Example for Configuring Dynamic BFD for IPv6 IS-IS
This section provides an example for configuring dynamic BFD to fast detect failures and trigger fast switchover of service traffic on IS-IS IPv6 networks.
Networking Requirements
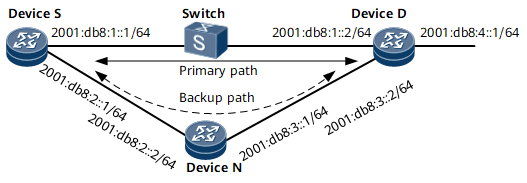
Figure 1 shows an IS-IS IPv6 network. The primary link between Device S and Device D is Device S -> Switch -> Device D; the backup link between Device S and Device D is Device S -> Device N -> Device D.
Device Name |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device S |
GE0/1/0 |
2001:db8:1::1/64 |
GE0/1/8 |
2001:db8:2::1/64 |
|
Device N |
GE0/1/0 |
2001:db8:2::2/64 |
GE0/1/8 |
2001:db8:3::1/64 |
|
Device D |
GE0/1/0 |
2001:db8:1::2/64 |
GE0/1/8 |
2001:db8:3::2/64 |
|
GE0/1/16 |
2001:db8:4::1/64 |
It is required to configure BFD for IPv6 IS-IS so that traffic between Device S and Device D can be rapidly switched to the backup path if the primary link or Switch fails.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic IS-IS IPv6 functions on each router to ensure that IPv6 routes are reachable.
Adjust the IS-IS cost on each router interface so that the link of Device S -> Switch -> Device D functions as the primary link and the link of Device S -> Device N -> Device D functions as the backup link.
Enable BFD globally on each router.
Enable BFD for IPv6 IS-IS in the IS-IS view of each router.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- IS-IS process ID
- IS-IS NET
- Level of each router
- IS-IS cost of each interface
- Numbers of interfaces to be enabled with BFD for IPv6 IS-IS
- Minimum interval at which BFD packets are received and sent, and BFD local detection time multiplier
Procedure
- Enable IPv6 and configure IPv6 addresses for all interfaces.
# Use the configuration of Device S as an example. The configuration of any other router is similar to that of Device S.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceS [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure basic IS-IS IPv6 functions.
# Configure Device S.
[~DeviceS] isis 10 [*DeviceS-isis-10] is-level level-2 [*DeviceS-isis-10] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*DeviceS-isis-10] ipv6 enable [*DeviceS-isis-10] quit [*DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device N.
[~DeviceN] isis 10 [*DeviceN-isis-10] is-level level-2 [*DeviceN-isis-10] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*DeviceN-isis-10] ipv6 enable [*DeviceN-isis-10] quit [*DeviceN] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceN] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] isis 10 [*DeviceD-isis-10] is-level level-2 [*DeviceD-isis-10] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*DeviceD-isis-10] ipv6 enable [*DeviceD-isis-10] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit
# Run the display ipv6 routing-table command. The command output shows that routers have learned IPv6 routes from each other.
- Configure the IS-IS cost for each interface.
# Configure Device S.
[~DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 cost 1 level-2 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceS] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 [*DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceS-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device N.
[~DeviceN] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceN] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 [*DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceN-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 cost 1 level-2 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Configure BFD for IPv6 IS-IS.
# Enable BFD for IPv6 IS-IS globally on Device S, Device N, and Device D, set the minimum interval at which BFD packets are received and sent to 150 ms, and set the default local detection time multiplier to 3.
# Configure Device S.
[~DeviceS] bfd [*DeviceS-bfd] quit [*DeviceS] isis 10 [*DeviceS-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable [*DeviceS-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 [*DeviceS-isis-10] commit [~DeviceS-isis-10] quit
# Configure Device N.
[~DeviceN] bfd [*DeviceN-bfd] quit [*DeviceN] isis 10 [*DeviceN-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable [*DeviceN-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 [*DeviceN-isis-10] commit [~DeviceN-isis-10] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] bfd [*DeviceD-bfd] quit [*DeviceD] isis 10 [*DeviceD-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable [*DeviceD-isis-10] ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 [*DeviceD-isis-10] commit [~DeviceD-isis-10] quit
# Run the display isis ipv6 bfd session all command on Device S or Device D. The command outputs show that the BFD parameters have taken effect. Use the command output on Device S as an example.
[~DeviceS] display isis ipv6 bfd session all IPv6 BFD session information for ISIS(10) ---------------------------------------- Peer System ID : 0000.0000.0003 Type : L2 Interface : GE0/1/0 IPv6 BFD State : up TX : 150 RX : 150 Multiplier : 3 LocDis : 16386 Local IPv6 Address: FE80::E0:2F47:B103:1 RemDis : 16386 Peer IPv6 Address : FE80::E0:2F47:B107:1 Diag : No diagnostic information Peer System ID : 0000.0000.0002 Type : L2 Interface : GE0/1/8 IPv6 BFD State : up TX : 150 RX : 150 Multiplier : 3 LocDis : 16386 Local IPv6 Address: FE80::C964:0:B203:1 RemDis : 16386 Peer IPv6 Address : FE80::C964:0:B8B6:1 Diag : No diagnostic information Total BFD session(s): 2
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:4::1 64 command on Device S to view the IPv6 routing table. The next hop address is FE80::E0:2F47:B107:1; the outbound interface is GE 0/1/0.
[~DeviceS] display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:4::1 64 Routing Table : public Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:db8:4:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : FE80::E0:2F47:B107:1 Preference : 15 Cost : 11 Protocol : ISIS RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D
# Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/0 of Device D to simulate a fault in the primary link.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] shutdown [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit
# Run the display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:4::1 64 command on Device S to check the IPv6 routing table.
[~DeviceS] display ipv6 routing-table 2001:db8:4::1 64 Routing Table : public Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:db8:4:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : FE80::C964:0:B8B6:1 Preference : 15 Cost : 20 Protocol : ISIS RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D
Based on the routing table, after the primary link fails, the backup link takes effect. The next hop address of the route to 2001:db8:4::/64 changes to FE80::C964:0:B8B6:1; the outbound interface changes to GE 0/1/8; the route cost also changes.
# Run the display isis ipv6 bfd session all command on Device S. The command output shows that only one BFD session is Up between Device S and Device N.
[~DeviceS] display isis ipv6 bfd 10 session all IPv6 BFD session information for ISIS(10) ---------------------------------------- Peer System ID : 0000.0000.0002 Type : L2 Interface : GE0/1/8 IPv6 BFD State : up TX : 150 RX : 150 Multiplier : 3 LocDis : 16386 Local IPv6 Address: FE80::C964:0:B203:1 RemDis : 16386 Peer IPv6 Address : FE80::C964:0:B8B6:1 Diag : No diagnostic information Total BFD session(s): 1
Configuration Files
Device S configuration file
# sysname DeviceS # bfd # isis 10 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 1 level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 # return
Device N configuration file
# sysname DeviceN # bfd # isis 10 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # bfd # isis 10 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 bfd all-interfaces enable ipv6 bfd all-interfaces min-tx-interval 150 min-rx-interval 150 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 1 level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 isis ipv6 cost 10 level-2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 10 # return
Switch configuration file:
The configuration is not provided here.