Configuring MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping enables a Layer 2 device to listen to and analyze MLD messages exchanged between a connected Layer 3 device and downstream user hosts. The Layer 2 device then uses the message information to set up multicast forwarding entries to implement on-demand multicast data forwarding at the data link layer.
Usage Scenario
On an IPv6 multicast network, after an upstream device sends the service flow of a multicast program, a Layer 2 device at the edge of the access layer forwards the flow to multicast users. The users can then enjoy the multicast program service. As shown in Figure 1, multicast data messages are broadcast at the data link layer by default, causing bandwidth waste.
To resolve this issue, configure MLD snooping on the Layer 2 device, allowing this device to listen to the MLD messages exchanged between the upstream device and downstream hosts. The Layer 2 device can then analyze the messages and generate Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries based on the message information to implement on-demand multicast data forwarding at the link layer.
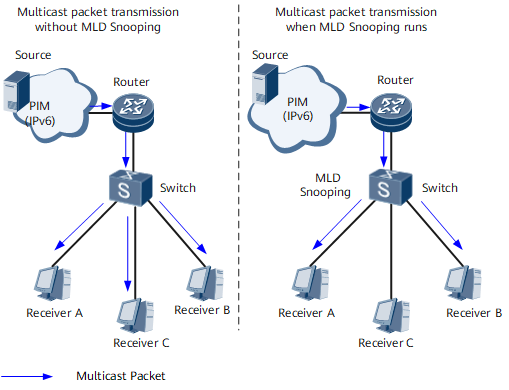
On the network shown in Figure 1, Receiver A and Receiver B request the service of a multicast group, but Receiver C does not. Before MLD snooping is configured, the Layer 2 device broadcasts the multicast data at the data link layer, and all the receivers can receive the data. After MLD snooping is configured, the Layer 2 device sends the multicast data only to Receiver A and Receiver B who request the data. Therefore, Receiver C does not receive the data of the multicast group.
Data Preparation
To configure MLD snooping, you need the following data.
No. |
Data |
|---|---|
1 |
VLAN ID or VSI name (for which MLD snooping needs to be configured) |
2 |
(Optional) Router interface aging time |
3 |
(Optional) Aging time of dynamic group members, and the range of group and source addresses that hosts can promptly join or leave |
4 |
(Optional) Range and number of multicast groups to be limited |
5 |
(Optional) Aging time of entries triggered by multicast traffic |
- Configuring Basic MLD Snooping Functions
- Configuring basic MLD snooping functions involves enabling MLD snooping and setting the MLD version. Those basic functions need to be configured before you configure other MLD snooping functions.
- (Optional) Setting the Aging Time for Router Interfaces
- The aging time of router interfaces can be set based on the network stability condition so that multicast entries are updated upon network changes.
- (Optional) Configuring Static Interfaces
- On a network with a stable topology, you can configure static interfaces, including static router interfaces and static group member interfaces.
- (Optional) Configuring Rapid Group Member Information Update
- Rapid group member information update can be configured to enable devices to quickly update Layer 2 multicast entries generated based on Report/Done messages received from group members, improving the multicast data forwarding efficiency.
- (Optional) Setting the Aging Time for Entries Triggered by Multicast Traffic
- Setting the aging time for Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries triggered by multicast traffic can balance the forwarding efficiency and system performance.
- (Optional) Configuring MLD Snooping Policies
- To improve service security, configure MLD snooping policies on a Layer 2 multicast device to filter multicast messages or restrict the multicast group range that hosts can join.
- (Optional) Configuring Prompt Response to Layer 2 Network Topology Changes
- Prompt response to Layer 2 network topology changes enables a device to correctly forward multicast data based on the current network topology, ensuring uninterrupted service forwarding.
- (Optional) Configuring the System to Retain the Tag Carried in an MLD Report Message
- When an L2VPN accesses an L3VPN, you can configure the system to retain the tag carried in an MLD Report message so that the message can be normally processed when being forwarded from an L2VE sub-interface to an L3VE QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface.
- Verifying the Configuration
- After MLD snooping is configured, you can view the router port and member port lists, forwarding table, and querier parameters.