Example for Configuring Route Import Between VPN and Public Network
In a traffic cleaning scenario, you can configure the function of route import between VPN and public network on a device to import public network routes to the VPN. This guides the reinjected traffic forwarding.
Networking Requirements
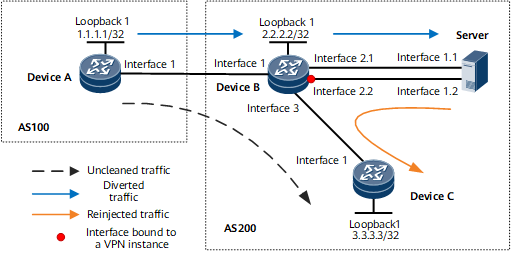
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A belongs to AS100, whereas Device B, Device C, and the traffic cleaning server (Server) belong to AS200. Device B is an ingress of AS200. AS200 communicates with AS100 through Device B.
If an attack originates in AS100, attack traffic will consume network resources in AS200 after being transmitted to AS200 through Device B. After a traffic analysis server is deployed, the attack traffic can be diverted to the cleaning server for cleaning. The cleaned traffic is injected back to the AS200 network through Device B. In this case, the public network routes destined for Device C need to be imported to the VPN routing table of Device B to forward the cleaned traffic to Device C. In addition, the public network routes sent by the cleaning server should not be imported to the VPN routing table. This prevents the reinjected traffic from being sent back to the cleaning server after reaching Device B, thereby preventing loops. To implement the preceding process, configure route import between VPN and public network on Device B, and configure a route-policy on Device B based on BGP peer relationships.

Interfaces 1 through 3 in this example represent GE 0/1/0, GE 0/1/8, and GE 0/1/16, respectively.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address/Mask |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
Loopback 1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
Device B |
Loopback 1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE 0/1/8 |
10.2.3.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/8.1 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/8.2 |
10.2.2.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/16 |
172.16.1.1/24 |
|
Device C |
Loopback 1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GE 0/1/0 |
172.16.1.2/24 |
|
Server |
Loopback 1 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
GE 0/1/0.1 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
|
GE 0/1/0.2 |
10.2.2.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each interface.
- Configure OSPF on Device B, Device C and Server.
Configure IBGP connections between Device B and Device C, and between Device B and the cleaning server.
Configure an EBGP connection between Device A and Device B.
Bind the Device B interface that is connected to the cleaning server to a VPN instance. Configure a route-policy on Device B to prevent routes sent by the cleaning server from being imported to the VPN routing table.
- Configure a static route with a 16-bit mask on Device C and a static route with 32-bit mask on the server. Import the static route into the BGP routing table. Divert traffic sent by Device A to the server to simulate the traffic cleaning process based on the longest match rule for route selection.
Configure route import between VPN and public network on Device B to import public network routes to the VPN routing table and guide the reinjected traffic forwarding to Device C.

The traffic analysis server is a third-party device. In this example, the server has only basic BGP configurations, OSPF configurations, and configurations of importing a static route into the BGP routing table. The traffic cleaning configuration is omitted here.
Data Preparation
DeviceRouter IDs of Device A, Device B, and Device C
DeviceAS number (100) for Device A; AS number (200) for Device B, Device C, and the cleaning server
VPN targets of vpna to send and receive routes
Route-policy on Device B
- Routes advertised by Device C and the server
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface.
For configuration details, see "Configuration Files" in this section.
- Configure OSPF.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospf 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] ospf 1 [*DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 [*DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
# Configure the cleaning server.
[~Server] ospf 1 [*Server-ospf-1] area 0 [*Server-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 [*Server-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*Server-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*Server-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~Server-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~Server-ospf-1] quit
- Configure IBGP connections.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.2.3.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure the cleaning server.
