Example for Configuring Public Network IPv6 FRR
With public network IPv6 FRR, traffic can be rapidly switched to a backup link if the primary link fails.
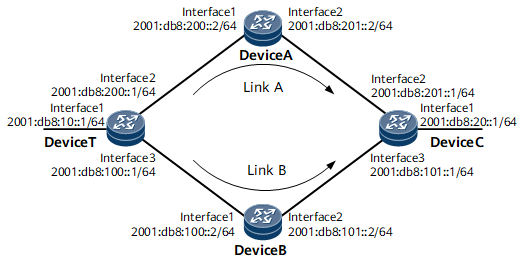
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, it is required that the backup outbound interface and backup next hop must be configured on Device T so that link B functions as the backup of link A. If link A fails, traffic is rapidly switched to the backup link (Link B).
Precautions
Before configuring public network IPv6 FRR, there must be at least two routes of different routing protocols but destined for the same IPv6 address.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable OSPFv3 on Device T, Device A, and Device C.
Enable IPv6 IS-IS on Device T, Device B, and Device C.
Enable public network IPv6 FRR on Device T, and then check information about the backup outbound interface and backup next hop.
Disable IPv6 FRR, and then check information about the backup outbound interface and backup next hop.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
OSPFv3 process IDs of Device T, Device A, and Device C
(OSPFv3 process ID is 1)
IPv6 IS-IS area addresses of Device T, Device B, and Device C
Procedure
- Configure an IPv6 address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure OSPFv3 on Device T, Device A, and Device C. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure IPv6 IS-IS on Device T, Device B, and Device C. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Check routing information.
# On Device T, check the routes to 2001:db8:20::1.
<DeviceT> display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:20::1 64 verbose Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 2 Destination : 2001:db8:20:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:200::2 Preference : 10 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 1 Label : NULL Protocol : OSPFv3 State : Active Adv Cost : 3 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x69 Age : 269sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : gigabitethernet 0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:20:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:100::2 Preference : 15 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 1 Label : NULL Protocol : ISIS State : Inactive Adv Cost : 30 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0xb5 Age : 201sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : gigabitethernet 0/1/16 Flags : 0
The preceding command output shows that there are two routes to 2001:db8:20::1/64 and that the route with 2001:db8:200::2 as the next hop is optimal because the OSPFv3 route priority is higher than the IPv6 IS-IS route priority.
- Enable public network IPv6 FRR.
# Enable IPv6 FRR on Device T.
[~DeviceT] ipv6 frr [*DeviceT] commit
# Check information about the backup outbound interface and backup next hop on Device T.
<DeviceT> display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:20::1 64 verbose Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 2 Destination : 2001:db8:20:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:200::2 Preference : 10 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 1 Label : NULL Protocol : OSPFv3 State : Active Adv Cost : 3 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x69 Age : 553sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : gigabitethernet 0/1/8 Flags : D BkNextHop : 2001:db8:100::2 BkInterface : gigabitethernet 0/1/16 BkLabel : NULL BkTunnelID : 0x0 BkPETunnelID : 0x0 BkIndirectID : 0xb5 Destination : 2001:db8:20:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:100::2 Preference : 15 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 1 Label : NULL Protocol : ISIS State : Inactive Adv Cost : 30 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0xb5 Age : 485sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : gigabitethernet 0/1/16 Flags : 0
The preceding command output shows that the route to 2001:db8:20::1/64 has a backup outbound interface and a backup next hop and that the IPv6 IS-IS route is the backup route.
- Verify the configuration.
# Simulate a link fault on Device T.
[~DeviceT] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [~DeviceT-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] shutdown [*DeviceT-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceT-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# On Device T, check the routes to 2001:db8:20::1/64.
<DeviceT> display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:20::1 64 verbose Routing Table : _public_ Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:db8:20:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:100:2 Preference : 15 Neighbour : :: ProcessID : 1 Label : NULL Protocol : ISIS State : Active Adv Cost : 30 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0xb5 Age : 1279sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : gigabitethernet 0/1/16 Flags : D
The preceding command output shows that traffic has been switched to link B.
Configuration Files
Device T configuration file
# sysname DeviceT # ipv6 frr # isis 1 is-level level-1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # ospfv3 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 area 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:10::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:200::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:100::1/64 isis enable 1 isis ipv6 enable 1 return
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # ospfv3 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:200::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:201::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # isis 1 is-level level-1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:100::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:101::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # isis 1 is-level level-1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # ospfv3 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 area 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:20::1/64 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:201::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:101::1/64 isis enable 1 isis ipv6 enable 1 # return