describes how to configure MPLS EVPN L3VPN E-LAN Option B to carry inter-AS Layer 3 service traffic.
Context
Networking Requirements
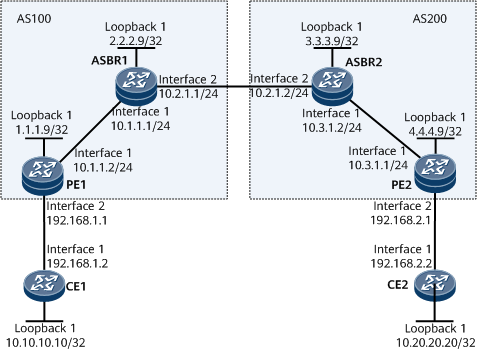
As shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE2 belong to the same VPN. CE1 is connected to PE1 in AS 100, and CE2 is connected to PE2 in AS 200. An EBGP EVPN peer relationship is configured between ASBR1 and ASBR2 to exchange EVPN routes so that an inter-AS Option B EVPN can carry Layer 3 service traffic.
Configuration Notes
When configuring MPLS EVPN L3VPN E-LAN Option B, note the following:
Establish an EBGP EVPN peer relationship between ASBR1 and ASBR2 and configure ASBR1 not to filter received EVPN routes based on RTs.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone networks in AS 100 and AS 200 to implement intra-AS communication.
Configure basic MPLS capabilities and MPLS LDP on the MPLS backbone networks of AS 100 and AS 200 to establish LDP LSPs.
Configure an L3VPN instance on each PE.
Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PE and ASBR in each AS.
Configure a VPN BGP peer relationship between the PE and CE in each AS.
Enable MPLS on the ASBR interfaces connected to the other ASBR, establish EBGP EVPN peer relationships between ASBRs, and configure ASBRs not to filter received EVPN routes based on RTs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Interface names and IP address
MPLS LSR IDs of the PEs and ASBRs
Names (vpn1), RDs (100:1 and 200:1), and VPN targets (1:1) of the L3VPN instances created on PE1 and PE2
Procedure
- Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone networks in AS 100 and AS 200 to implement intra-AS communication.
In this example, OSPF is used in AS 100, and IS-IS is used in AS 200. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic MPLS capabilities and MPLS LDP on the MPLS backbone networks of AS 100 and AS 200 to establish LDP LSPs.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an L3VPN instance on each PE.# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 evpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] evpn mpls routing-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish BGP EVPN peer relationships between PEs and ASBRs.# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] commit
The configurations of ASBR1, ASBR2, and PE2 are similar to that of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure VPN BGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs.# Configure PE1.
[~PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 65410 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
The configuration of PE2 is similar to that of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure CE1.[~CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] peer 192.168.1.1 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] import-route direct [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
The configuration of CE2 is similar to the configuration of CE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS on the interfaces that connect ASBRs to each other, establish EBGP EVPN peer relationships between ASBRs, and configure ASBRs not to filter received EVPN routes based on RTs.# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] bgp 100 [*ASBR1-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 200 [*ASBR1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*ASBR1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 10.2.1.2 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*ASBR1-bgp] quit [*ASBR1] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.1 24 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*ASBR1] commit
The configuration of ASBR2 is similar to the configuration of ASBR1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Verify the configuration.
# After completing the configuration, run the display ip routing-table command on each CE to view the route to the remote CE. The command output on CE1 is used as an example.
[~CE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 10 Routes : 10 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.10.10.10/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 10.20.20.20/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.2.0/24 EBGP 255 0 RD 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity evpn evpn mpls routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 65410 # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # evpn source-address 1.1.1.9 # return
ASBR1 configuration file
# sysname ASBR1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 10.2.1.2 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 10.2.1.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
ASBR2 configuration file
# sysname ASBR2 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 00.1111.1111.1111.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 200 peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 200 peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 4.4.4.9 enable peer 10.2.1.1 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 4.4.4.9 enable peer 10.2.1.1 enable # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity evpn evpn mpls routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 00.1111.1111.2222.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 200 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 200 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn peer 192.168.2.2 as-number 65420 # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # evpn source-address 4.4.4.9 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 192.168.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 192.168.1.1 enable # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.20.20.20 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65420 peer 192.168.2.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 192.168.2.1 enable # return