Example for Associating a Multicast VLAN with Specified User VLANs
This section provides an example for associating a multicast VLAN with specified user VLANs.
Context
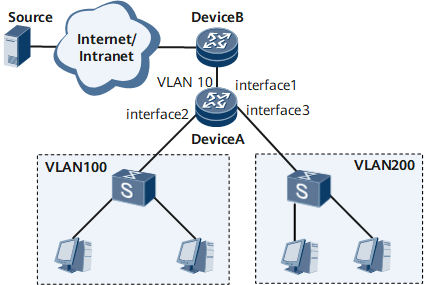
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A's GE 0/1/1 connects to Device B, and Device A's GE 0/1/2 and GE 0/1/3 connect to VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 respectively. Users in VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 request data from the same multicast source. Therefore, Device A requests a separate copy of data for VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 from Device B, consuming bandwidth resources and increasing the workload of Device B.
To resolve this issue, configure a multicast VLAN (VLAN 10) on Device A for the two user VLANs, so that Device A uses VLAN 10 to request only one copy of data from Device B and then replicates a separate copy for VLAN 100 and VLAN 200.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a multicast VLAN and user VLANs.
Enable the multicast VLAN function.
Associate the multicast VLAN with the user VLANs.
Add Device A's interfaces to VLANs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Device A's interface connected to an upstream device: GE 0/1/1; GE 0/1/1's VLAN ID: 10
Device A's interfaces connected to user VLANs: GE 0/1/2 and GE 0/1/3; GE 0/1/2's VLAN ID: 100; GE 0/1/3's VLAN ID: 200
Procedure
- Create a multicast VLAN and user VLANs.
# Create a multicast VLAN.
<HUAWEIA> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceA [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceA] igmp-snooping enable [*DeviceA] vlan 10 [*DeviceA-vlan10] igmp-snooping enable [*DeviceA-vlan10] commit [~DeviceA-vlan10] quit
# Create user VLANs.
[~DeviceA] vlan batch 100 200 [*DeviceA] commit
- Enable the multicast VLAN function.
[~DeviceA] vlan 10 [*DeviceA-vlan10] multicast-vlan enable [*DeviceA-vlan10] commit
- Associate the multicast VLAN with the user VLANs.
[~DeviceA-vlan10] multicast-vlan user-vlan 100 [*DeviceA-vlan10] multicast-vlan user-vlan 200 [*DeviceA-vlan10] commit [~DeviceA-vlan10] quit
- Add Device A's interfaces to VLANs.
# Add GE 0/1/1 to VLAN 10.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Add GE 0/1/2 to VLAN 100.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
# Add GE 0/1/3 to VLAN 200.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configurations, run the display multicast-vlan command to view configurations of the multicast VLAN.
[~DeviceA] display multicast-vlan vlan 10 Multicast-vlan : 10 User-vlan Number : 2 IGMP snooping state : Enable Prune-source-port state : Disable User-vlan Snooping-state ----------------------------------------------- 100 IGMP Enable 200 IGMP Enable
Run the display user-vlan command to view configurations of the user VLANs.
[~DeviceA] display user-vlan vlan Total user vlan 2 user-vlan snooping-state multicast-vlan snooping-state --------------------------------------------------------- 100 IGMP Enable 10 IGMP Enable 200 IGMP Enable 10 IGMP Enable
The command output shows the user VLAN IDs and the multicast VLAN ID of the user VLANs.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # vlan batch 10 100 200 # igmp-snooping enable # vlan 10 igmp-snooping enable multicast-vlan enable multicast-vlan user-vlan 100 200 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port trunk allow-pass vlan 200 # return