[~Server] bgp 200 [*Server-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*Server-bgp] peer 10.2.3.1 as-number 200 [*Server-bgp] import-route direct [*Server-bgp] commit [~Server-bgp] quit
- Configure an EBGP connection.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceA-bgp] import-route direct [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
- Create a VPN instance, bind it to the Device B interface that is connected to the cleaning server, and configure a route-policy.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB]ip vpn-instance vpna [*DeviceB-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*DeviceB-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*DeviceB-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [*DeviceB-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*DeviceB-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.2 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.2] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.2] ip address 10.2.2.1 24 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.2] quit [*DeviceB] ospf 2 vpn-instance vpna [*DeviceB-ospf-2] area 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceB-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] quit [*DeviceB-ospf-2] quit [*DeviceB] ip community-filter basic serverRoute index 10 permit 100:100 [*DeviceB] route-policy noexportServer deny node 10 [*DeviceB-route-policy] if-match community-filter serverRoute [*DeviceB-route-policy] quit [*DeviceB] route-policy noexportServer permit node 100 [*DeviceB-route-policy] quit [*DeviceB] route-policy setCom permit node 10 [*DeviceB-route-policy] apply community 100:100 [*DeviceB-route-policy] quit [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.2.3.2 route-policy setCom import [*DeviceB-bgp] quit [*DeviceB] commit
- Configure Device C and the server to import a static route to the BGP routing table. The static routes are used to simulate traffic to divert traffic to the server based on the longest match rule for route selection.
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] ip route-static 33.33.0.0 16 NULL 0 [~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] network 33.33.0.0 16 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure Server.
[~Server] ip route-static 33.33.33.33 32 NULL 0 [~Server] bgp 200 [*Server-bgp] network 33.33.33.33 32 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
- Enable Device B to import public network BGP routes to the VPN routing table. Routes are advertised to simulate traffic, so that injected traffic can be forwarded to Device C.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*DeviceB-bgp-vpna] import-rib public route-policy noexportServer [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Check the BGP public network routing table on Device B. The command output shows the public network routes learned from Device A, Device C, and the cleaning server.
For traffic destined for the network segment 33.33.0.0, Device B forwards the traffic preferentially through the server over the route destined for 33.33.33.33/32 with the next-hop IP address 10.2.3.2 based on the longest match rule for route selection.
<DeviceB> display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 9 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 1.1.1.1/32 10.1.1.1 0 0 100? *> 2.2.2.2/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 ? *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.2.3.2 0 100 0 ? 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 0 100? *> 10.2.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 ? i 10.2.3.2 0 100 0 ? *>i 33.33.0.0/16 172.16.1.2 0 100 0 i *>i 33.33.33.33/32 10.2.3.2 0 100 0 i *> 172.16.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 ?# Check the BGP VPN routing table on Device B. The command output shows that the public network BGP routes are imported to the VPN routing table and no public network routes are learned from the cleaning server. The server transmits traffic to DeviceC over the route destined for 33.33.0.0/16 with the next-hop IP address 172.16.1.2.
<DeviceB> display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpna routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 2.2.2.2: Total Number of Routes: 2 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 1.1.1.1/32 10.1.1.1 0 0 100? *>i 33.33.0.0/16 172.16.1.2 0 100 0 i# Check the BGP VPN routing table on Device B. The next-hop IP address in the route destined for 33.33.33.33 has been set to the IP address of Device C's outbound interface.
<DeviceB> display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpna routing-table 33.33.33.33 BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2 Local AS number : 200 VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 2.2.2.2: Paths: 1 available, 1 best, 1 select, 0 best-external, 0 add-path BGP routing table entry information of 33.33.0.0/16: Route Distinguisher: 100:1 From: 172.16.1.2 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d03h12m45s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.1.2 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 Original nexthop: 172.16.1.2 Qos information : 0x0 Primary Routing Table: public AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255 Not advertised to any peer yetThe public network routes to Device C are imported to the VPN routing table of Device B. The traffic from the cleaning server is injected back to Device C through Device B. In addition, public network routes to the cleaning server are not imported to the VPN routing table of Device B, thereby preventing loops.
Configuration Files
DeviceDevice A configuration file
sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 10.1.1.2 enable # returnDeviceDevice B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1 ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.2 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 10.2.3.2 as-number 200 peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospf 1 peer 10.1.1.1 enable peer 10.2.3.2 enable peer 10.2.3.2 route-policy setCom import peer 172.16.1.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna import-rib public route-policy noexportServer # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy noexportServer deny node 10 if-match community-filter serverRoute # route-policy noexportServer permit node 100 # route-policy setCom permit node 10 apply community 100:100 # ip community-filter basic serverRoute index 10 permit 100:100 # return
DeviceDevice C configuration file
sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 33.33.0.0 255.255.0.0 peer 172.16.1.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ip route-static 33.33.0.0. 255.255.0.0 NULL0 # returnServer configuration file
sysname Server # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.2 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 10.2.3.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.255 import-route direct peer 10.2.3.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ip route-static 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.255 NULL0 # return